The Sukhoi Su-7 is a swept wing, supersonic fighter aircraft developed by the Soviet Union in 1955. Originally, it was designed as a tactical, low-level dogfighter, but was not successful in this role. On the other hand, the soon-introduced Su-7B series became the main Soviet fighter-bomber and ground-attack aircraft of the 1960s. The Su-7 was rugged in its simplicity, but its Lyulka AL-7 engine had such high fuel consumption that it seriously limited the aircraft's payload, as even short-range missions required that at least two hardpoints be used to carry drop tanks rather than ordnance.

The Sukhoi Su-15 is a twinjet supersonic interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union. It entered service in 1965 and remained one of the front-line designs into the 1990s. The Su-15 was designed to replace the Sukhoi Su-11 and Sukhoi Su-9, which were becoming obsolete as NATO introduced newer and more capable strategic bombers.

The Tupolev Tu-28 is a long-range interceptor aircraft introduced by the Soviet Union in the 1960s. The official designation was Tu-128, but this designation was less commonly used in the West. It was the largest and heaviest fighter ever in service.

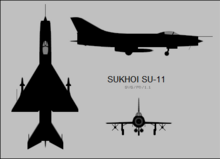
The Sukhoi Su-9 is a single-engine, all-weather, missile-armed interceptor aircraft developed by the Soviet Union.

The Yakovlev Yak-27 is a family of Soviet supersonic aircraft developed in 1958 from the Yak-121 prototype. The most built variant was the tactical reconnaissance Yak-27R.

The Tupolev Tu-98 was a prototype swept wing jet bomber developed by Tupolev for the Soviet Union.

The Sukhoi Su-9 was an early jet fighter built in the Soviet Union shortly after World War II. The design began in 1944 and was intended to use Soviet-designed turbojet engines. The design was heavily influenced by captured German jet fighters and it was subsequently redesigned to use a Soviet copy of a German turbojet. The Su-9 was slower than competing Soviet aircraft and it was cancelled as a result. A modified version with different engines and a revised wing became the Su-11, but this did not enter production either. The Su-13 was a proposal to re-engine the aircraft with Soviet copies of the Rolls-Royce Derwent turbojet as well as to modify it for night fighting, but neither proposal was accepted.

The Myasishchev M-50 is a Soviet prototype four-jet engine supersonic strategic bomber which never attained service. Only one flightworthy prototype was built, which was first flown in October 1959. The M-50 was constructed by the Myasishchev design bureau.

The Lyulka AL-7 was a turbojet designed by Arkhip Mikhailovich Lyulka and produced by his Lyulka design bureau. The engine was produced between 1954 and 1970.

The Lavochkin La-250 "Anakonda" was a high-altitude interceptor aircraft prototype developed in the Soviet Union by the Lavochkin design bureau in the 1950s. Its nickname "Anaconda" was invented during the flight test and referred to both the elongated body shape as well as the relatively critical flight characteristics of the machine.

The Sukhoi Su-6 was a Soviet ground-attack aircraft developed during World War II. The mixed-power high-altitude interceptor Su-7 was based on the single-seat Su-6 prototype.
The Sukhoi Su-10 or Izdeliye Ye was a Soviet turbojet-powered bomber aircraft built shortly after World War II.

The Sukhoi Su-15 was a prototype Soviet all-weather interceptor which never reached production.

The Sukhoi Su-17 was a prototype Soviet fighter. The name was later reused for an entirely different fighter-bomber, see Sukhoi Su-17.
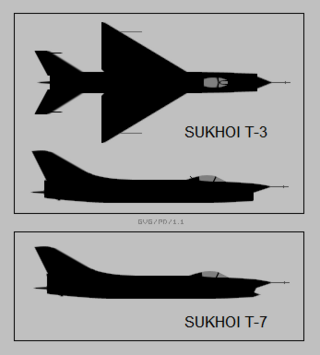
The Sukhoi T-3 was a prototype Soviet fighter aircraft.

The Sukhoi P-1 was a prototype Soviet interceptor.

The Il-54 was a transonic bomber developed in the USSR in the 1950s. Only two examples were built before the project was abandoned.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich I-75 was the final design of a series of three experimental swept-wing interceptors developed in the Soviet Union in the mid-late 1950s by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau from their Mikoyan-Gurevich I-3 airframe. All the aircraft in the I-3 program were affected by delays in the development of the Klimov VK-3 turbojet engine, its cancellation and ultimate replacement by the Lyulka AL-7F turbojet engine.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich I-3 was the first of three interrelated fighter prototype programs developed by the Mikoyan-Gurevich design bureau in the Soviet Union in the mid/late 1950s – starting with the I-3, continuing with the I-7 and finally evolving into the I-75. On several occasions airframes were rebuilt and/or reused, both within a program or in a succeeding program. All the aircraft in the I-3 program were affected by delays in the development of the Klimov VK-3 afterburning bypass turbojet engine, and its cancellation and replacement by the Lyulka AL-7F turbojet engine.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich I-7 was a development of the Mikoyan-Gurevich I-3 experimental fighter. Planned as a Mach 2-class aircraft, the I-7 was the second of a series of three experimental fighter aircraft from the Mikoyan-Gurevich design Bureau. Like the Mikoyan-Gurevich I-3, the I-7 was to be one of the components of the automated Uragan-1 then under development by protivovozdushnaya oborona strany, the Soviet defense system.