Related Research Articles
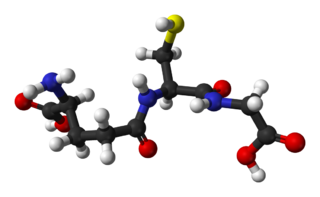
Glutathione is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine.
HMCS may refer to:

Thiocyanates are salts containing the thiocyanate anion [SCN]−. [SCN]− is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common salts include the colourless salts potassium thiocyanate and sodium thiocyanate. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrotechnics.
Cysteine metabolism refers to the biological pathways that consume or create cysteine. The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to creating complex systems.

Thiosulfate is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2O2−3. Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, e.g. sodium thiosulfate Na2S2O3. Thiosulfate also refers to the esters of thiosulfuric acid. The prefix thio- indicates that the thiosulfate is a sulfate with one oxygen replaced by sulfur. Thiosulfate is tetrahedral at the central S atom. Thiosulfate salts occur naturally. Thiosulfate ion has C3v symmetry, and is produced by certain biochemical processes. It rapidly dechlorinates water and is notable for its use to halt bleaching in the paper-making industry. Thiosulfate salts are mainly used in dying in textiles and the bleaching of natural substances.

Rhodanese is a mitochondrial enzyme that detoxifies cyanide (CN−) by converting it to thiocyanate. In enzymatology, the common name is listed as thiosulfate sulfurtransferase. The diagram on the right shows the crystallographically-determined structure of rhodanese.

In enzymology, a 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactions of 3-mercaptopyruvate. This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically the sulfurtransferases. This enzyme participates in cysteine metabolism. It is encoded by the MPST gene.
Biotin synthase (BioB) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of dethiobiotin (DTB) to biotin; this is the final step in the biotin biosynthetic pathway. Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is a cofactor used in carboxylation, decarboxylation, and transcarboxylation reactions in many organisms including humans. Biotin synthase is an S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) dependent enzyme that employs a radical mechanism to thiolate dethiobiotin, thus converting it to biotin.
In enzymology, a cysteine desulfurase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Lipoyl synthase is an enzyme that belongs to the radical SAM (S-adenosyl methionine) family. Within the radical SAM superfamily, lipoyl synthase is in a sub-family of enzymes that catalyze sulfur insertion reactions. The enzymes in this subfamily differ from general radical SAM enzymes, as they contain two 4Fe-4S clusters. From these clusters, the enzymes obtain the sulfur groups that will be transferred onto the corresponding substrates. This particular enzyme participates in the final step of lipoic acid metabolism, transferring two sulfur atoms from its 4Fe-4S cluster onto the protein N6-(octanoyl)lysine through radical generation. This enzyme is usually localized to the mitochondria. Two organisms that have been extensively studied with regards to this enzyme are Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is currently being studied in other organisms including yeast, plants, and humans.
In enzymology, a thiosulfate-dithiol sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiosulfate-thiol sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tRNA sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TST gene.

Adenylyltransferase and sulfurtransferase MOCS3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MOCS3 gene.
Molybdopterin-synthase adenylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:molybdopterin-synthase adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Molybdenum cofactor sulfurtransferase (EC 2.8.1.9, molybdenum cofactor sulfurase, ABA3, MoCo sulfurase, MoCo sulfurtransferase) is an enzyme with systematic name L-cysteine:molybdenum cofactor sulfurtransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Thiazole synthase (EC 2.8.1.10, thiG (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate:thiol sulfurtransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Molybdopterin synthase sulfurtransferase is an enzyme with systematic name persulfurated L-cysteine desulfurase:(molybdopterin-synthase sulfur-carrier protein)-Gly-Gly sulfurtransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Sulfurtransferases at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)