
Gentianaceae is a family of flowering plants of 103 genera and about 1600 species.

Hevea is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, with about ten members. It is also one of many names used commercially for the wood of the most economically important rubber tree, H. brasiliensis. The genus is native to tropical South America but is widely cultivated in other tropical countries and naturalized in several of them. It was first described in 1775.

Couroupita guianensis, known by a variety of common names including cannonball tree, is a deciduous tree in the flowering plant family Lecythidaceae. It is native to the tropical forests of Central and South America, and it is cultivated in many other tropical areas throughout the world because of its beautiful, fragrant flowers and large, interesting fruits. Fruits are brownish grey. There are potential medicinal uses for many parts of Couroupita guianensis, and the tree has cultural and religious significance in India. In Sri Lanka, the cannonball tree has been widely misidentified as Sal, after its introduction to the island by the British in 1881, and has been included as a common item in Buddhist temples as a result.

Couroupita is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lecythidaceae first described as a genus in 1775. It is native to tropical South America and Central America.
- Couroupita guianensis - Cannonball tree -Guyana, Colombia, Ecuador east to Amapá and south to Bolivia; naturalized in the West Indies as well as in Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Andaman & Nicobar
- Couroupita nicaraguarensis – Bala de cañón, coco de mono, paraíso, zapote de mico, or zapote de mono -Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Honduras, Panama
- Couroupita subsessilis - northern Brazil, northern Peru

Vismia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Hypericaceae. Members of the genus are small trees and shrubs found in tropical and subtropical areas of Central America and South America. Including the countries of Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panamá, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad-Tobago and Venezuela.

Guapira is a genus of Neotropical shrubs in four o'clock family. Its species are native to Mesoamerica, South America, the West Indies, and the extreme southern part of Florida.

Marcgravia is a genus of plants in the Marcgraviaceae family commonly eaten by the dwarf little fruit bat. The genus is native to the Caribbean Islands, Central America, and South America, and genus is named in memory of the German naturalist Georg Marcgraf. The plant is visited by Thomas's nectar bat.
Perebea is a genus of plant in family Moraceae.

Tolumnia, is a genus in the family Orchidaceae. Previously known as the "equitant oncidiums," the species were segregated from the mega-genus Oncidium by Guido Braem in 1986. Dancing-lady orchid is a common name for some species in this genus.

Ficus americana, commonly known as the West Indian laurel fig or Jamaican cherry fig, is a tree in the family Moraceae which is native to the Caribbean, Mexico in the north, through Central and South America south to southern Brazil. It is an introduced species in Florida, USA. The species is variable; the five recognised subspecies were previously placed in a large number of other species.
Marcgravia evenia is a species of flowering vine in the family Marcgraviaceae. Within this family it belongs to the Galetae group, which is characterized by a long inflorescence axis and boat shaped nectaries. The plant is endemic to Cuba.
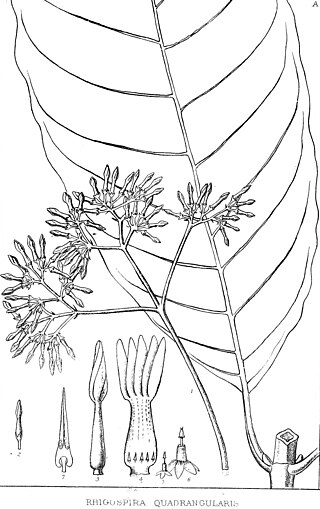
Rhigospira is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1878 by John Miers. The species, Rhigospira quadrangularis was first described as Ambelania quadrangularis by Johannes Müller Argoviensis in 1860 but was transferred to the genus, Rhigospira, in 1878 by John Miers. The genus contains only one known species, Rhigospira quadrangularis, native to northwestern South America.

Doliocarpus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Dilleniaceae, native to Central and South America.

Myrcia guianensis (pedra-ume-caá) is a species of plant in the genus Myrcia of the family Myrtaceae native to South America.

Rourea is a genus of plants in the family Connaraceae. They are found worldwide across the tropics and subtropics.

Matourea is a genus in the family Plantaginaceae. It is found in South America. It is the correct name for former genus Achetaria that contained ten species.
Norantea is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Marcgraviaceae.
Sarcopera is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Marcgraviaceae.

Schwartzia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Marcgraviaceae. It is found in tropical parts of South America, mainly within the rainforest. It has greenish, white, reddish or red coloured flowers.















