Nyctimystes perimetri, also known as the archipelago big-eyed treefrog, is a species of frog in the family Pelodryadidae, also treated as the subfamily Pelodryadinae in the family Hylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and currently only known from the Louisiade Archipelago, although it might also occur in the Owen Stanley Range of the mainland Papua New Guinea. It has also been suggested that the Rossel Island population might represent a distinct species.
Nyctimystes persimilis, also known as the Milne big-eyed treefrog, is a species of frog in the family Pelodryadidae, also treated as the subfamily Pelodryadinae in the family Hylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from Mount Dayman and Mount Simpson in the Owen Stanley Range.

Aphantophryne minuta is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and is known from its type locality near Myola Guest House in the Owen Stanley Range, Northern Province, from another locality in the same province, Mount Tafa; only a single specimen is known from each locality. The specific name minuta refers to the very small size of this species. Common name Myola Guinea frog has been coined for it.
Austrochaperina adamantina is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and occurs in the Torricelli and Bewani Mountains in the West Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. The specific name adamantina is Latin for "like a diamond" and refers to Jared Diamond, credited as the collector of the holotype and "great many other valuable herpetological specimens from Papua New Guinea".
Austrochaperina basipalmata is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the mountain ranges of northern New Guinea and is found between Tawarin River in Papua, Western New Guinea (Indonesia) and Torricelli Mountains in Papua New Guinea.
Austrochaperina blumi is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and known from the northern slopes of the New Guinean Central Range in Western New Guinea (Indonesia), and from the Bewani, Torricelli, and Hunstein Mountains in Papua New Guinea. The specific name blumi honors J. Paul Blum, the herpetologist who collected the type series. Common name Kosarek land frog has been proposed for it.

Copiula derongo is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to New Guinea and found in both Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. The specific name derongo refers to its type locality, the village of Derongo in the Western Province. Based on molecular evidence, it was transferred from Austrochaperina to Copiula in 2016.

Copiula guttata is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from around the head of the Gulf of Papua in the Gulf and Chimbu Provinces. The specific name is the Latin adjective guttata that means "spotted" and refers to the dorsal colour pattern of this species. Based on molecular evidence, it was transferred from Austrochaperina to Copiula in 2016.

Copiula rivularis is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from near the Indonesian border east to the Morobe Province; it is expected to occur in the Papua province of Indonesia. The specific name comes from the Latin adjective pertaining to small brooks or streams and refers to the habitat of this species. Based on molecular evidence, it was transferred from Austrochaperina to Copiula in 2016.

Barygenys atra is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to eastern New Guinea and is known from the Morobe and Northern Provinces, Papua New Guinea. Common name Gunther's Papua frog has been proposed for it.
Barygenys exsul is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea. It is known from Rossel and Sudest Islands in the Louisiade Archipelago, east of New Guinea. It is uncertain whether the specimens from Sudest really are conspecific with this species. Barygenys apodasta and Barygenys resima were mixed with this species prior to their description in 2013.

Callulops boettgeri, also known as Boettger's Callulops frog, is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Halmahera in the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. It is only known from the holotype collected from Galela in 1894. The genus-level placement of this little known frog has changed many times, and it is still unclear whether it should be placed in some other genus.
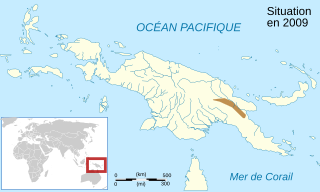
Cophixalus parkeri is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea where it occurs in the central mountainous region between Chimbu and Morobe Provinces. The specific name parkeri presumably honours Hampton Wildman Parker, an English zoologist and herpetologist to whose perusal Arthur Loveridge sent the holotype. Common name Papua rainforest frog has been coined for it.
Cophixalus riparius is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands in Madang, Southern Highlands, and Western Highlands provinces southeastward to the Morobe Province. The specific name riparius refers to the creek-side habitat from which many specimens in the type series were collected. Common name Wilhelm rainforest frog has been coined for this species.
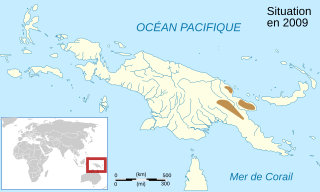
Cophixalus shellyi is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and occurs in the New Guinea Highlands as well as in the Adelbert Range and on the Huon Peninsula. The specific name shellyi honors Father Otto Schellenberger ("Shelly"), an American missionary and former professor in mathematics who collected the type series.

Cophixalus tagulensis is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and only known from the Tagula Island in the Louisiade Archipelago, east of New Guinea. It is only known from the type series of three specimens collected in 1956.

Aphantophryne nana is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the Philippines and is known with certainty only from the island of Camiguin. It is unclear whether similar frogs from northeast Mindanao are referable to this species. It was described as Oreophryne nana, but based on molecular data it was moved to Aphantophryne in 2017. Common names Camiguin cross frog, Camiguin narrow-mouthed frog, and volcano cross frog have been coined for the species.
Aphantophryne parkeri is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to the north coast of New Guinea and only known from Matapan and the Bewani Mountains in the West Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea, and from Sentani in the Papua Province, Western New Guinea (Indonesia). This species was formerly included in the genus Oreophryne, but was in 2017 moved to Aphantophryne based on molecular data. The specific name parkeri honours Hampton Wildman Parker, an English zoologist and herpetologist. Common name Parker's cross frog has been coined for it.
Copiula alpestris is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and known from the Western Highlands, Chimbu, and Eastern Highlands Provinces at elevations of 1,800–2,800 m (5,900–9,200 ft) above sea level. The specific name is a Latin adjective meaning "living in high mountains", in reference to its relatively high-altitude habitats. Based on molecular evidence, the species was transferred from Oxydactyla to Copiula in 2016.
Xenorhina subcrocea is a species of frog in the family Microhylidae. It is endemic to Papua New Guinea and is known from the New Guinean north coast, including coastal ranges between Vanimo and Lae. Common name Lae fanged frog has been coined for it.










