Related Research Articles
The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya.
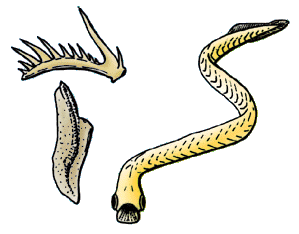
Conodonts are extinct agnathan chordates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from tooth-like microfossils found in isolation and now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. The animals are also called Conodontophora to avoid ambiguity.
The Tremadocian is the lowest stage of Ordovician. Together with the later Floian stage it forms the Lower Ordovician epoch. The Tremadocian lasted from 485.4 to 477.7 million years ago. The base of the Tremadocian is defined as the first appearance of the conodont species Iapetognathus fluctivagus at the Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) section on Newfoundland.
The Darriwilian is the upper stage of the Middle Ordovician. It is preceded by the Dapingian and succeeded by the Upper Ordovician Sandbian stage. The lower boundary of the Darriwilian is defined as the first appearance of the graptolite species Undulograptus austrodentatus around 467.3 million years ago. It lasted for about 8.9 million years until the beginning of the Sandbian around 458.4 million years ago.
In the geological timescale, the Llandovery epoch occurred at the beginning of the Silurian period. The Llandoverian epoch follows the massive Ordovician-Silurian extinction events, which led to a large decrease in biodiversity and an opening up of ecosystems.
The Dapingian is the third stage of the Ordovician and the first stage of the Middle Ordovician. It is preceded by the Floian and succeeded by the Darriwilian. The top of the Floian is defined as the first appearance of the conodont species Baltoniodus triangularis which happened about 470 million years ago. The Dapingian lasted for about 2.7 million years until about 467.3 million years ago.
The Whiterockian, often referred to simply as the Whiterock, is an earliest or lowermost stage of the Middle Ordovician. Although the Whiterockian or Whiterock Stage refers mainly to the early Middle Ordovician in North America, it is often used in the older literature in a global sense.

Lonchodomas is a genus of trilobites, that lived during the Ordovician. It was eyeless, like all raphiophorids, and had a long straight sword-like frontal spine, that gradually transforms into the relatively long glabella. Both the glabellar spine and the backward directed genal spines are subquadrate in section. Lonchodomas has five thorax segments and the pleural area of the pygidium has two narrow furrows. Lonchodomas occurred in what are today Argentina, Canada (Newfoundland), Estonia, Latvia, Norway, Sweden, the Russian Federation and the United States.
Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician Promissum (Prioniodinina) from the Soom Shale and the Carboniferous specimens from the Granton Shrimp bed (Ozarkodinina). They are euconodonts, in that their elements are composed of two layers; the crown and the basal body, and are assumed to be a clade.
Nealeodus is a genus of conodonts which existed in what is now Canada during the middle Ordovician. It was described as a new genus for the species Lenodus martinpointensis by Svend Stouge in 2012.
Periodon is a genus of conodonts which existed in what is now Canada, Iran, Argentina, China, Russia, and the United States during the Ordovician Period. It was described by Hadding in 1913, and the type species is P. aculeatus.
Iapetognathus fluctivagus is a species of denticulate cordylodan conodonts belonging to the genus Iapetognathus. It existed during the Tremadocian Age of the Ordovician. It is an important index fossil in biostratigraphy.
Galbagnostus is an extinct genus of agnostid trilobite. It lived during the Lower and Middle Ordovician.
Westergaardodina is a species-rich genus of spine, U or W-shaped paraconodont known from Middle Cambrian to Lower Ordovician strata.
The Beekmantown Group is a late Cambrian to lower–middle Ordovician geologic group that occurs in the northeastern United States, datable from its conodont fauna. It contains dolomitic sandstones and carbonates from just off land from the palaeocoastline.
The Skoki Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early to Middle Ordovician age that is present on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in the Canadian Rockies of Alberta and British Columbia. It was named for Skoki Mountain near Lake Louise in Banff National Park by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1928. The Skoki Formation is fossiliferous and includes remains of brachiopods and other marine invertebrates, as well as conodonts and oncolites.
Iapetognathus is a genus of cordylodan conodonts. It is one of the oldest denticulate euconodont genera known.
Furnishina is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Furnishinidae from the Cambrian.
Stig M. Bergström is a Swedish-American paleontologist.
Histiodella is an extinct genus of conodonts.
References
- ↑ Svend Stouge (2012). "Middle Ordovician (late Dapingian–Darriwilian) conodonts from the Cow Head Group and Lower Head Formation, western Newfoundland, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 49 (1): 59–90. doi:10.1139/e11-057.