Related Research Articles

A copycat suicide is defined as an emulation of another suicide that the person attempting suicide knows about either from local knowledge or due to accounts or depictions of the original suicide on television and in other media. The publicized suicide serves as a trigger, in the absence of protective factors, for the next suicide by a susceptible or suggestible person. This is referred to as suicide contagion.
Suicide is the second leading cause of death for people in the United States from the ages of 9 to 56.

Suicide prevention is a collection of efforts to reduce the risk of suicide. Suicide is often preventable, and the efforts to prevent it may occur at the individual, relationship, community, and society level. Suicide is a serious public health problem that can have long-lasting effects on individuals, families, and communities. Preventing suicide requires strategies at all levels of society. This includes prevention and protective strategies for individuals, families, and communities. Suicide can be prevented by learning the warning signs, promoting prevention and resilience, and committing to social change.
There are more than 700,000 estimated suicide deaths every year. Suicide affects every demographic, yet there are some populations that are more impacted than others. For example, among 15–29 year olds, suicide is much more prominent; this being the fourth leading cause of death within this age group.

Suicidal ideation, or suicidal thoughts, is the thought process of having ideas, or ruminations about the possibility of committing suicide. It is not a diagnosis but is a symptom of some mental disorders, use of certain psychoactive drugs, and can also occur in response to adverse life events without the presence of a mental disorder.
Men's health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, as experienced by men, and not merely the absence of disease. Differences in men's health compared to women's can be attributed to biological factors, behavioural factors, and social factors.
Suicide risk assessment is a process of estimating the likelihood for a person to attempt or die by suicide. The goal of a thorough risk assessment is to learn about the circumstances of an individual person with regard to suicide, including warning signs, risk factors, and protective factors. Risk for suicide is re-evaluated throughout the course of care to assess the patient's response to personal situational changes and clinical interventions. Accurate and defensible risk assessment requires a clinician to integrate a clinical judgment with the latest evidence-based practice, although accurate prediction of low base rate events, such as suicide, is inherently difficult and prone to false positives.
Youth suicide is when a young person, generally categorized as someone below the legal age of majority, deliberately ends their own life. Rates of youth suicide and attempted youth suicide in Western societies and other countries are high. Youth suicide attempts are more common among girls, but adolescent males are the ones who usually carry out suicide. Suicide rates in youths have nearly tripled between the 1960s and 1980s. For example, in Australia suicide is second only to motor vehicle accidents as its leading cause of death for people aged 15 to 25.

Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse are risk factors. Some suicides are impulsive acts due to stress, relationship problems, or harassment and bullying. Those who have previously attempted suicide are at a higher risk for future attempts. Effective suicide prevention efforts include limiting access to methods of suicide such as firearms, drugs, and poisons; treating mental disorders and substance abuse; careful media reporting about suicide; improving economic conditions; and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT). Although crisis hotlines are common resources, their effectiveness has not been well studied.
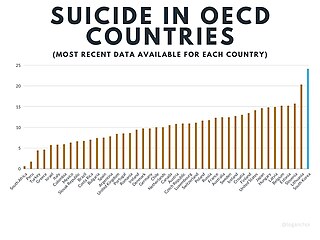
Suicide in South Korea occurs at the 12th highest rate in the world. South Korea has the highest recorded suicide rate in the OECD. In South Korea, it is estimated to affect 0.02 percent of the population by the WHO. In 2012, suicide was the fourth-highest cause of death. The suicide rate has consistently declined between 2012 and 2019, the year when the latest data are available.

