
In biochemistry, a transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups from one molecule to another. They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes.
Sulfation is the chemical reaction that entails the addition of SO3 group. In principle, many sulfations would involve reactions of sulfur trioxide (SO3). In practice, most sulfations are effected less directly. Regardless of the mechanism, the installation of a sulfate-like group on a substrate leads to substantial changes.

In biochemistry, sulfotransferases (SULTs) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol or amine. The most common sulfo group donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS). In the case of alcohol as acceptor, the product is a sulfate :

Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes tyrosine sulfation.
Amine N-methyltransferase, also called indolethylamine N-methyltransferase, and thioether S-methyltransferase, is an enzyme that is ubiquitously present in non-neural tissues and catalyzes the N-methylation of tryptamine and structurally related compounds. More recently, it was discovered that this enzyme can also catalyze the methylation of thioether and selenoether compounds, although the physiological significance of this biotransformation is not yet known.
In enzymology, an amine sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
An aryl sulfotransferase is an enzyme that transfers a sulfate group from phenolic sulfate esters to a phenolic acceptor substrate.
In enzymology, a tyrosine-ester sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate is a form of an adenosine nucleotide with two phosphate groups attached to different carbons in the ribose ring. This is distinct from adenosine diphosphate, where the two phosphate groups are attached in a chain to the 5' carbon atom in the ring.

Sulfotransferase 1A1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1A1 gene.

Estrogen sulfotransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1E1 gene.

Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 2B member 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT2B1 gene.

Sulfotransferase 1A2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1A2 gene.

Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 1B member 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1B1 gene.

Sulfotransferase 1C4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1C4 gene.

Bile salt sulfotransferase also known as hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (HST) or sulfotransferase 2A1 (ST2A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT2A1 gene.

Sulfotransferase 1C3, also known as ST1C3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SULT1C3 gene.
Sulfate conjugates are a heterogeneous class of polar, anionic organosulfate compounds containing an ester of sulfuric acid. Sulfate conjugates commonly result from the metabolic conjugation of endogenous and exogenous compounds with sulfate (-OSO3−).
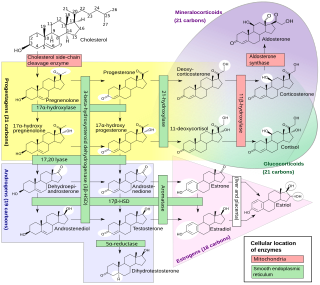
Steroidogenic enzymes are enzymes that are involved in steroidogenesis and steroid biosynthesis. They are responsible for the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones, including sex steroids and corticosteroids, as well as neurosteroids, from cholesterol. Steroidogenic enzymes are most highly expressed in classical steroidogenic tissues, such as the testis, ovary, and adrenal cortex, but are also present in other tissues in the body.
Phenol sulfur transferase deficiency, in short PST deficiency, is the lack or the reduced activity of the functional enzyme phenol sulfur transferase, which is crucial in the detoxification of mainly phenolic compounds by catalysing the sulfate conjugation of the hydroxyl groups in the toxic phenolic compounds to result in more hydrophilic forms for more efficient excretion. This metabolic disorder was first discovered in the late 1990s by Dr. Rosemary Waring during her researches with autistic children, which also made this deficiency commonly associated to the topics of autism. Mutations in the PST genes account for the genetic causes of the deficiency, of which single nucleotide polymorphism and methylation of promoters are two examples of mutations that respectively cause conformational abnormalities and diminished expressions to the enzyme, resulting in the reduced detoxification of phenolic compounds and regulation of phenolic neurotransmitter. The deficiency may cause symptoms like flushing, tachycardia, and depression, and be a risk factor for disorders like autism, migraine, and cancer, while it also limits the use of phenolic drugs in PST deficient patients. There is currently no drug available for treating PST deficiency. However, some people suffering from PST deficiency have found taking a digestive enzyme supplement containing Xylanase 10 minutes before eating to greatly reduce symptoms.















