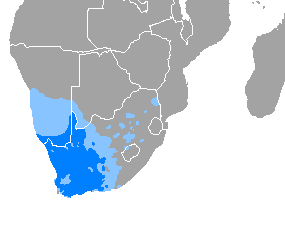
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken in South Africa, Namibia and Botswana, Zambia and Zimbabwe. It evolved from the Dutch vernacular of South Holland spoken by the predominantly Dutch settlers and enslaved population of the Dutch Cape Colony, where it gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics in the 17th and 18th centuries.

The Dravidian languages are a family of languages spoken by 250 million people, mainly in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia.

German is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western and Central Europe. It is the most spoken native language within the European Union. It is the most widely spoken and official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, Belgium and the Italian autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in France (Alsace), the Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, Denmark, Romania and Hungary (Sopron). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in Brazil, South Africa (Kroondal), Namibia, among others, some communities have decidedly Austrian German or Swiss German characters.

Modern Standard Hindi, commonly referred to as Hindi, is the standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is the official language of India alongside English and the lingua franca of North India. Hindi is considered a Sanskritised register of Hindustani, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country from June 2023 onwards; and since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia.

Korean is the native language for about 81 million people, mostly of Korean descent. It is the national language of both North Korea and South Korea.
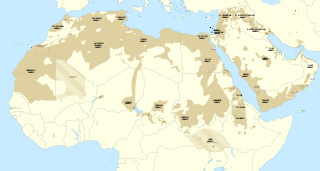
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew, Maltese and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.

Sanskrit is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies.

South African English is the set of English language dialects native to South Africans.

The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, known initially as India Nova, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America. When viewed as a single continent, the Americas or America is the 2nd largest continent right after Asia, and is the 3rd largest continent by population. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.

Tamil is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India, along with Sanskrit, attested since c. 300 BCE. The language belongs to the southern branch of the Dravidian language family and shares close ties with Malayalam and Kannada. Despite external influences, Tamil has retained a sense of linguistic purism, especially in formal and literary contexts.

Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. It also has an official status in several Indian states.

Telugu is a classical Dravidian language native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, where it is also the official language. Spoken by about 96 million people (2022), Telugu is the most widely spoken member of the Dravidian language family, and one of the twenty-two scheduled languages of the Republic of India. It is one of the few languages that has primary official status in more than one Indian state, alongside Hindi and Bengali. Telugu is one of the languages designated as a classical language by the Government of India. It is the 14th most spoken native language in the world. Modern Standard Telugu is based on the dialect of erstwhile Krishna, Guntur, East Godavari and West Godavari districts of Coastal Andhra.
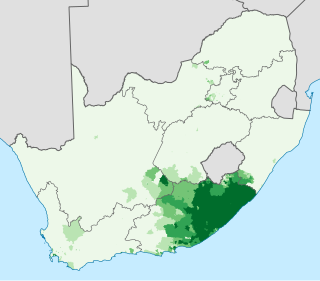
Xhosa, formerly spelled Xosa and also known by its local name isiXhosa, is a Bantu language, indigenous to Southern Africa and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 8 million people and as a second language in South Africa, particularly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Northern Cape and Gauteng, and also in parts of Zimbabwe and Lesotho. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.

Azerbaijani or Azeri, also referred to as Azeri Turkic or Azeri Turkish, is a Turkic language from the Oghuz sub-branch. It is spoken primarily by the Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan, where the North Azerbaijani variety is spoken, while Iranian Azerbaijanis in the Azerbaijan region of Iran, speak the South Azerbaijani variety. Azerbaijani has official status in the Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan, but it does not have official status in Iran, where the majority of Iranian Azerbaijani people live. Azerbaijani is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Azerbaijani communities of Georgia and Turkey and by diaspora communities, primarily in Europe and North America.
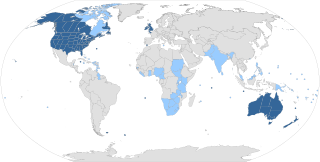
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language by number of speakers, the third largest language by number of native speakers and the most widespread language geographically. The countries in which English is the native language of most people are sometimes termed the Anglosphere. Speakers of English are called Anglophones.

English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, whose speakers, called Anglophones, originated in early medieval England on the island of Great Britain. The namesake of the language is the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that migrated to Britain after its Roman occupiers left. English is the most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire and the United States. English is the third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers.

Dutch is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken by about 25 million people as a first language and 5 million as a second language and is the third most spoken Germanic language. In Europe, Dutch is the native language of most of the population of the Netherlands and Flanders. Dutch was one of the official languages of South Africa until 1925, when it was replaced by Afrikaans, a separate but partially mutually intelligible daughter language of Dutch. Afrikaans, depending on the definition used, may be considered a sister language, spoken, to some degree, by at least 16 million people, mainly in South Africa and Namibia, and evolving from Cape Dutch dialects.
On 30 September 1899 the island of Ceram, Dutch East Indies, was struck by an Ms 7.8 earthquake which was accompanied by a 10-meter landslide-induced tsunami. According to the Batavian Magnetic and Meteorological Observatory, the shock occurred at 01:42 AM Amahei local time. The study about the quake and its effects was published by Dr. R. D. M. Verbeek in an article named Short Report about the earth- and sea-quake in Ceram, the 30th September 1899, which serves as the only extensive source on this earthquake.
Saunulu is a village in Tehoru district, Central Maluku Regency in Maluku Province, Indonesia. Its population in 2010 was 1172.


















