
Ahn Chang Ho, sometimes An Chang-ho, was a prominent Korean politician, Korean independence activist, and an early leader of the Korean-American immigrant community in the United States. He is also commonly referred to by his art name Dosan.

Philip Ahn was an American actor and activist of Korean descent. With over 180 film and television credits between 1935 and 1978, he was one of the most recognizable and prolific Asian-American character actors of his time. He is widely regarded as the first Korean American film actor in Hollywood. He is not to be confused with Philson Ahn, another screen actor who broke into films in the late 1930s; Philson was Philip's younger brother.

Dorothy Constance Stratton is best known as the first director of the SPARS, the U.S. Coast Guard Women's Reserve.
Thomas Jefferson Cuddy, known as T.J. Cuddy, nicknamed Tom, was a 19th-century police chief in Los Angeles, California, until bribery forced resignation, and member of the Los Angeles Common Council, the city's governing body. He served a six-month jail term for contempt of court.
This timeline of women in warfare and the military (1900–1945) deals with the role of women in the military around the world from 1900 through 1945. The two major events in this time period were World War I and World War II. Please see Women in World War I and Women in World War II for more information.
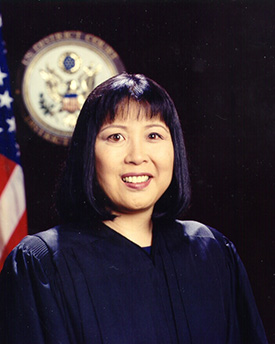
Susan Naomi Oki Mollway is a senior United States district judge of the United States District Court for the District of Hawaii and the first East Asian woman and Japanese-American woman ever appointed to a life-time position on the federal bench.

Arden Lim Cho is an American actress, singer and model known for portraying Kira Yukimura in the 2011 MTV television series Teen Wolf and Ingrid Yun in the 2022 Netflix television series Partner Track.
Cuddy is an Irish surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Asian Californians are residents of the state of California who are of Asian ancestry. California has the largest Asian American population in the U.S., and second highest proportion of Asian American residents, after Hawaii. As of the 2020 U.S. Census, there were over 6 million Asian-Americans in California; 15.5% of the state's population. If including those with partial Asian ancestry, this figure is around 17%. This is a jump from 13.8% recorded in 2010.

As of 2008, the 60,000 ethnic Koreans in Greater Los Angeles constituted the largest Korean community in the United States. Their number made up 15 percent of the country's Korean American population.

Ralph Philander Ahn was an American actor. He was the last surviving son of leading Korean independence activist Dosan Ahn Chang-ho. His father's contributions to the Korean independence movement influenced Ahn's involvement in politics, World War II, and support for the Korean community of Los Angeles.
Asian American women during World War II served many crucial functions that tend to be overlooked, or erased entirely, from modern history books. Women’s roles are under-appreciated or unmentioned in the context of war; these women, however, were tasked with various duties that greatly aided American forces going into combat. Japanese American women, known as “Nisei”, contributed to war efforts by providing medical care as nurses and doctors, as well as serving as military intelligence officials and linguists. These women were also on the front lines of combat in many instances, with Filipino American women fighting as an underground coalition resistance in the Philippines. Asian American women initially began their involvement with the formation of the Army Nurse Corps (ANC) and Women's Army Corps (WAC), serving as linguists and translators at Fort Snelling, Minnesota. Their roles became increasingly more prominent and involved, however, with the bombing at Pearl Harbor and the United States' entry into the war against Japan.

Pachappa Camp was founded in 1904 and is one of the earliest significant Korean settlements established in the United States. It was founded by Ahn Changho, one of the earliest Korean immigrants to the United States and a prominent Korean independence activist. Located in downtown Riverside, California, the original address of the site was 1532 Pachappa Avenue but has since been changed to 3096 Cottage Street. The settlement was active until 1918 and at peak season hosted nearly 300 people. Pachappa Camp is labeled the first Korean settlement in the United States by several historians and the Riverside City government, but this label is disputed by historian John Cha. On March 23, 2017, the Riverside City Council designated the Pachappa Camp site as a “Point of Cultural Interest.”
Anna May Wong: In Her Own Words is a 2010 American documentary film written, directed, and produced by Yunah Hong. It chronicles the life and career of the first Asian American Hollywood film star, Anna May Wong. The film later aired on KPBS (TV) May 23, 2014.

ROKS Dosan Ahn Changho (SS-083) is the lead ship of Dosan Ahn Changho-class submarines. She is expected to be commissioned in 2020.

ROKS Ahn Mu (SS-085) is the second ship of Dosan Ahn Changho-class submarines of the Republic of Korea Navy (ROKN).

The Dosan Ahn Chang Ho Memorial Interchange, also known as the Harbor–Santa Monica Freeway Interchange, is a three-level cloverstack interchange that serves as the junction between the Harbor and Santa Monica Freeways at the southern edge of Downtown Los Angeles, California.
Asian Americans is a five-hour PBS documentary film series made by ITVS, WETA, and the Center for Asian American Media. The series focus on the history of Asian and Asian American people in the United States and first aired on May 11, 2020. It received a Peabody Award in 2021.












