
The Antilles is an archipelago bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the south and west, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east.

The Greater Antilles is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, Navassa Island and the Cayman Islands. Six island states share the region of the Greater Antilles, with Haiti and the Dominican Republic sharing the island of Hispaniola. Together with the Lesser Antilles, they make up the Antilles.
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Ciguayo and Macorix of parts of Hispaniola, and the Guanahatabey of western Cuba. The Kalinago have maintained an identity as an indigenous people, with a reserved territory in Dominica.

The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island countries and 19 dependencies in three archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago.

Hurricane Debby caused minor damage in the Greater and Lesser Antilles in August 2000. The seventh tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, and second hurricane of the annual season, Debby developed from a tropical wave east of the Lesser Antilles on August 19. Favorable conditions allowed the depression to become Tropical Storm Debby early on August 20, and further strengthening into a hurricane occurred 24 hours later. Sustained winds peaked at 85 mph (137 km/h) on August 21. Debby made three landfalls on August 22, in Barbuda, Saint Barthélemy, and Virgin Gorda, before re-entering the Atlantic north of Puerto Rico. As Debby moved parallel to the north coast of Hispaniola late on August 23, it weakened back to a tropical storm. The storm tracked westward and weakened further, instead of approaching Florida and strengthening into a major hurricane. While south of eastern Cuba on August 24, Debby was downgraded to a tropical depression, six hours before completely dissipating.

Cyclargus is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. It was split off from the genus Hemiargus in 1948 by Vladimir Nabokov, although many lepidopterists have not accepted the new genus as valid. Nabokov designated C. ammon as the type species for the genus, and included C. dominica, C. thomasi, C. woodruffi and C. erembis. In 1992 K. Johnston and Matusik described C. sorpresus and C. kathleena, both from Hispaniola.
The Athletics Competition at the 1995 Pan American Games was held in Mar del Plata, Argentina between 17 and 25 March.
The Caribbean bioregion is a biogeographic region that includes the islands of the Caribbean Sea and nearby Atlantic islands, which share a fauna, flora and mycobiota distinct from surrounding bioregions.

The 2005 Central American and Caribbean Championships in athletics were held at the Thomas Robinson Stadium in Nassau, Bahamas, between 8–11 July 2005.
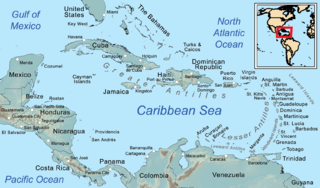
The Caribbean is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are often also included in the region. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America.

Battus polydamas, also known as the gold rim swallowtail, the Polydamas swallowtail or the tailless swallowtail, is a species of butterfly in the family Papilionidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 10th edition of Systema Naturae, published in 1758.

Synchlora is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae erected by Achille Guenée in 1857. Adult Synchlora members often have leaf green wings, while larvae occasionally have the property of adorning themselves with pieces of plants in the pursuit of camouflage. The name of the genus comes from Greek, with "syn-" meaning "with", and "chlor" meaning "green".

Synchlora cupedinaria is a moth in the family Geometridae first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1880. It is found in Florida, the Bahamas, the Virgin Islands, Guadeloupe, Martinique and possibly St. Kitts and Puerto Rico.
Ercta vittata is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1794. It is found in the West Indies and South America. It has also been recorded from Costa Rica and southern Florida.

Diaprepes Schönherr 1823: 1140 is a genus of broad-nosed weevil belonging to the family Curculionidae, subfamily Entiminae, tribe Eustylini.
The Americas Zone was the unique zone within Group 3 of the regional Davis Cup competition in 2019. The zone's competition was held in round robin format in Escazú, Costa Rica, from 17 to 22 June 2019.
The following lists events that happened during 2021 in the Caribbean.

Lachnopus is a genus of broad-nosed weevils in the family Curculionidae distributed in the Caribbean Region.
The following lists events that happened during 2022 in the Caribbean.












