
Vanguard 1 is an American satellite that was the fourth artificial Earth-orbiting satellite to be successfully launched, following Sputnik 1, Sputnik 2, and Explorer 1. It was launched 17 March 1958. Vanguard 1 was the first satellite to have solar electric power. Although communications with the satellite were lost in 1964, it remains the oldest human-made object still in orbit, together with the upper stage of its launch vehicle.

STS-66 was a Space Shuttle program mission that was flown by the Space Shuttle Atlantis. STS-66 launched on November 3, 1994, at 11:59:43.060 am EDT from Launch Pad 39-B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base on November 14, 1994, at 10:33:45 am EST.

STS-96 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle Discovery, and the first shuttle flight to dock[a] at the International Space Station. The shuttle carried the Spacehab module in the payload, filled with cargo for station outfitting. STS-96 launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 27 May 1999 at 06:49:42 AM EDT and returned to Kennedy on 6 June 1999, 2:02:43 AM EDT.

The Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) was a NASA-operated orbital observatory whose mission was to study the Earth's atmosphere, particularly the protective ozone layer. The 5,900-kilogram (13,000 lb) satellite was deployed from Space Shuttle Discovery during the STS-48 mission on 15 September 1991. It entered Earth orbit at an operational altitude of 600 kilometers (370 mi), with an orbital inclination of 57 degrees.

Vanguard 2 is an Earth-orbiting satellite launched 17 February 1959 at 15:55:02 GMT, aboard a Vanguard SLV-4 rocket as part of the United States Navy's Project Vanguard. The satellite was designed to measure cloud cover distribution over the daylight portion of its orbit, for a period of 19 days, and to provide information on the density of the atmosphere for the lifetime of its orbit. As the first weather satellite and one of the first orbital space missions, the launch of Vanguard 2 was an important milestone in the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union. Vanguard 2 remains in orbit.

Vanguard 3 is a scientific satellite that was launched into Earth orbit by the Vanguard SLV-7 on 18 September 1959, the third successful Vanguard launch out of eleven attempts. Vanguard rocket: Vanguard Satellite Launch Vehicle-7 (SLV-7) was an unused Vanguard TV-4BU rocket, updated to the final production Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV).

Project Echo was the first passive communications satellite experiment. Each of the two American spacecraft, launched in 1960 and 1964, were metalized balloon satellites acting as passive reflectors of microwave signals. Communication signals were transmitted from one location on Earth and bounced off the surface of the satellite to another Earth location.

Explorer 32, also known as Atmosphere Explorer-B (AE-B), was a NASA satellite launched by the United States to study the Earth's upper atmosphere. It was launched from Cape Canaveral on a Delta C1 launch vehicle, on 25 May 1966. It was the second of five "Atmosphere Explorer", the first being Explorer 17. Though it was placed in a higher-than-expected orbit by a malfunctioning second stage on its launch vehicle, Explorer 32 returned data for ten months before failing due to a sudden depressurization. The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 22 February 1985.
Ajisai is a Japanese satellite sponsored by NASDA, launched in 1986 on the maiden flight of the H-I rocket. It is also known as the Experimental Geodetic Satellite (EGS), as it carries the Experimental Geodetic Payload (EGP).

The STARSHINE series of three artificial satellites were student participatory missions sponsored by the United States Naval Research Laboratory.
Spacecraft collision avoidance is the implementation and study of processes minimizing the chance of orbiting spacecraft inadvertently colliding with other orbiting objects. The most common subject of spacecraft collision avoidance research and development is for human-made satellites in geocentric orbits. The subject includes procedures designed to prevent the accumulation of space debris in orbit, analytical methods for predicting likely collisions, and avoidance procedures to maneuver offending spacecraft away from danger.
DANDE is a 50 kg class spacecraft developed by the University of Colorado Boulder was the winner of the 5th iteration of the Air Force Research Laboratory's University Nanosat Program.

Orbiting Vehicle or OV, originally designated SATAR, comprised five disparate series of standardized American satellites operated by the US Air Force, launched between 1965 and 1971. Forty seven satellites were built, of which forty three were launched and thirty seven reached orbit. With the exception of the OV3 series and OV4-3, they were launched as secondary payloads, using excess space on other missions. This resulted in extremely low launch costs and short proposal-to-orbit times. Typically, OV satellites carried scientific and/or technological experiments, 184 being successfully orbited through the lifespan of the program.

Explorer 9, known as S-56A before launch, was a NASA satellite which was launched in February 1961 to study the density and composition of the upper thermosphere and lower exosphere. It was a reflight of the failed Explorer S-56 mission, and consisted of a 7 kg (15 lb), 3.66 m (12.0 ft) balloon which was deployed into a medium Earth orbit. The mission was conducted by NASA's Langley Research Center.
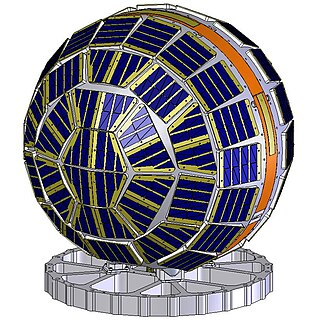
ADEOS I was an Earth observation satellite launched by NASDA in 1996. The mission's Japanese name, Midori means "green". The mission ended in July 1997 after the satellite sustained structural damage to the solar panel. Its successor, ADEOS II, was launched in 2002. Like the first mission, it ended after less than a year, also following solar panel malfunctions.
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a successful nano-sat flight series conducted from the NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with numerous universities. While one of the principal aims has been to introduce young professionals and university students to the practical realm of developing space flight hardware, considerable innovations have been introduced. In addition, this evolving flight platform has tested concepts for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sample return, as well as planetary nano-sat class mission concepts.

OSCAR IV was the fourth amateur radio satellite launched by Project OSCAR and the first targeted for Geostationary orbit on 12 December 1965. The satellite was launched piggyback with three United States Air Force satellites on a Titan IIIC launch vehicle. Due to a booster failure, OSCAR 4 was placed in an unplanned and largely unusable Geostationary transfer orbit.

Student Nitric Oxide Explorer, was a NASA small scientific satellite which studied the concentration of nitric oxide in the thermosphere. It was launched in 1998 as part of NASA's Explorer program. The satellite was the first of three missions developed within the Student Explorer Demonstration Initiative (STEDI) program funded by the NASA and managed by the Universities Space Research Association (USRA). STEDI was a pilot program to demonstrate that high-quality space science can be carried out with small, low-cost free-flying satellites on a time scale of two years from go-ahead to launch. The satellite was developed by the University of Colorado Boulder's Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) and had met its goals by the time its mission ended with reentry in December 2003.

Orbiting Vehicle 3-6, launched 5 December 1967, was the sixth and last satellite to be launched in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. The satellite measured electron density and neutral density ion composition, as functions of latitude and time. The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 9 March 1969.

















