
Anthurium is a genus of about 1,000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, and laceleaf.

Caperonia is a genus of plants of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1825. The genus is native to tropical and subtropical America and Africa.
Romanoa tamnoides is a species of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus Romanoa, first described in 1824. It is native to Brazil and Paraguay.

Dracontium is a genus of flowering plants similar to those of Amorphophallus. Unlike Amorphophallus which is found in the Old World, this genus has a New World distribution and is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, and the West Indies.

Spathiphyllum montanum is a flowering plant of the genus Spathiphyllum in the family Araceae. It is native to Panama and Costa Rica.

Spathiphyllum silvicola is a flowering plant of the genus Spathiphyllum in the family Araceae. It is native to Colombia and Costa Rica.

Heteropsis is a genus of plants in the family Araceae, native to Central and South America.

Ambrosina is a genus in the family Araceae that consists of only one species, Ambrosina bassii, and the only genus in the tribe Ambrosineae. This species is the smallest aroid in the Mediterranean, growing only to 8 cm tall. It is usually found growing in woodlands on north faces of hillsides and in humus soil that is covering limestone. It is distributed in Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, southern mainland Italy, Tunisia, and Algeria.

Asterostigma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Brazil and Argentina. The leaves are pinnate and the plant is tuberous.
- Asterostigma cryptostylumBogner - Brasília, Goiás, Minas Gerais
- Asterostigma cubense(A.Rich.) K.Krause ex Bogner - São Paulo
- Asterostigma lividum(G.Lodd.) Engl. - southern Brazil; Misiones Province of Argentina
- Asterostigma lombardiiE.G.Gonç. - Minas Gerais, Espírito Santo
- Asterostigma luschnathianumSchott - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma reticulatumE.G.Gonç - southern Brazil
- Asterostigma riedelianum(Schott) Kuntze - eastern Brazil
- Asterostigma tweedieanumSchott - Santa Catarina in southern Brazil
Alloschemone is a genus of evergreen root climbing plants in the family Araceae that is native to the Amazon region of Bolivia and Brazil. There are only two species in the genus and both are extremely rare. These two species are Alloschemone occidentalis and Alloschemone inopinata. At one point in history, the genus Alloschemone was dissolved and added to Scindapsus, but it has since been reinstated after further observations of the plants.

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of approximately 10 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.
Anaphyllopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to northern South America.
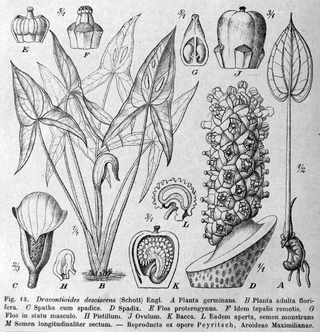
Dracontioides is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It was long thought to contain only a single species until a second species was described in 2005. Both are endemic to Brazil.

Lasimorpha is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The single species that makes up the genus is Lasimorpha senegalensis. This species is native to western and central Africa, from Liberia east to Chad and south to Angola.
Zomicarpella is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to Colombia, Peru and Brazil. The leaves are hastate or sagittate. The chromosome number for Zomicarpella species is 2n=26. Additionally, the seeds have an endosperm.
- Zomicarpella amazonicaBogner - Amazonas State of northwestern Brazil
- Zomicarpella maculataN.E.Br. - Colombia, Peru
Mangonia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus contains only two known species native to southern Brazil and Uruguay.
- Mangonia tweedieanaSchott. - Rio Grande do Sul, Uruguay
- Mangonia uruguaya(Hicken) Bogner - Cerro Largo in Uruguay

Pseudohydrosme is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It contains only three species, Pseudohydrosme buettneri, Pseudohydrosme gabunensis, and more recently Pseudohydrosme ebo, two being endemic to tropical rain forests in Gabon, and the other being native to the Ebo Forest of Cameroon. The genus is believed to be closely related to Anchomanes and is likely to be sunk into Anchomanes due to molecular evidence.
Spathantheum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. The genus contains two species, Spathantheum fallax and Spathantheum orbignyanum. Spathantheum is believed to be closely related to Spathicarpa. The genus is endemic to the Andes of Peru, Bolivia, and northern Argentina and is found growing in grasslands in rocky soil.
- Spathantheum fallax Hett., Ibisch & E.G.Gonç. - Bolivia
- Spathantheum orbignyanumSchott - Peru, northwestern Argentina, Bolivia

Taccarum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is endemic to South America. The genus tends to grow in rocky areas.
- Taccarum caudatumRusby - Bolivia, Peru, Acre State in western Brazil
- Taccarum crassispathumE.G.Gonç. - central Brazil
- Taccarum peregrinum(Schott) Engl. - Paraguay, southern Brazil, Misiones Province of Argentina
- Taccarum uleiEngl. & K.Krause - eastern Brazil
- Taccarum warmingiiEngl. - southern Brazil
- Taccarum weddellianumBrongn. ex Schott - Bolivia, Peru, Paraguay, central and western Brazil
Philonotion is a genus of plants in the family Araceae. It has three known species, native to tropical South America. Some authorities regard it as part of the related genus Schismatoglottis.
- Philonotion americanum(A.M.E.Jonker & Jonker) S.Y.Wong & P.C.Boyce - Brazil, Colombia, Venezuela, the Guianas
- Philonotion bolivaranum(G.S.Bunting & Steyerm.) S.Y.Wong & P.C.Boyce - Venezuela
- Philonotion spruceanumSchott - Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, northwestern Brazil













