| Nasolabial fold | |
|---|---|
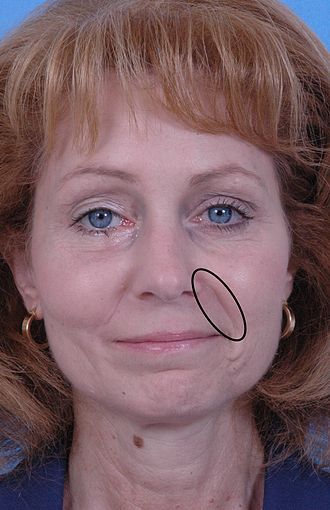 Human face, with left nasolabial fold marked in black ellipse | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D060052 |
| TA98 | A01.2.01.017 |
| TA2 | 220 |
| FMA | 75018 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The nasolabial folds, commonly known as "smile lines" [1] or "laugh lines", [2] [ self-published source ] are facial features. They are the two skin folds that run from each side of the nose to the corners of the mouth. They are defined by facial structures that support the buccal fat pad. [3] They separate the cheeks from the upper lip. The term derives from Latin nasus for "nose" and labium for "lip". Other people suggest the term melolabial fold,[ clarification needed ] [4] or the lip-cheek fold or groove. [5] It is also known as the nasolabial sulcus.