
The Cthulhu Mythos is a mythopoeia and a shared fictional universe, originating in the works of Anglo-American horror writer H. P. Lovecraft. The term was coined by August Derleth, a contemporary correspondent and protégé of Lovecraft, to identify the settings, tropes, and lore that were employed by Lovecraft and his literary successors. The name "Cthulhu" derives from the central creature in Lovecraft's seminal short story "The Call of Cthulhu", first published in the pulp magazine Weird Tales in 1928.

Hallucigenia is a genus of lobopodian known from Cambrian aged fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, H. sparsa was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. Lobopodians are a grade of Paleozoic panarthropods from which the velvet worms, water bears, and arthropods arose.

Cthulhu is a fictional cosmic entity created by writer H. P. Lovecraft. It was introduced in his short story "The Call of Cthulhu", published by the American pulp magazine Weird Tales in 1928. Considered a Great Old One within the pantheon of Lovecraftian cosmic entities, this creature has since been featured in numerous pop culture references. Lovecraft depicts it as a gigantic entity worshipped by cultists, in the shape of a green octopus, dragon, and a caricature of human form. The Lovecraft-inspired universe, the Cthulhu Mythos, where it exists with its fellow entities, is named after it.
Heloplax is a genus of worm-like molluscs. Its soft parts are preserved in three dimensions in the Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstatte; its disarticulated valves are known from other Silurian deposits. It is very bizarre by modern standards; it bears serially repeated units, and has spines. It probably falls somewhere between the aplacophorans and polyplacophora; its valves were composed of aragonite
Acaenoplax is an extinct worm-shaped mollusc known from the Coalbrookdale Formation of Herefordshire, England. It lived in the Silurian period. It was a couple of centimetres long and half a centimetre wide, and comprises serially repeated units with seven or eight shells, and rings of 'spines'.
Cinerocaris is an extinct genus of phyllocarid crustaceans known from the Silurian aged Coalbrookdale Formation in Herefordshire, England. It contains the species Cinerocaris magnifica.
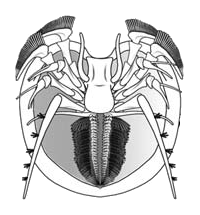
Xylokorys is a genus of marrellomorph known from two specimens from the Silurian Herefordshire lagerstatte; it filter-fed on mud particles on the sea floor. It is the only marrellomorph known from the Silurian period.
Pauline avibella is a fossil ostracod from the Silurian with unusually well preserved soft parts, including limbs, eyes, gills and alimentary system.
Pauline is a fossil genus of ostracods from the Silurian. Genus contains two species: Pauline avibella found in 425-million-year-old rocks in the Herefordshire Lagerstätte in England near the Welsh Border and Pauline nivisis, known from the Lower Silurian Pentamerus Bjerge Formation of north Greenland.

Kenostrychus is a monospecific genus of polychaete worms known from exceptional 3D fossils from the Silurian aged Herefordshire lagerstatte of England.

Invavita piratica is an extinct, parasitic species of tongue worm, provisionally assigned to the order Cephalobaenida, from Herefordshire Lagerstätte, Ludlow-aged England. It possessed a head, a worm-like body, and two pairs of limbs.
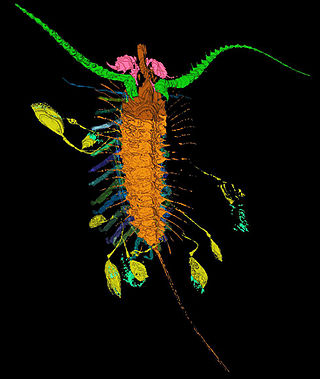
Aquilonifer spinosus is an extinct species of arthropod from the Silurian period. It is known from a single fossil specimen found in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England, in rocks about 430 million years old. The 1 cm long specimen is a stem-group mandibulate, not directly related to any living species. The many-legged, eyeless adult has ten unusual tethered appendages, interpreted as juveniles attached to the parent, in a unique form and previously unknown brooding behaviour.

Offacolus is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Its only species, O. kingi, has been found in deposits from the Silurian period in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England. Offacolidae, the family to which O. kingi belongs was once considered a monotypic family. Offacolidae currently includes along with O. kingi, Dibasterium and Setapedites and represent the sister group of Prosomapoda. The genus is named after Offa, a king from the ancient kingdom of Mercia, and colus, a person who dwelled among the Offa's Dyke. The species name honors Robert Joseph King, a British mineralogist who found the fossils of Offacolus.
The Bertie Group or Bertie Limestone, also referred to as the Bertie Dolomite and the Bertie Formation, is an upper Silurian geologic group and Lagerstätte in southern Ontario, Canada, and western New York State, United States. Details of the type locality and of stratigraphic nomenclature for this unit as used by the U.S. Geological Survey are available on-line at the National Geologic Map Database. The formation comprises dolomites, limestones and shales and reaches a thickness of 495 feet (151 m) in the subsurface, while in outcrop the group can be 60 feet (18 m) thick.

Thanahita is a genus of extinct lobopodian and known from the middle Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstätte at the England–Wales border in UK. It is monotypic and contains one species, Thanahita distos. Discovered in 2018, it is estimated to have lived around 430 million years ago and is the only known extinct lobopodian in Europe, and the first Silurian lobopodian known worldwide.

Hallucigeniidae is a family of extinct worms belonging to the group Lobopodia that originated during the Cambrian explosion. It is based on the species Hallucigenia sparsa, the fossil of which was discovered by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1911 from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The name Hallucigenia was created by Simon Conway Morris in 1977, from which the family was erected after discoveries of other hallucigeniid worms from other parts of the world. Classification of these lobopods and their relatives are still controversial, and the family consists of at least four genera.

Coalbrookdale Formation, earlier known as Wenlock Shale or Wenlock Shale Formation and also referred to as Herefordshire Lagerstätte in palaeontology, is a fossil-rich deposit (Konservat-Lagerstätte) in Powys and Herefordshire at the England–Wales border in UK. It belongs to the Wenlock Series of the Silurian Period within the Homerian Age. It is known for its well-preserved fossils of various invertebrate animals many of which are in their three-dimensional structures. Some of the fossils are regarded as earliest evidences and evolutionary origin of some of the major groups of modern animals.
Carbotubulus is a genus of extinct worm belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the Carboniferous Carbondale Formation of the Mazon Creek area in Illinois, US. A monotypic genus, it contains one species Carbotubulus waloszeki. It was discovered and described by Joachim T. Haug, Georg Mayer, Carolin Haug, and Derek E.G. Briggs in 2012. With an age of about 300 million years, it is the first long-legged lobopodian discovered after the period of Cambrian explosion.

Enalikter is an extinct arthropod described from the middle Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstätte at the England–Wales border in UK. This genus is known from only one species, E. aphson. Enalikter is described as late-living example of Megacheira, "great-appendage arthropod". It subsequently suggested to be an annelid by other researchers, however subsequent studies rejected this interpretation. Its interpretation as megacheiran arthropod has been questioned in later studies.
Tanazios is a genus of Silurian stem-mandibulate.









