
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy including solar water heating, and solar architecture.

Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially utilized for electricity generation and as photosensors.
In the 19th century, it was observed that the sunlight striking certain materials generates detectable electric current - the photoelectric effect. This discovery has laid the foundation of solar cells. Solar cells have gone on to be used in many applications. They have historically been used in situations where electrical power from the grid was unavailable.

A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electrical device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon. It is a form of photoelectric cell, defined as a device whose electrical characteristics, such as current, voltage, or resistance, vary when exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as solar panels. The common single junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage of approximately 0.5 volts to 0.6 volts.

A solar cell panel, solar electric panel, photo-voltaic (PV) module or solar panel is an assembly of photo-voltaic cells mounted in a framework for installation. Solar panels use sunlight as a source of energy to generate direct current electricity. A collection of PV modules is called a PV panel, and a system of PV panels is called an array. Arrays of a photovoltaic system supply solar electricity to electrical equipment.

Hybrid power are combinations between different technologies to produce power.

Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) are photovoltaic materials that are used to replace conventional building materials in parts of the building envelope such as the roof, skylights, or facades. They are increasingly being incorporated into the construction of new buildings as a principal or ancillary source of electrical power, although existing buildings may be retrofitted with similar technology. The advantage of integrated photovoltaics over more common non-integrated systems is that the initial cost can be offset by reducing the amount spent on building materials and labor that would normally be used to construct the part of the building that the BIPV modules replace. In addition, BIPV allows for more widespread solar adoption when the building's aesthetics matter and traditional rack-mounted solar panels would disrupt the intended look of the building.

Solar power is the conversion of renewable energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV), indirectly using concentrated solar power, or a combination. Concentrated solar power systems use lenses or mirrors and solar tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic effect.

A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
The balance of system (BOS) encompasses all components of a photovoltaic system other than the photovoltaic panels. This includes wiring, switches, a mounting system, one or many solar inverters, a battery bank and battery charger.
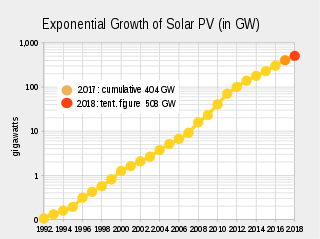
Worldwide growth of photovoltaics has been close to exponential between 1992 and 2018. During this period of time, photovoltaics (PV), also known as solar PV, evolved from a niche market of small-scale applications to a mainstream electricity source.
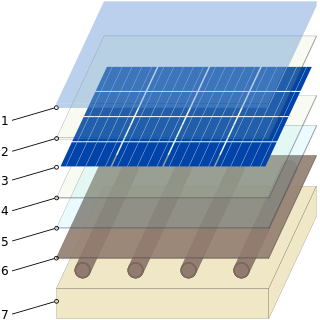
Photovoltaic thermal collectors, typically abbreviated as PVT collectors and also known as hybrid solar collectors, photovoltaic thermal solar collectors, PV/T collectors or solar cogeneration systems, are power generation technologies that convert solar radiation into usable thermal and electrical energy. PVT collectors combine photovoltaic solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity, with a solar thermal collector, which transfers the otherwise unused waste heat from the PV module to a heat transfer fluid. By combining electricity and heat generation within the same component, these technologies can reach a higher overall efficiency than solar photovoltaic (PV) or solar thermal (T) alone.
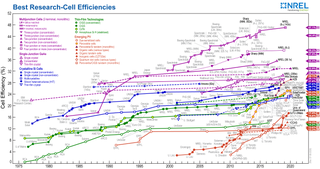
There are currently many research groups active in the field of photovoltaics in universities and research institutions around the world. This research can be categorized into three areas: making current technology solar cells cheaper and/or more efficient to effectively compete with other energy sources; developing new technologies based on new solar cell architectural designs; and developing new materials to serve as more efficient energy converters from light energy into electric current or light absorbers and charge carriers.

Photovoltaic mounting systems are used to fix solar panels on surfaces like roofs, building facades, or the ground. These mounting systems generally enable retrofitting of solar panels on roofs or as part of the structure of the building.
Polarizing organic photovoltaics (ZOPV) is a concept for harvesting energy from Liquid crystal display screens, developed by engineers from UCLA. This concept enables devices to use external light and the LCD screen's backlight using photovoltaic polarizers. Photovoltaic polarizers convert this light into electricity which can be used to power the device. This concept also provides multifunctional capability to devices with LCD screens as they act as photovoltaic devices and also as polarisers.
Flexible solar cell research is a research-level technology, an example of which was created at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in which solar cells are manufactured by depositing photovoltaic material on flexible substrates, such as ordinary paper, using chemical vapor deposition technology. The technology for manufacturing solar cells on paper was developed by a group of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology with support from the National Science Foundation and the Eni-MIT Alliance Solar Frontiers Program.

A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system designed for the supply of merchant power. They are differentiated from most building-mounted and other decentralised solar power because they supply power at the utility level, rather than to a local user or users. The generic expression utility-scale solar is sometimes used to describe this type of project.
Solar energy – radiant light and heat from the sun. It has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar energy technologies include solar heating, solar photovoltaics, solar thermal electricity and solar architecture, which can make considerable contributions to solving some of the most urgent problems that the world now faces.

The Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute is a public engineering research and development institution in Durgapur, West Bengal, India. It is a constituent laboratory of the Indian Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). This institute is the only national level research institute in the field of mechanical engineering in India.

Agrivoltaics or agrophotovoltaics is the simultaneous use of areas of land for both solar photovoltaic power generation and agriculture. The coexistence of solar panels and crops implies a sharing of light between these two types of production, so the design of agrivoltaic facilities may require trading off such objectives as optimizing crop yield, crop quality, and energy production. However, in some cases crop yield increased due to the shade of the solar panels mitigating some of the stress on plants caused by high temperatures and UV damage.

















