
The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on the water surface, and, in some cases, diving in at least shallow water. The family contains around 174 species in 43 genera.

Chevrotains, or mouse-deer, are diminutive, even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, and are the only living members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known only from fossils. The extant species are found in forests in South and Southeast Asia; a single species, the water chevrotain, is found in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. In November 2019, conservation scientists announced that they had photographed silver-backed chevrotains in a Vietnamese forest for the first time since the last confirmed sightings in 1990.

Podocnemididae is a family of pleurodire (side-necked) turtles, once widely distributed. Most of its 41 genera and 57 species are now extinct. Seven of its eight surviving species are native to South America: the genus Peltocephalus, with two species, only one of which is extant ; and the genus Podocnemis, with six living species of South American side-necked river turtles and four extinct. There is also one genus native to Madagascar: Erymnochelys, the Madagascan big-headed turtle, whose single species E. madagascariensis.

Ostriches are large flightless birds. Two living species are recognised, the common ostrich, native to large areas of sub-Saharan Africa, and the Somali ostrich, native to the Horn of Africa.

Pierolapithecus catalaunicus is an extinct species of primate which lived around 12.5-13 million years ago during the Miocene in what is now Hostalets de Pierola, Catalonia, Spain. Some researchers believe that it is a candidate for common ancestor to the great ape clade, or is at least closer than any previous fossil discovery. Others suggest it being a pongine, or a dryopith. On 16 October 2023, scientists reported the facial reconstruction of the great ape.

Crocodylus is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae.

Ouranopithecus is a genus of extinct Eurasian great ape represented by two species, Ouranopithecus macedoniensis, a late Miocene hominoid from Greece and Ouranopithecus turkae, also from the late Miocene of Turkey.

Simocyon is a genus of extinct carnivoran mammal in the family Ailuridae. Simocyon, which was about the size of a mountain lion, lived in the late Miocene and early Pliocene epochs, and has been found in Europe, Asia, and rarely, North America and Africa.

The Palaeomerycidae is an extinct family of Neogene ruminants belonging to the infraorder Pecora. Palaeomerycids lived in Europe and Asia exclusively during the Miocene, coevolving with cervids, bovids, moschids, and tragulids there as part of a dramatic radiation of ruminants by the early Miocene.
Anoiapithecus is an extinct ape genus thought to be closely related to Dryopithecus. Both genera lived during the Miocene, approximately 12 million years ago. Fossil specimens named by Salvador Moyà-Solà are known from the deposits from Spain.
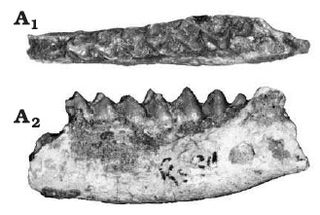
Afrotragulus is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Kenya during the early Miocene period. It contains the species Afrotragulus moruorotensis and Afrotragulus parvus, formerly classified in genus Dorcatherium, as well as A. akhtari, A. megalomilos, and A. moralesi.
In biostratigraphy, MN 4 is one of the MN zones used to characterize the fossil mammal faunas of the Neogene of Europe. It is preceded by MN 3 and followed by MN 5; together, these three zones form the Orleanian age of the middle Miocene. This zone starts within magnetostratigraphic chron C5Dr, at 18 million years ago, and ends within chron C5Cr, at 17.0 million years ago, although some different correlations have been proposed.

Dorcatherium is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Europe, East Africa and the Siwaliks during the Miocene and Possibly Pliocene.

Cainotheriidae is an extinct family of artiodactyls known from the Late Eocene to Middle Miocene of Europe. They are mostly found preserved in karstic deposits.

Enhydriodon is an extinct genus of mustelids known from Africa, Pakistan, and India that lived from the late Miocene to the early Pleistocene. It contains nine confirmed species, two debated species, and at least a few other undescribed species from Africa. The genus belongs to the tribe Enhydriodontini in the otter subfamily Lutrinae. Enhydriodon means "otter tooth" in Ancient Greek and is a reference to its dentition rather than to the Enhydra genus, which includes the modern sea otter and its two prehistoric relatives.

Microstonyx was an extinct genus of suid that existed during the Miocene in Asia and Europe.
Semigenetta is an extinct genus of viverrid. It lived in Europe, China, and Thailand in the Miocene, and was very similar to the extant genus Genetta, but lacked a molar that Genetta still possesses.
Katifelis is an extinct genus of felids that lived in what is now Kenya during the Early Miocene and is notable for its dental features, which are intermediate between basal and modern cats. It contains a single species, Katifelis nightingalei.
Namafelis is an extinct genus of felids that lived in what is now Namibia during the Early Miocene. It contains a single species, Namafelis minor. Closely related to Diamantofelis, it is of “Pseudaelurus-grade”, and therefore a rather basal member of the cat family.














