Function
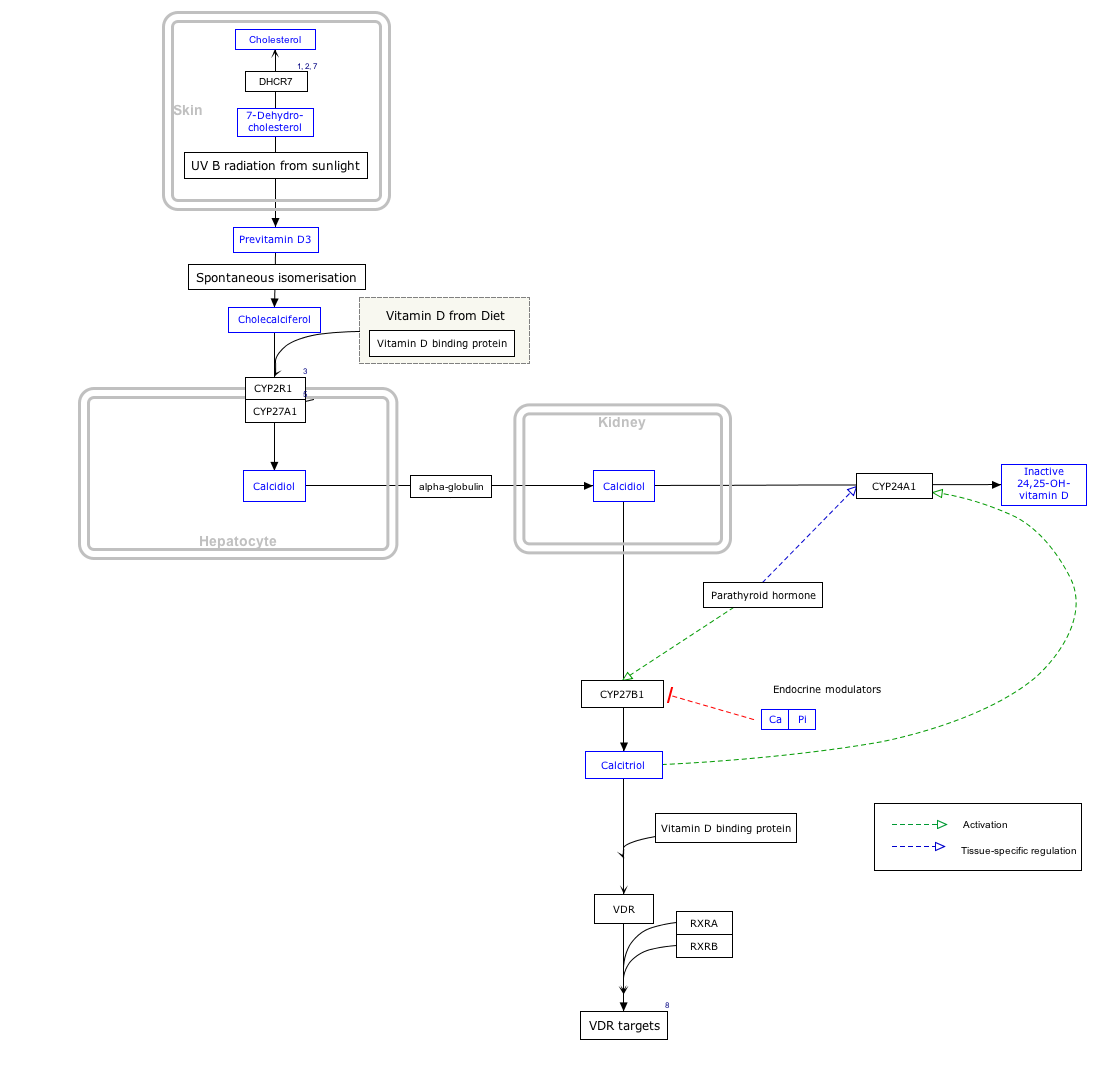
The protein encoded by this gene is an enzyme catalyzing the reversible production of cholesterol from 7-dehydrocholesterol using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) as its cofactor. [8]
The DHCR7 gene encodes delta-7-sterol reductase (EC 1.3.1.21), the ultimate enzyme of mammalian sterol biosynthesis that converts 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) to cholesterol. This enzyme removes the C(7-8) double bond introduced by the sterol delta8-delta7 isomerases. In addition, its role in drug-induced malformations is known: inhibitors of the last step of cholesterol biosynthesis such as AY9944 and BM15766 severely impair brain development. [5]
It displays a modest level of enzyme promiscuity, being able to catalyze analogous reactions with (substrate in forward direction) brassicasterol, [9] 20S(OH)7DHC, 27(OH)DHC and 7-dehydrodesmosterol. [10]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.