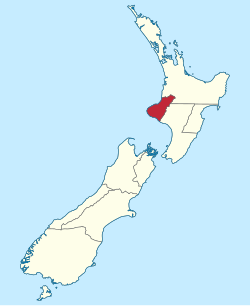
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
Iwi are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori, iwi roughly means 'people' or 'nation', and is often translated as "tribe," or "a confederation of tribes." The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, and is typically pluralised as such in English.

The provinces of the Colony of New Zealand existed as a form of sub-national government. Initially established in 1846 when New Zealand was a Crown colony without responsible government, two provinces were first created. Each province had its own legislative council and governor. With the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 the provinces were recreated around the six planned settlements or "colonies". By 1873 the number of provinces had increased to nine, but they had become less isolated from each other and demands for centralised government arose. In 1875 the New Zealand Parliament decided to abolish the provincial governments, and they came to an end in November 1876. They were superseded by counties, which were later replaced by territorial authorities.
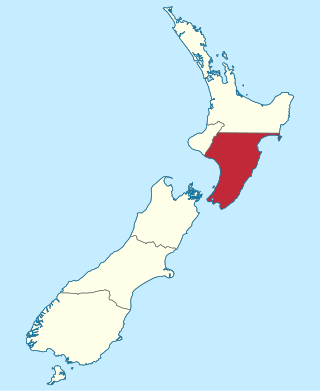
Wellington Province, governed by the Wellington Provincial Council, was one of the provinces of New Zealand from 1853 until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. It covered much of the southern half of the North Island until November 1858, when Hawke's Bay Province split off, taking about a third of its area.

Ngāti Toa, Ngāti Toarangatira or Ngāti Toa Rangatira, is a Māori iwi (tribe) based in the southern North Island and in the northern South Island of New Zealand. Its rohe extends from Whanganui in the north, Palmerston North in the east, and Kaikōura and Hokitika in the south. Ngāti Toa remains a small iwi with a population of only about 9000. The iwi is centred around Porirua, Plimmerton, Kāpiti, Blenheim and Arapaoa Island. It has four marae: Takapūwāhia and Hongoeka in Porirua City, and Whakatū and Wairau in the north of the South Island. Ngāti Toa's governing body has the name Te Rūnanga o Toa Rangatira.

Waitara is a town in the northern part of the Taranaki region of the North Island of New Zealand. Waitara is located just off State Highway 3, 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) northeast of New Plymouth.

Pōtatau Te Wherowhero was a Māori warrior, leader of the Waikato iwi, the first Māori King and founder of the Te Wherowhero royal dynasty. He was first known just as Te Wherowhero and took the name Pōtatau after he became king in 1858. As disputes over land grew more severe Te Wherowhero found himself increasingly at odds with the Government and its policies.
Richard Barrett (1807–1847) was one of the first European traders to be based in New Zealand. He lent his translation skills to help negotiate the first land purchases from Maori in New Plymouth and Wellington and became a key figure in the establishment of the settlement of New Plymouth. He was described by Edward Jerningham Wakefield, son of New Zealand Company founder Edward Gibbon Wakefield, as short, stout and "perfectly round all over" and fond of relating "wild adventures and hairbreadth 'scapes".

Ngāti Ruanui is a Māori iwi traditionally based in the Taranaki region of New Zealand. In the 2006 census, 7,035 people claimed affiliation to the iwi. However, most members now live outside the traditional areas of the iwi.
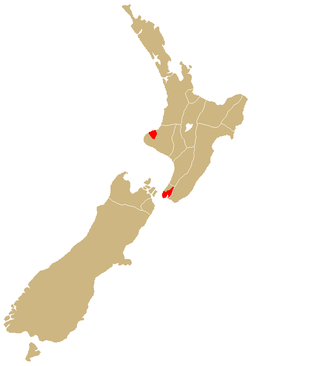
Te Āti Awa is a Māori iwi with traditional bases in the Taranaki and Wellington regions of New Zealand. Approximately 17,000 people registered their affiliation to Te Āti Awa in 2001, with around 10,000 in Taranaki, 2,000 in Wellington and around 5,000 of unspecified regional location.

