
The Moraceae—often called the mulberry family or fig family—are a family of flowering plants comprising about 38 genera and over 1100 species. Most are widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, less so in temperate climates; however, their distribution is cosmopolitan overall. The only synapomorphy within the Moraceae is presence of laticifers and milky sap in all parenchymatous tissues, but generally useful field characters include two carpels sometimes with one reduced, compound inconspicuous flowers, and compound fruits. The family includes well-known plants such as the fig, banyan, breadfruit, jackfruit, mulberry, and Osage orange. The 'flowers' of Moraceae are often pseudanthia.

Diospyros is a genus of over 700 species of deciduous and evergreen trees and shrubs. The majority are native to the tropics, with only a few species extending into temperate regions. Individual species valued for their hard, heavy, dark timber, are commonly known as ebony trees, while others are valued for their fruit and known as persimmon trees. Some are useful as ornamentals and many are of local ecological importance. Species of this genus are generally dioecious, with separate male and female plants.

Elaeocarpus is a genus of nearly five hundred species of flowering plants in the family Elaeocarpaceae native to the Western Indian Ocean, Tropical and Subtropical Asia, and the Pacific. Plants in the genus Elaeocarpus are trees or shrubs with simple leaves, flowers with four or five petals usually, and usually blue fruit.

Phaius, commonly known as swamp orchids or in Chinese as 鶴頂蘭屬/鹤顶兰属 , is a genus of forty-five species of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. They are evergreen, terrestrial herbs which form clumps with crowded, sometimes stem-like pseudobulbs, large, pleated leaves and relatively large, often colourful flowers. Species in this genus are found in the tropical parts of Africa, Asia, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, Australia, and various islands of the Pacific and Indian Oceans. One species is also naturalized in Hawaii, Florida, and the Caribbean.

Dipterocarpus is a genus of flowering plants and the type genus of family Dipterocarpaceae.

Dysoxylum is a genus of rainforest trees and shrubs in the flowering plant family Meliaceae. About 34 species are recognised in the genus, distributed from India and southern China, through southeast Asia to New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Australia. The name Dysoxylum derives from the Greek word ‘Dys’ meaning "bad" referring to "ill-smelling" and ‘Xylon’ meaning "wood".

Derris is genus of leguminous plants. It contains 65 species, which range from eastern Africa to the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, New Guinea, northern Australia, and the southwest Pacific islands. The roots of D. elliptica contain rotenone, a strong insecticide and fish poison.

Chionanthus, common name: fringetrees, is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae.

Actinodaphne is an Asian genus of flowering plants in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It contains approximately 125 species of dioecious evergreen trees and shrubs.

Goniothalamus is one of the largest palaeotropical genera of plant in family Annonaceae.

Mastixia is a genus of about 19 species of resinous evergreen trees, usually placed in the family Cornaceae. Its range extends from India through Southeast Asia and New Guinea to the Solomon Islands. Mastixia species have alternate or opposite simple broad leaves, many-flowered inflorescences, and blue to purple drupaceous fruits.

Memecylon is a plant group in Melastomataceae. It consists of 350-400 species of small to medium-sized trees and shrubs occurring in the Old World tropics. Memecylon is a monophyletic group basal to the Melastomataceae clade. Memecylon taxa have more than 600 published basionyms. Diversity of this group is concentrated in tropical Africa, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, India and Malaysia.

Polyalthia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Annonaceae. There are approximately 90 species distributed from Africa to Asia and the Pacific.
Pseudocarapa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Meliaceae. It includes five species which range from Sri Lanka to Sumatra, Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, and New Guinea.

Saprosma is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. There are about 40 species distributed from south China to tropical Asia.
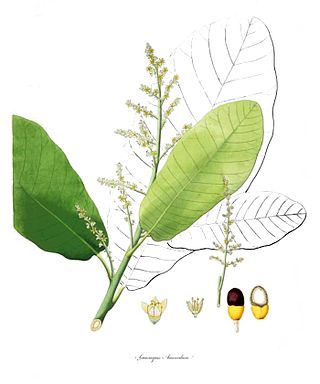
Semecarpus is a genus of plants in the family Anacardiaceae. It includes 87 species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, Malesia, Taiwan, Papuasia, Queensland, and the South Pacific.

Streblus is a genus of flowering plants in the mulberry family, Moraceae. It includes five species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, southern China, and Malesia.

Vatica is a genus of plants in the family Dipterocarpaceae. Its species range from India and southern China through Sri Lanka, Indochina, Indonesia, the Philippines, and New Guinea.

Hetaeria, commonly known as hairy jewel orchids, is a genus of about thirty species of flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae. Plants in this genus are terrestrial herbs with a succulent rhizome and a loose rosette of leaves. Small, pale, hairy non-resupinate flowers are borne on a thin, hairy flowering stem. They are found in tropical Africa and Asia to New Guinea, Australia and some Pacific Islands.

Sciaphila is a genus of mycoheterotrophic plants in the family Triuridaceae. These plants receive nutrition from fungi and neighboring trees and have less need for photosynthesis. It is widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, found in Africa, China, Japan, the Indian Subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Latin America and on various islands Pacific Islands. The most noteworthy feature of the genus is the number of the various flower parts 99.9 percent of Monocots are trimerous, but Sciaphila spp. can have eight or even ten parts in a whorl.


















