
Prasiolales is an order of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. Members of this order are ecologically widespread and are found in freshwater, marine, and terrestrial habitats from the Arctic to the Antarctic.

Prasiolaceae is a family of green algae in the order Prasiolales. Members of this family are found in freshwater, terrestrial, and marine habitats.

Selenastraceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. Members of this family are common components of the phytoplankton in freshwater habitats worldwide. A few species have been found in brackish and marine habitats, such as in the Baltic Sea.
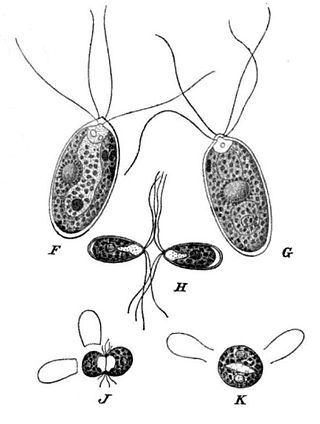
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Cylindrocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.
Desmococcus is a genus of green algae in the family Stichococcaceae. It is a subaerial genus of algae with a cosmopolitan distribution.
Dictyochloris is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is the sole genus of the family Dictyochloridaceae. It is commonly found in terrestrial and subaerial habitats.

Geminella is a genus of green algae in the phylum Chlorophyta. Once considered part of the order Ulotrichales, molecular phylogenetics have shown that Geminella and related genera form a well-supported clade within the class Trebouxiophyceae.

Gloeotila is a genus of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. It is typically found in freshwater habitats, either attached to surfaces or planktonic, or found in soil.
Koliella is a genus of green algae in the order Prasiolales. Members of this genus are found in freshwater plankton, but some are also found on snow and ice.

Microthamnion is a genus of green algae in the family Microthamniaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats around the world, preferably with low levels of pollution; it is typically attached to solid substrates.

Radiofilum is a genus of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. It is a freshwater genus; they are often found in soft, boggy or acidic waters.

Rosenvingiella is a genus of green algae in the family Prasiolaceae. Members of this genus are found in marine or terrestrial habitats.
Vitreochlamys is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. It is sometimes known by the name Sphaerellopsis, published by Aleksandr Arkadievich Korshikov. However, that name is an illegitimate later homonym, preceded by SphaerellopsisM.C.Cooke. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats.

Cosmarium is a large genus of desmids (Desmidiaceae), a group of green algae closely related to the land plants (Embryophyta). Members of this genus are microscopic and found in freshwater habitats around the world.
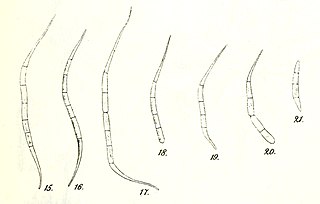
Raphidonema is a genus of filamentous green alga comprising five species. It is a member of the Trebouxiophyceae.

Klebsormidium is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae comprising 20 species. The name was proposed in 1972 to resolve confusion in application and status of Hormidium and was given for the German botanist Georg Albrecht Klebs.
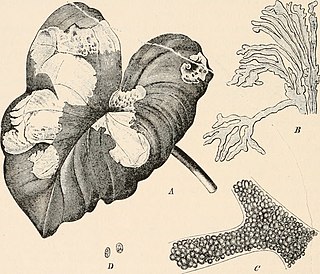
Phyllosiphon is a genus of green algae in the class Trebouxiophyceae. Unusually among the green algae, members of Phyllosiphon are often parasitic within the leaves of Araceae, causing necrosis. It has a mostly tropical to subtropical distribution, and is found primarily in the Mediterranean region, but has also been isolated in North America, Australia, Africa, and China.

Koliellaceae is a family of green algae in the order Prasiolales.















