
Aneto is the highest mountain in the Pyrenees and in Aragon, Spain's third-highest mountain, reaching a height of 3,404 metres. It is in the Spanish province of Huesca, the northernmost of three Aragonese provinces, 6 kilometres south of the France–Spain border. It forms the southernmost part of the Maladeta massif.
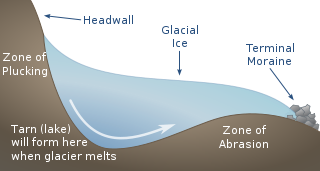
A tarn is a mountain lake, pond or pool, formed in a cirque excavated by a glacier. A moraine may form a natural dam below a tarn.

An arête is a narrow ridge of rock that separates two valleys. It is typically formed when two glaciers erode parallel U-shaped valleys. Arêtes can also form when two glacial cirques erode headwards towards one another, although frequently this results in a saddle-shaped pass, called a col. The edge is then sharpened by freeze-thaw weathering, and the slope on either side of the arête steepened through mass wasting events and the erosion of exposed, unstable rock. The word arête is French for "edge" or "ridge"; similar features in the Alps are often described with the German equivalent term Grat.

A pyramidal peak, sometimes called a glacial horn in extreme cases, is an angular, sharply pointed mountain peak which results from the cirque erosion due to multiple glaciers diverging from a central point. Pyramidal peaks are often examples of nunataks.

Rila is the highest mountain range of Bulgaria, the Balkan Peninsula, and Southeast Europe. It is situated in southwestern Bulgaria and forms part of the Rila–Rhodope Massif. The highest summit is Musala at an elevation of 2,925 m which makes Rila the sixth highest mountain range in Europe after the Caucasus, the Alps, Sierra Nevada, the Pyrenees and Mount Etna, and the highest one between the Alps and the Caucasus. It spans a territory of 2,629 km2 with an average elevation of 1487 m. The mountain is believed to have been named after the river of the same name, which comes from the Old Bulgarian verb "рыти" meaning "to grub".

The Pirin Mountains are a mountain range in southwestern Bulgaria, with the highest peak, Vihren, at an altitude of 2,914 m (9,560 ft).

A cirque is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie and cwm. A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform arising from fluvial erosion.

Europe is traditionally defined as one of seven continents. Physiographically, it is the northwestern peninsula of the larger landmass known as Eurasia ; Asia occupies the centre and east of this continuous landmass. Europe's eastern frontier is usually delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia, which is the largest country by land area in the continent. The southeast boundary with Asia is not universally defined, but the modern definition is generally the Ural River or, less commonly, the Emba River. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains, and on to the Black Sea. The Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean. Iceland is usually included in Europe because it is over twice as close to mainland Europe as mainland North America. There is ongoing debate on where the geographical centre of Europe falls.

Vihren is the highest peak of Bulgaria's Pirin Mountains. Reaching 2,914 metres (9,560 ft), it is Bulgaria's second and the Balkans' third highest, after Musala and Mount Olympus. Although Vihren is deprived of lakes and streams due to the karst topography, a number of Pirin's lakes are located around the peak, as is Europe's southernmost glacial mass, the Snezhnika glacieret. Until 1942 Vihren was known as Eltepe ; it was also called Buren (stormy) and Malnienosets (lightning-bringer). The UNESCO World Heritage Site Pirin National Park was originally known as the Vihren National Park. Vihren is included in the 100 Tourist Sites of Bulgaria under No. 2.

Jezercë is the highest peak in the Dinaric Alps, the second highest in Albania and the sixth highest in Southeast Europe, standing at 2,694 m (8,839 ft) above sea level. It is the 28th most prominent mountain peak in Europe, and is regarded as one of the toughest and most dangerous climbs in the Albanian Alps.

The Accursed Mountains, also known as the Albanian Alps, is a mountain range in coastal Southeast Europe adjacent to the Adriatic Sea. It is the southernmost subrange of the 1,000-kilometre-long (621 mi) Dinaric Alps range (Dinarides), extending from northern Albania to western Kosovo and northeastern Montenegro. Maja Jezercë, standing at 2,694 m (8,839 ft), is the highest point of the Accursed Mountains and of all Dinaric Alps, and the fifth highest peak in Albania. The range includes the mountain Zla Kolata, which, at 2,534 m (8,314 ft), is the tallest mountain in Montenegro. The range also includes the mountain Gjeravica, which, at 2,656 m (8,714 ft), is the second tallest mountain in Kosovo. One of the southernmost glacial masses in Europe was discovered in the Albanian part of the range in 2009.

Kutelo is a summit in the Pirin mountain range, southwestern Bulgaria. With a height of 2,908 m it is the second highest peak in Pirin after Vihren (2,914 m), and the third one in Bulgaria, behind Musala (2,925 m) in Rila and Vihren. Kutelo is a double peak with a small saddle between the two parts, the lower being only one meter shorter than the higher one, at 2,907 m. Seen from the town of Bansko, it appears higher than Vihren.

The Calderone glacier is a glacier located in the Apennine Mountains in Abruzzo, Italy. Found in the Gran Sasso d'Italia mountain group, it lies just beneath the Corno Grande, the highest peak in the Apennines.

The Banski Suhodol Glacier is a glacieret in the Pirin Mountains of Bulgaria. It lies below the Kutelo peak in the upper Banski Suhodol Valley.

Erebia cassioides, the common brassy ringlet, is a member of the subfamily Satyrinae of family Nymphalidae.

Geum montanum, the Alpine avens, is a species of flowering plant of the genus Geum in the Rosaceae family, native to the mountains of central and southern Europe.

Maja e Thatë is a 2,406-metre-high (7,894 ft) mountain peak of the Albanian Alps in Albania. It is located within Valbonë Valley National Park, roughly 2 km (1 mi) northwest of Valbonë and rises more than 1,500 m (4,921 ft) above the village. The mountain's southern and western lower slopes are relatively rich in beech and pine forests, while the higher slopes consist of very steep dolomite and limestone rock walls, suitable for mountaineering and rock climbing.

Snezhnika is a glacieret in the Pirin Mountains of Bulgaria, a remnant of the former Vihren Glacier. The glacieret lies at an elevation between 2,425 m (7,956 ft) and 2,480 m (8,140 ft) in the deep Golemiya Kazan cirque at the steep northern foot of Vihren, Pirin's highest summit. Due to the relatively easy access and its location along a popular hiking trail, Snezhnika is Bulgaria's most famous glacieret. Snezhnika has an average area of 0.01 km2 (0.0039 sq mi) and in 2006 it had a volume of 30,000 m3 (1,100,000 cu ft).

A glacieret is a very small glacier, with a surface area less than 0.1 km2. The term is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to a large, persistent snow patch of firn or névé.





















