
Caviinae is a subfamily uniting all living members of the family Caviidae with the exception of the maras, capybaras, and Kerodon. The subfamily traditionally contained the guinea pig or cavy-like forms along with the cursorially adapted (running) Kerodon. Molecular results suggest the Caviinae as so defined would be paraphyletic and Kerodon is more closely related to maras and capybaras than to other caviines. This led Woods and Kilpatrick (2005) to unite Kerodon and capybaras into the subfamily Hydrochoerinae within the Caviidae. These studies also suggest Microcavia and Cavia are more closely related to one another than either is to Galea.

The black agouti is a South American species of agouti from the family Dasyproctidae.

Azara's agouti is an agouti species from the family Dasyproctidae. Found in Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina, it is named after Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara. The population is unknown and may have gone locally extinct in some areas due to hunting; it is listed as vulnerable in Argentina.

The rock cavy or mocó is a cavy species endemic to eastern Brazil which has also been introduced to the Atlantic island of Fernando de Noronha.
The Brazilian yellow-toothed cavy is a cavy species from South America. It is found in Brazil.

Fischer's guiara, is a spiny rat species found in Argentina, Brazil and Paraguay. It is one of only two species in the genus Euryzygomatomys. Its karyotype has 2n=46 and FN=88.
The long-tailed armored tree-rat, is a spiny rat species from South America. It is found in Brazil, with a population in Ecuador which is referable either to this species or to Makalata didelphoides. Initially considered a large form of the latter species, it actually represents a distinct species as supported by morphological and molecular characters.

The white-spined Atlantic spiny rat is a spiny rat species endemic to Brazil.

Oecomys concolor, also known as the unicolored oecomys, unicolored rice rat, or unicolored arboreal rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oecomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome, but its range is poorly documented; it has been recorded in northwestern Brazil, southeastern Colombia, and southern Venezuela.
Oecomys paricola, also known as the Brazilian oecomys, Brazilian arboreal rice rat, or South Amazonian arboreal rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oecomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in northeastern Peru as well as central Brazil south of the Amazon, where it lives in lowland tropical rainforests.
Oligoryzomys microtis, also known as the small-eared colilargo or small-eared pygmy rice rat, is a species of rodent in the genus Oligoryzomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in western Brazil, eastern Peru, Bolivia, and northern Paraguay.
Neacomys spinosus, also known as the common neacomys, common bristly mouse, or bristly mouse, is a nocturnal rodent species from South America in the genus Neacomys. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, where it often lives in transition areas between lowland forest and open regions. Its diet consists of insects, seeds and fruit.
Nectomys rattus, the small-footed bristly mouse, Amazonian nectomys, Amazonian mouse, or common water rat is a species of rodent in the genus Nectomys of family Cricetidae. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, and Venezuela, where it lives in a variety of habitats including lowland tropical rainforest, cerrado and caatinga. It is mainly found in areas close to water. It was recognized as distinct only in 2000 and its limits with other Nectomys, including Nectomys apicalis and Nectomys squamipes, remain unclear.
Oyapock's fish-eating rat is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in French Guiana and Brazil.
The common yellow-toothed cavy is a species of rodent in the family Caviidae, closely related to the domesticated guinea pig. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru. Its karyotype has 2n = 68 and FN = 136. G. musteloides is the most common and widely found member of Galea, and is present at elevations ranging from 20 to 5000 m above sea level. It has yellow teeth.
The blackish grass mouse also formerly called the ebony akodont, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. It is the only species in the genus Thaptomys.
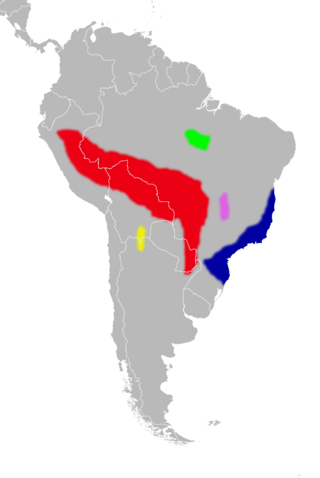
Euryoryzomys macconnelli, also known as MacConnell's rice rat or MacConnell's oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela, where it lives in lowland tropical rainforest. It was formerly placed in the genus Oryzomys, as Oryzomys macconnelli, but in 2006 it was reclassified as the type species of the new genus Euryoryzomys.

The Muenster yellow-toothed cavy is a species of rodent in the family Caviidae. It is known only from one location in Valle Hermoso in the Bolivian Andes, at an elevation of 2,557 m (8,389 ft). Specimens from this location were shipped to Muenster, Germany, in 1997 for laboratory research, where the species was recognized and described. Galea monasteriensis was recognized on the basis of morphological, behavioral, and reproductive differences from related species. However, its habits in the wild have not been studied.
Cerradomys scotti, also known as Lindbergh's oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America in the genus Cerradomys. It is terrestrial and is found in the cerrado (savanna) ecozone of south central Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay. The species is common and appears to tolerate a degree of agricultural habitat modification.

Galea is a genus of South American rodents of the family Caviidae. 5-6 extant species are known, found in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Peru and Brazil. They are:










