
The Canadian Pacific Railway, also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), was a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway was owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001.

The Union Pacific Railroad is a Class I freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over 32,200 miles (51,800 km) routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United States after BNSF, with which it shares a duopoly on transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western, Midwestern and West South Central United States.
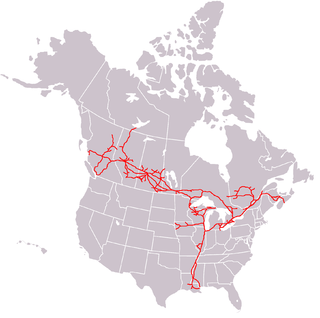
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad in the United States. One of six North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 35,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and nearly 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

Via Rail Canada Inc., operating as Via Rail or Via, is a Canadian Crown corporation that is mandated to operate intercity passenger rail service in Canada.

The Adirondack is an intercity rail passenger train operated daily, partially along the Empire Corridor, by Amtrak between New York City and Montreal. Trains take approximately 11 hours to travel the 381 miles (613 km) route through the scenic Hudson Valley and along the eastern border of the Adirondack Mountains. Operation of the Adirondack is supported by the New York State Department of Transportation and Via Rail. Service was suspended in March 2020 due to the closure of the Canada–United States border in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, resumed in spring 2023, and suspended again at the end of June 2023 because of track conditions in Canada. Service again resumed in September.

The Grand Trunk Western Railroad Company was an American subsidiary of the Grand Trunk Railway, later of the Canadian National Railway operating in Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio. Since a corporate restructuring in 1971, the railroad has been under CN's subsidiary holding company, the Grand Trunk Corporation. Grand Trunk Western's routes are part of CN's Michigan Division. Its primary mainline between Chicago and Port Huron, Michigan serves as a connection between railroad interchanges in Chicago and rail lines in eastern Canada and the Northeastern United States. The railroad's extensive trackage in Detroit and across southern Michigan has made it an essential link for the automotive industry as a hauler of parts and automobiles from manufacturing plants.

The Canadian is a transcontinental passenger train operated by Via Rail with service between Union Station in Toronto, Ontario, and Pacific Central Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.

Rail freight transport is the use of railroads and trains to transport cargo as opposed to human passengers.

The Forks is a historic site, meeting place, and green space in downtown Winnipeg located at the confluence of the Red River and the Assiniboine River.

Transport in Winnipeg involves various transportation systems, including both private and public services, and modes of transport in the capital city of Manitoba.

MacMillan Yard is the main Toronto-area railway classification yard for Canadian National Railway (CN), and is located in the nearby suburb of Vaughan, Ontario. It is the 2nd largest railway classification yard in Canada, after CN's Symington Yard in Winnipeg. It was originally opened in 1965 as Toronto Yard, but was renamed MacMillan Yard in 1975 after former CN president Norman John MacMillan.

The Carlton Trail Railway is a shortline railway with its headquarters in Prince Albert, Saskatchewan. It is operated by OmniTRAX, an American transportation company in Denver, Colorado. Carlton Trail has been operating on ex-Canadian National track since Dec 8, 1997; however, after the acquisition of the branch line CTRW also purchased from CN the Birch Hills-Fenton-Prince Albert branch line in 2001. Since the closure of the pulp mill in 2006, Carlton Trail has typically adhered to a schedule of twice weekly rail service, hauling approximately 2000 carloads per year. According to OmniTrax president Darcy Brede, when the mill reopens in 2014, the railway will begin six days a week service, hauling approximately 3000 carloads a year.
Greenville Yard is a freight rail yard in the Port of New York and New Jersey. It is located on Upper New York Bay in Jersey City, New Jersey, adjacent and north of Port Jersey. Originally developed in 1904 by the Pennsylvania Railroad, it was later taken over by Conrail. It has been owned by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey since 2010. It takes its name from the former municipality of Greenville, now part of the city.
CentrePort Canada is a tri-modal dry port and Foreign Trade Zone located partly in northwest Winnipeg, Manitoba and partly in the Rural Municipality of Rosser, and situated adjacent to the Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport (YWG). With 20,000 acres (81 km2) of industrial land, it is the largest tri-modal inland port and foreign trade zone in North America.

From the start of railroading in America through the first half of the 20th century, New York City and Long Island were major areas for rail freight transportation. However, their relative isolation from the mainland United States has always posed problems for rail traffic. Numerous factors over the late 20th century have caused further declines in freight rail traffic. Efforts to reverse this trend are ongoing, but have been met with limited success.

The Battle River Railway Trestle, commonly known as the Fabyan Trestle Bridge, was constructed between 1907 and December 10, 1908 west of Fabyan, Alberta, Canada at the cost of $600,000. The bridge is located at approximately mile 149 of Canadian National Railway's (CN) Wainwright subdivision.
Canadian National Railway facilities in Peel Region consists of two specialized facilities, which are both accessed using the CN Halton Subdivision.

Canadian National 6218 is a 4-8-4 U-2-g Confederation built by the Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) in 1942 for the Canadian National Railway. It became famous after it was brought back by CN for their Steam Excursion Program from 1964 to 1971. It is now on static display at the Fort Erie Railway Museum in Fort Erie, Ontario.

















