
Branchiopoda is a class of crustaceans. It comprises fairy shrimp, clam shrimp, Diplostraca, Notostraca and the Devonian Lepidocaris. They are mostly small, freshwater animals that feed on plankton and detritus.
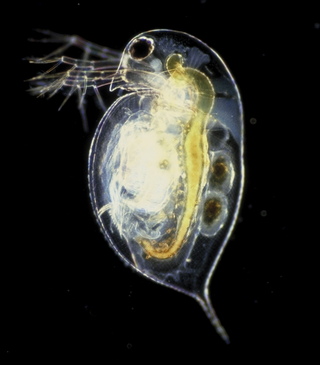
Daphnia is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, 0.2–6.0 mm (0.01–0.24 in) in length. Daphnia are members of the order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. Daphnia spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to freshwater lakes and ponds.

Onychopoda are a specialised order of branchiopod crustaceans, belonging to the superorder Cladocera.
Daphnia occidentalis is a species of crustacean in the family Daphniidae. It is endemic to Australia, and is the only species in the subgenus Australodaphnia.

Bosmina is a genus in the order Cladocera, the water fleas. Its members can be distinguished from those of Bosminopsis by the separation of the antennae; in Bosminopsis, the antennae are fused at their bases.

The Diplostraca or Cladocera, commonly known as water fleas, is a superorder of small, mostly freshwater crustaceans, most of which feed on microscopic chunks of organic matter, though some forms are predatory.
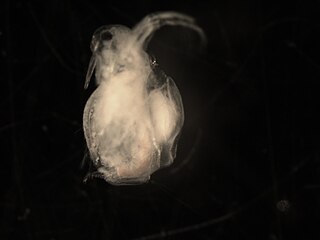
Moina is a genus of crustaceans within the family Moinidae. The genus was first described by W. Baird in 1850. They are referred to as water fleas, but are related to the much larger Daphnia magna and the larger Daphnia pulex. This genus demonstrates the ability to survive in waters containing low oxygen levels, high salinity, and other impurities, including salt pans, and commonly eutrophication. An example of such an extreme habitat is the highly saline Makgadikgadi Pans of Botswana, which supports prolific numbers of Moina belli.

Daphniidae is a family of water fleas in the order Anomopoda.

Leptodora is a genus containing two species of large, nearly transparent predatory water fleas. They grow up to 21 mm (0.83 in) long, with two large antennae used for swimming and a single compound eye. The legs are used to catch copepods that it comes into contact with by chance. Leptodora kindtii is found in temperate lakes across the Northern Hemisphere and is probably the only water flea species ever described in a newspaper; L. richardi is only known from eastern Russia. For most of the year, Leptodora reproduces parthenogenetically, with males only appearing late in the season, to produce winter eggs which hatch the following spring. Leptodora is the only genus in its family, the Leptodoridae, and suborder, Haplopoda.
Pseudopenilia bathyalis is a species of diplostracan, described in 2004, that lives at depths of 1,900–2,140 m (6,230–7,020 ft) in the anoxic zone of the Black Sea. Originally described in the family Sididae, it was transferred to its own family, the Pseudopenilidae, in 2008.
Daphnia commutata is a species of water flea.

Daphnia longispina is a planktonic crustacean of the family Daphniidae, a cladoceran freshwater water flea. It is native to Eurasia. D. longispina is similar in size and sometimes confused with the often sympatric D. pulex, but much smaller than D. magna. D. longispina is found in a wide range of standing freshwater bodies from small, ephemeral rock-pools to large lakes.

Sididae is a family of ctenopods in the order Diplostraca. There are about 6 genera and at least 20 described species in Sididae. Some Sididae are non-native species.

Penilia avirostris is a species of ctenopod in the family Sididae. It is found in temperate Asia, Europe, and New Zealand.

Penilia is a genus of ctenopods in the family Sididae. There is one described species in Penilia, P. avirostris.

Holopedium gibberum is a species of water flea in the family Holopediidae. It is found in Europe.

Holopedium is the sole genus of water fleas in the family Holopediidae. There are about seven described species in Holopedium.

Sida crystallina is a species of ctenopod in the family Sididae. It is found in Europe.

Chydoridae is a family of water fleas in the order Anomopoda. There are more than 50 genera and 520 described species in Chydoridae. A lot of Chydoridae species are non-native species, many of which pose a great threat to aquatic ecosystems.
Diaphanosoma is a genus of Sididae.













