
A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first working sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Elias Howe and Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has greatly improved the efficiency and productivity of the clothing industry.

Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving fabric, archaeologists believe Stone Age people across Europe and Asia sewed fur and skin clothing using bone, antler or ivory needles and "thread" made of various animal body parts including sinew, catgut, and veins.

A tailor is a person who makes, repairs, or alters clothing professionally, especially suits and men's clothing.

A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the garment.

A dressmaker is a person who makes custom clothing for women, such as dresses, blouses, and evening gowns. A dressmaker is also called a mantua-maker (historically), modiste, or fabrician.

In sewing and fashion design, a pattern is the template from which the parts of a garment are traced onto fabric before being cut out and assembled. Patterns are usually made of paper, and are sometimes made of sturdier materials like paperboard or cardboard if they need to be more robust to withstand repeated use. The process of making or cutting patterns is sometimes condensed to the one-word Patternmaking, but it can also be written pattern(-)making or pattern cutting.

Mary Brooks Picken was an American author of 96 books on needlework, sewing, and textile arts. Her Fashion Dictionary, published by Funk and Wagnalls in 1957, is the first dictionary in the English language to be published by a woman.

The running stitch or straight stitch is the basic stitch in hand-sewing and embroidery, on which all other forms of sewing are based. The stitch is worked by passing the needle in and out of the fabric at a regular distance.

A selvage or selvedge is a "self-finished" edge of a piece of fabric which keeps it from unraveling and fraying. The term "self-finished" means that the edge does not require additional finishing work, such as hem or bias tape, to prevent fraying.

Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories. It is influenced by cultural and social attitudes, and has varied over time and place.

Gathering is a sewing technique for shortening the length of a strip of fabric so that the longer piece can be attached to a shorter piece. It is commonly used in clothing to manage fullness, as when a full sleeve is attached to the armscye or cuff of a shirt, or when a skirt is attached to a bodice.

Charmeuse is a lightweight fabric woven with a satin weave, in which the warp threads cross over four or more of the backing (weft) threads. These float threads give the front of the fabric a smooth, shiny finish, whereas the back has a dull finish. Charmeuse differs from plain satin in that charmeuse has a different ratio of float (face) threads, and is of a lighter weight. Charmeuse may be made of silk, polyester, or Rayon. Charmeuse woven from blended fibers is becoming more common. It is used in women's clothing such as lingerie, evening gowns, and blouses, especially garments with a bias cut. It is occasionally used in menswear.

Sew Fast Sew Easy was a corporation based in the Garment District in New York City, that is best known for sewing classes, sewing patterns and sewing books. It was founded in 1991 by Elissa K. Meyrich, a designer in New York City's garment district for over 26 years, an instructor at Parsons School of Design, and an author and contributing writer to sewing publications. Sew Fast Sew Easy classes were part of a resurgence in traditional home economics enabled by networked technologies including Internet chat groups and digitally-adjustable patterns. The company created NYC's first Stitch and Bitch group in 1997. The company started an Internet guestbook, the Stitch and Bitch Cafe, in 1998.

Darts are folds and sewn into fabric to take in ease and provide shape to a garment, especially for a woman's bust. They are used frequently in all sorts of clothing to tailor the garment to the wearer's shape, or to make an innovative shape in the garment. Fabric may be thought of as flat, and a dart has the effect of removing a wedge shaped piece and pulling the edges of that wedge together to create a shallow cone. This effect can be seen quite easily with a paper pattern by pulling together the edges of a dart intake as it would be sewn. Since fabric is generally more flexible than paper the fabric will shift around the apex of the cone and form a softer, but still curved, shape. In a garment a dart ends in a point at a full area of the body.

Ironing is the use of a machine, usually a heated tool, to remove wrinkles from fabric. The heating is commonly done to a temperature of 180–220 °Celsius, depending on the fabric. Ironing works by loosening the bonds between the long-chain polymer molecules in the fibers of the material. While the molecules are hot, the fibers are straightened by the weight of the iron, and they hold their new shape as they cool. Some fabrics, such as cotton, require the addition of water to loosen the intermolecular bonds. Many modern fabrics are advertised as needing little or no ironing. Permanent press clothing was developed to reduce the ironing necessary by combining wrinkle-resistant polyester with cotton.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.

In sewing, a seam is the join where two or more layers of fabric, leather, or other materials are held together with stitches. Prior to the invention of the sewing machine, all sewing was done by hand. Seams in modern mass-produced household textiles, sporting goods, and ready-to-wear clothing are sewn by computerized machines, while home shoemaking, dressmaking, quilting, crafts, haute couture and tailoring may use a combination of hand and machine sewing.

In sewing and tailoring, a lining is an inner layer of fabric, fur, or other material inserted into clothing, hats, luggage, curtains, handbags and similar items.

In sewing and tailoring, facing is a small piece of fabric, separate or a part of the fabric itself, used to finish the fabric edges. Facing makes a garment look professionally finished with the seams well hidden inside the folds of the facing. Facing is mostly used to finish the edges in necklines, armholes, hems and openings. They are also used widely in all other sewing like quilts and home decor items like curtain hems.
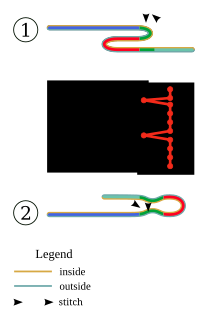
A blind stitch in sewing is a method of joining two pieces of fabric so that the stitch thread is invisible, or nearly invisible. Blind stitching hides stitching under folded edges; therefore, this type of stitch can be used to create a blind hem or to join two folded edges together.



