Ngā Rauru is a Māori iwi in the South Taranaki region of New Zealand. In the 2006 census, 4,047 Māori claimed affiliation to Ngā Rauru, representing 12 hapū.
The city of New Plymouth, New Zealand, has a history that includes a lengthy occupation and residence by Maori, the arrival of white traders and settlers in the 19th century and warfare that resulted when the demands of the two cultures clashed.

Ngāti Hauā is a Māori iwi of the eastern Waikato of New Zealand. It is part of the Tainui confederation. Its traditional area includes Matamata, Cambridge, Maungakawa, the Horotiu district along the Waikato River and the Maungatautari district, and its eastern boundary is the Kaimai Range. Leaders of the tribe have included Te Waharoa, his son Wiremu Tamihana and Tamihana's son Tupu Taingakawa. The tribe has played a prominent role in the Māori King Movement, with Tamihana and descendants being known as the "Kingmakers".
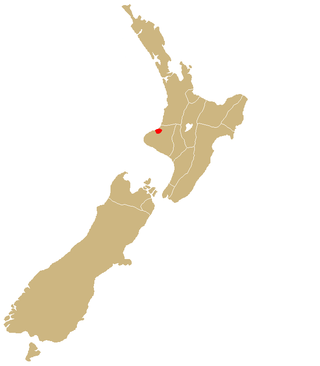
Ngāti Mutunga is a Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand, whose original tribal lands were in north Taranaki. They migrated from Taranaki, first to Wellington, and then to the Chatham Islands in the 1830s. The rohe of the iwi include Wharekauri, Te Whanga Lagoon and Waitangi on Chatham Island, and Pitt Island, also part of the Chatham Islands. The principal marae are at Urenui in Taranaki, and on the Chatham Islands.
The New Zealand land confiscations took place during the 1860s to punish the Kīngitanga movement for attempting to set up an alternative, Māori, form of government that forbade the selling of land to European settlers. The confiscation law targeted Kīngitanga Māori against whom the government had waged war to restore the rule of British law. More than 1,200,000 hectares or 4.4 percent of land were confiscated, mainly in Waikato, Taranaki and the Bay of Plenty, but also in South Auckland, Hauraki, Te Urewera, Hawke's Bay and the East Coast.

Frederic Alonzo Carrington was a 19th-century New Zealand politician and surveyor. He is regarded as the Father of New Plymouth.

Hōniana Te Puni was a Te Ati Awa leader and government member who played a significant role in the Wellington region in the early to mid 19th century.
Wiremu Kīngi Moki Te Matakātea was a principal chief and warrior of the Ngāti Haumiti hapū (subtribe) of the Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand known as Taranaki.
Taranaki Whānui ki te Upoko o te Ika is a Māori collective that was formed to lodge claims with the Waitangi Tribunal relating to the New Zealand Company's purchase of land in the vicinity of Wellington in 1839 and 1844. Following on from the Tribunal's 2003 report WAI145, a settlement of these claims was signed in 2008 between the New Zealand Government and the collective.
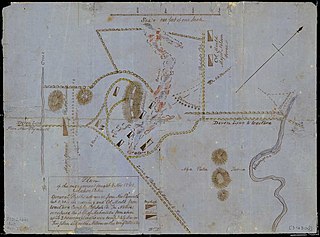
The Battle of Mahoetahi was fought as part of the First Taranaki War. In November 1860 a small force of around 150 Ngāti Hauā warriors travelled to Taranaki from the Waikato and challenged the British to battle at Mahoetahi, near New Plymouth. The British replied with a much larger force of British Army regulars and New Zealand colonial units and effectively encircled and defeated the Ngāti Hauā force.