
Bryozoa are a phylum of aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all forming sedentary colonies. Typically about 0.5 millimetres long, they are filter feeders that sieve food particles out of the water using a retractable lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles lined with cilia. Most marine species live in tropical waters, but a few occur in oceanic trenches, and others are found in polar waters. One class lives only in freshwater environments, and a few members of a mostly marine class prefer brackish water. 5869 living species are known. One genus is solitary and the rest are colonial.
Stenolaemata are a class of marine bryozoans. This class originated in the Ordovician, and members still live today. All extant species are in the order Cyclostomatida.

Cheilostomatida is an order of Bryozoa in the class Gymnolaemata.

The Catenicellidae are a family of bryozoans in the suborder Ascophora.
Victorella is a genus of bryozoans in the family Victorellidae.

Cristatella mucedo is a bryozoan in the family Cristatellidae, and the only species of the genus Cristatella. They are noted for their elongated shape and colorless, transparent bodies.
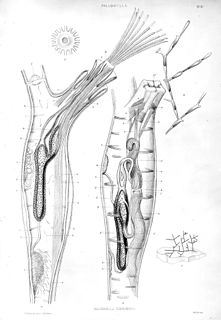
Paludicella is a genus of freshwater bryozoans in the family Paludicellidae.

Schizoporella unicornis is a species of bryozoans in the family Schizoporellidae.

Reteporella grimaldii is a species of bryozoans in the family Phidoloporidae.
Articulina is an extant suborder of bryozoans in the order Cyclostomatida.
Zoobotryon verticillatum, commonly known as the spaghetti bryozoan, is a species of colonial bryozoans with a bush-like structure. It is found in shallow temperate and warm waters in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea and has spread worldwide as a fouling organism. It is regarded as an invasive species in some countries.
Conopeum seurati is a species of colonial bryozoan in the order Cheilostomatida. It is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. This species has been introduced to New Zealand and Florida.
Fenestrulina rugula is a bryozoan species from the genus Fenestrulina. The scientific name of the species was first published in 1990 by Hayward & Ryland.

Bugula neritina is a cryptic species complex of sessile marine animal in the genus Bugula.

Catenicella are a genus of bryozoans in the family Catenicellidae.
Cribella is a genus of bryozoans in the family Bitectiporidae.
Petrophile incurvata is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to southwestern Western Australia. It is a shrub with flattened, sometimes pinnately-divided leaves with up to five sharply pointed lobes, and cylindrical to oval heads of silky-hairy, cream-coloured to yellowish-white flowers.
Bryosartor is a genus of bryozoan described by Gordon and Braga in 1994. The only species is Bryosartor sutilis. It belongs to the family Catenicellidae. No subspecies are listed.

Electra posidoniae is a species of bryozoan in the family Electridae. It is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea, and is commonly known as the Neptune-grass bryozoan because it is exclusively found growing on seagrasses, usually on Neptune grass, but occasionally on eelgrass.
Callopora lineata is a species of colonial bryozoan in the family Calloporidae. It is found on rocky shores in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.