Gender differences in suicide rates have been shown to be significant. There are different rates of suicides and suicidal behavior between males and females. While females more often have suicidal thoughts, males die by suicide more frequently. This discrepancy is also known as the gender paradox in suicide.
Research has found that attempted suicide rates and suicidal ideation among lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) youth are significantly higher than among the general population.
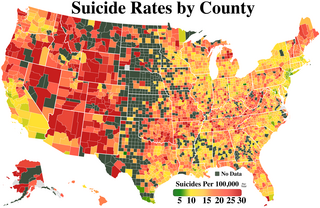
Suicide is a major national public health issue in the United States. The country has one of the highest suicide rates among wealthy nations. In 2020, there were 45,799 recorded suicides, up from 42,773 in 2014, according to the CDC's National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). On average, adjusted for age, the annual U.S. suicide rate increased 30% between 2000 and 2020, from 10.4 to 13.5 suicides per 100,000 people. In 2018, 14.2 people per 100,000 died by suicide, the highest rate recorded in more than 30 years. Due to the stigma surrounding suicide, it is suspected that suicide is generally underreported. In April 2016, the CDC released data showing that the suicide rate in the United States had hit a 30-year high, and later in June 2018, released further data showing that the rate has continued to increase and has increased in every U.S. state except Nevada since 1999. From 2000 to 2020, more than 800,000 people died by suicide in the United States, with males representing 78.7% of all suicides that happened between 2000 and 2020. In 2022, a record high 49,500 people died by suicide, while the suicide rate in 2022 reached its highest level since 1941 at 14.3 per 100,000 persons. Surging death rates from suicide, drug overdoses and alcoholism, what researchers refer to as "deaths of despair", are largely responsible for a consecutive three year decline of life expectancy in the U.S. This constitutes the first three-year drop in life expectancy in the U.S. since the years 1915–1918.
A suicide attempt is an act in which an individual tries to kill themselves but survives. Mental health professionals discourage describing suicide attempts as "failed" or "unsuccessful", as doing so may imply that a suicide resulting in death is a successful or desirable outcome.
In 2014, the WHO ranked Nepal as the 7th in the global suicide rate. The estimated annual suicides in Nepal are 6,840 or 24.9 suicides per 100,000 people. Data on suicide in Nepal are primarily based on police reports and therefore rely on mortality statistics. However, the burden of suicide in communities is likely to be higher, particularly among women, migrant workers, and populations affected by disasters.
In colleges and universities in the United States, suicide is one of the most common causes of death among students. Each year, approximately 24,000 college students attempt suicide while 1,100 students succeed in their attempt, making suicide the second-leading cause of death among U.S. college students. Roughly 12% of college students report the occurrence of suicide ideation during their first four years in college, with 2.6% percent reporting persistent suicide ideation. 65% of college students reported that they knew someone who has either attempted or died by suicide, showing that the majority of students on college campuses are exposed to suicide or suicidal attempts.
Suicide among Native Americans in the United States, both attempted and completed, is more prevalent than in any other racial or ethnic group in the United States. Among American youths specifically, Native American youths also show higher rates of suicide than American youths of other races. Despite making up only 0.9% of the total United States population, American Indians and Alaska Natives (AIANs) are a significantly heterogeneous group, with 560 federally recognized tribes, more than 200 non-federally recognized tribes, more than 300 languages spoken, and one half or more of them living in urban areas. Suicide rates are likewise variable within AIAN communities. Reported rates range from 0 to 150 per 100,000 members of the population for different groups. Native American men are more likely to commit suicide than Native American women, but Native American women show a higher prevalence of suicidal behaviors. Interpersonal relationships, community environment, spirituality, mental healthcare, and alcohol abuse interventions are among subjects of studies about the effectiveness of suicide prevention efforts. David Lester calls attention to the existence and importance of theories of suicide developed by indigenous peoples themselves, and notes that they "can challenge traditional Western theories of suicide." Studies by Olson and Wahab as well as Doll and Brady report that the Indian Health Service has lacked the resources needed to sufficiently address mental health problems in Native American communities. The most complete records of suicide among Native Americans in the United States are reported by the Indian Health Service.
A disease of despair is one of three classes of behavior-related medical conditions that increase in groups of people who experience despair due to a sense that their long-term social and economic prospects are bleak. The three disease types are drug overdose, suicide, and alcoholic liver disease.

Suicide cases have remained constant or decreased since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. According to a study done on twenty-one high and upper-middle-income countries in April–July 2020, the number of suicides has remained static. These results were attributed to a variety of factors, including the composition of mental health support, financial assistance, having families and communities work diligently to care for at-risk individuals, discovering new ways to connect through the use of technology, and having more time spent with family members which aided in the strengthening of their bonds. Despite this, there has been an increase in isolation, fear, stigma, abuse, and economic fallout as a result of COVID-19. Self-reported levels of depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts were elevated during the initial stay-at-home periods, according to empirical evidence from several countries, but this does not appear to have translated into an increase in suicides.
Youth suicide in India is when young Indian people deliberately end their own life. People aged 15 to 24 years have the highest suicide rate in India, which is consistent with international trends in youth suicide. 35% of recorded suicides in India occur in this age group. Risk factors and methods of youth suicide differ from those in other age groups.
References
- ↑ Ramsawak and Umraw, Rampersad and Ralph (2003). modules in social studies. La Romaine, Trinidad: caribbean educational publisher. ISBN 978-9768014061.
- ↑ "Why Does Guyana Have The Highest Suicide Rate In The World?". 2014-10-14. Retrieved 2015-08-27.
- ↑ Rudatsikira & Muula (23 August 2007). "Prevalence and associated factors of suicidal ideation among school-going adolescents in Guyana: results from a cross sectional study". Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health. 3 (13): 13. doi: 10.1186/1745-0179-3-13 . PMC 2014747 . PMID 17716374.
- ↑ Shaw, Charlotte; Stuart, Jaimee; Thomas, Troy; Kõlves, Kairi (July 2022). "Suicidal behaviour and ideation in Guyana: A systematic literature review". The Lancet Regional Health - Americas. 11: 100253. doi:10.1016/j.lana.2022.100253. PMC 9903603 . PMID 36778929.
- ↑ "Gov't votes down opposition's 'political' motion on suicide". Stabroek News. 6 August 2016. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
