An oblast is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Ukraine, and the former Soviet Union and Kingdom of Yugoslavia.

Suraż is a town in north-eastern Poland situated in the Podlaskie Voivodeship since 1999 and, from 1975 to 1998, in the Białystok Voivodeship.

Vitebsk Region, Vitsebsk Voblast, or Vitebsk Oblast is a region (voblast) of Belarus with its administrative center being Vitebsk (Vitsebsk). It is located near the border with Russia.
Urban-type settlement is an official designation for a semi-urban settlement, used in several Eastern European countries. The term was historically used in Bulgaria, Poland, and the Soviet Union, and remains in use today in 10 of the post-Soviet states.
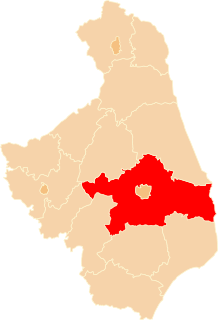
Białystok County is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Podlaskie Voivodeship, north-eastern Poland, on the border with Belarus. It was created on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Białystok, although the city is not part of the county. The county contains nine towns: Łapy, 25 km (16 mi) south-west of Białystok, Czarna Białostocka, 22 km (14 mi) north of Białystok, Wasilków, 11 km (7 mi) north of Białystok, Choroszcz, 13 km (8 mi) west of Białystok, Supraśl, 16 km (10 mi) north-east of Białystok, Michałowo, 13 km (8 mi) east of Białystok, Zabłudów, 16 km (10 mi) south-east of Białystok, Tykocin, 29 km (18 mi) west of Białystok, and Suraż, 23 km (14 mi) south-west of Białystok.

The Lovat is a river in Vitebsk Oblast of Belarus, Usvyatsky, Velikoluksky, and Loknyansky Districts, as well as of the city of Velikiye Luki, of Pskov Oblast and Kholmsky, Poddorsky, Starorussky, and Parfinsky Districts of Novgorod Oblast in Russia. The source of the Lovat is Lake Lovatets in northeastern Belarus, and the Lovat is a tributary of Lake Ilmen. Its main tributaries are the Loknya (left), the Kunya (right), the Polist (left), the Redya (left), and the Robya (right) Rivers. The towns of Velikiye Luki and Kholm, as well as the urban-type settlement of Parfino, are located on the banks of the Lovat.

Klintsy is a town in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, located on the Turosna River, 164 kilometers southwest of Bryansk. Population: 62,510 (2010 Census); 67,325 (2002 Census); 71,161 (1989 Census); 60,000 (1972).
Kasplya is a river in Smolensky, Demidovsky, and Rudnyansky Districts of Smolensk Oblast of Russia and in Vitebsk Region of Belarus, and a major left tributary of the Daugava River. Its length is 136 kilometres (85 mi), the first 116 kilometres (72 mi) are in Russia, and the rest in Belarus. It joins the Daugava in the urban-type settlement of Surazh. The town of Demidov is situated on the Kasplya.
Surazh is a town and the administrative center of Surazhsky District in Bryansk Oblast, Russia, located on the Iput River 177 kilometers (110 mi) southwest of Bryansk, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 11,640 (2010 Census); 12,046 (2002 Census); 12,559 (1989 Census); 1,599 (1897).

The Iput, or Ipuć is a river in Mogilev and Gomel Regions in Belarus and Smolensk and Bryansk Oblasts in Russia. It is a left tributary of the Sozh River. The length of the Iput River is 437 kilometres (272 mi). The area of its basin is 10,900 square kilometres (4,200 sq mi). It freezes up in late November and stays icebound until late March to early April. Its main tributaries are the Voronitsa and Unecha Rivers. The towns of Surazh and Dobrush are located on the Iput River.
In Soviet and Belarusian historiography, the Vitebsk or Surazh gate was the name given to the corridor connecting Soviet and German-occupied territories during World War II. The 40km area between Velizh and Usvyaty was a point of contact between the German Army Groups North and Centre. The gate, created by the Soviet 4th Shock Army Toropets–Kholm Offensive during the winter of 1941–42, existed from 10 February to 28 September 1942.
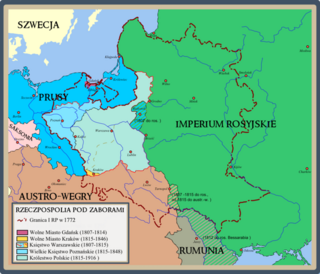
Belostok Oblast was an administrative division in the Russian Empire. The region had a capital in Belostok.

Minay Filippovich Shmyryov, also transliterated as Minay Shmyrev and Minai Shmyrev, was one of the leaders of the Belarusian partisan resistance against the German occupation during World War II.
Kastsyukovichy is a town in Mogilev Region, Eastern Belarus. It is located in the east of the Region, close to the border with Russia, and serves as the administrative center of Kastsyukovichy District. As of 2009, its population was 15,993.

Vitebsk Governorate was an administrative unit (guberniya) of the Russian Empire, with the seat of governorship in Vitebsk. It was established in 1802 by splitting the Byelorussia Governorate and existed until 1924. Today most of the area belongs to Belarus, the northwestern part to Latvia and the northeastern part to Pskov and Smolensk Oblasts of Russia.

The Usvyacha is a river in Kunyinsky and Usvyatsky Districts of Pskov Oblast in Russia and in Vitebsk Raion of Vitebsk Region in Belarus. It is a right tributary of the Daugava River. It is 100 kilometres (62 mi) long, and the area of its basin 2,340 square kilometres (900 sq mi).

In the history of Poland, a royal city or royal town was an urban settlement within the crown lands.
Surazh is an urban-type settlement in Vitebsk Region of Belarus, approximately 45km northeast from the city of Vitebsk. It is situated at the crossing of the Daugava and Kasplya rivers.