
A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has greatly improved the efficiency and productivity of the clothing industry.

Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with a sewing needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic era. Before the invention of spinning yarn or weaving fabric, archaeologists believe Stone Age people across Europe and Asia sewed fur and leather clothing using bone, antler or ivory sewing-needles and "thread" made of various animal body parts including sinew, catgut, and veins.

A lockstitch is the most common mechanical stitch made by a sewing machine. The term "single needle stitching", often found on dress shirt labels, refers to lockstitch.

A button is a fastener that joins two pieces of fabric together by slipping through a loop or by sliding through a buttonhole.

Interfacing is a textile used on the unseen or "wrong" side of fabrics to make an area of a garment more rigid.

A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the garment.
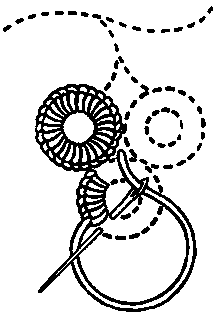
In everyday language, a stitch in the context of embroidery or hand-sewing is defined as the movement of the embroidery needle from the back of the fibre to the front side and back to the back side. The thread stroke on the front side produced by this is also called stitch. In the context of embroidery, an embroidery stitch means one or more stitches that are always executed in the same way, forming a figure. Embroidery stitches are also called stitches for short.
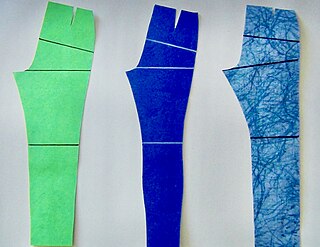
In sewing and fashion design, a pattern is the template from which the parts of a garment are traced onto woven or knitted fabrics before being cut out and assembled. Patterns are usually made of paper, and are sometimes made of sturdier materials like paperboard or cardboard if they need to be more robust to withstand repeated use. The process of making or cutting patterns is sometimes compounded to the one-word Patternmaking, but it can also be written pattern(-)making or pattern cutting.

A cuff is a layer of fabric at the lower edge of the sleeve of a garment at the wrist, or at the ankle end of a trouser leg. The function of turned-back cuffs is to protect the cloth of the garment from fraying, and, when frayed, to allow the cuffs to be readily repaired or replaced, without changing the garment. Cuffs are made by turning back (folding) the material, or a separate band of material can be sewn on, or worn separately, attached either by buttons or studs. A cuff may display an ornamental border or have lace or some other trimming. In US usage, the word trouser cuffs refers to the folded, finished bottoms of the legs of a pair of trousers. In the UK, while this usage is now sometimes followed, the traditional term for the turned up trouser hem is 'turnup'.

In clothing, a collar is the part of a shirt, dress, coat or blouse that fastens around or frames the neck. Among clothing construction professionals, a collar is differentiated from other necklines such as revers and lapels, by being made from a separate piece of fabric, rather than a folded or cut part of the same piece of fabric used for the main body of the garment.

A buttonhole is a reinforced hole in fabric that a button can pass through, allowing one piece of fabric to be secured to another. The raw edges of a buttonhole are usually finished with stitching. This may be done either by hand or by a sewing machine. Some forms of button, such as a frog, use a loop of cloth or rope instead of a buttonhole.

In sewing, to tack or baste is to sew quick, temporary stitches that will later be removed. Tacking is used for a variety of reasons, such as holding a seam in place until it is sewn properly, or transferring pattern markings onto the garment. Tacking is typically sewn using a specialised tacking thread, which may snap easily in order for it to be easily removed from the garment when necessary.

A placket is a finished opening in the upper part of trousers or skirts, or at the neck, front, or sleeve of a garment. The finish frequently consists of a fold of fabric that is attached to the opening in order for the fasteners to be sewn to it. In modern usage, the term placket often refers to these double layers of fabric.

Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller pieces, making it ideal for socks and hats.

Helen Augusta Blanchard was an American inventor who received 28 patents between 1873 and 1915. She was known for her numerous inventions dealing with sewing machines and sewing technology.

Locking clothing are garments which prevent the person wearing the clothing from removing the clothing. One example would be clothing designed to prevent a person with dementia from inappropriate undressing. Sometimes locking clothes are used for sexual purposes, such as in feminization.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.

A blind stitch in sewing is a method of joining two pieces of fabric so that the stitch thread is invisible during the normal use of the finished product. Blind stitching uses a folded edge of the fabric to hide the stitches; therefore, this type of stitch can be used to create a blind hem or to join two folded edges together.

A presser foot is an attachment used with sewing machines to hold fabric flat as it is fed through the machine and stitched. Sewing machines have feed dogs in the bed of the machine to provide traction and move the fabric as it is fed through the machine, while the sewer provides extra support for the fabric by guiding it with one hand. A presser foot keeps the fabric flat so that it does not rise and fall with the needle and pucker as it is stitched. When especially thick workpieces are to be sewn, such as quilts, a specialized attachment called a walking foot is often used rather than a presser foot.

A coverstitch is formed by two or more needles which add straight stitches to one side of the fabric and a looper thread on the opposite side of the fabric that zig-zags between the straight stitches. A coverstitch results in parallel lines of straight stitches on one side of the fabric and an overcast stitch on the reverse side. It is widely used in garment construction, particularly for attaching trims and flat seaming where the raw edges can be finished in the same operation as forming the seam.






















