
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus", a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens such as Cladonia belong to the Ascomycota.

The Oomycetes, or Oomycota, form a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms within the Stramenopiles. They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospore is the result of contact between hyphae of male antheridia and female oogonia; these spores can overwinter and are known as resting spores. Asexual reproduction involves the formation of chlamydospores and sporangia, producing motile zoospores. Oomycetes occupy both saprophytic and pathogenic lifestyles, and include some of the most notorious pathogens of plants, causing devastating diseases such as late blight of potato and sudden oak death. One oomycete, the mycoparasite Pythium oligandrum, is used for biocontrol, attacking plant pathogenic fungi. The oomycetes are also often referred to as water molds, although the water-preferring nature which led to that name is not true of most species, which are terrestrial pathogens.

The Potamogetonaceae, commonly referred to as the pondweed family, is an aquatic family of monocotyledonous flowering plants. The roughly 110 known species are divided over six genera. The largest genus in the family by far is Potamogeton, which contains about 100 species.

Zosteraceae is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses complete their entire life cycle under water, having filamentous pollen especially adapted to dispersion in an aquatic environment and ribbon-like leaves that lack stomata. Seagrasses are herbaceous and have prominent creeping rhizomes. A distinctive characteristic of the family is the presence of characteristic retinacules, which are present in all species except members of Zostera subgenus Zostera.

The Phytomyxea are a class of parasites that are cosmopolitan, obligate biotrophic protist parasites of plants, diatoms, oomycetes and brown algae. They are divided into the orders Plasmodiophorida and Phagomyxida. Plasmodiophorids are best known as pathogens or vectors for viruses of arable crops.

Potamogeton is a genus of aquatic, mostly freshwater, plants of the family Potamogetonaceae. Most are known by the common name pondweed, although many unrelated plants may be called pondweed, such as Canadian pondweed. The genus name means "river neighbor", originating from the Greek potamos (river) and geiton (neighbor).

Ruppia, also known as the widgeonweeds, ditch grasses or widgeon grass, is the only extant genus in the family Ruppiaceae, with eight known species. These are aquatic plants widespread over much of the world. The genus name honours Heinrich Bernhard Rupp, a German botanist (1688-1719). They are widespread outside of frigid zones and the tropics.

Potamogeton perfoliatus is a perennial aquatic plant in the family Potamogetonaceae occurring in both standing and flowing freshwater habitats. It is widely distributed globally, occurring in all continents except South America and Antarctica.

Potamogeton coloratus, the fen pondweed, is an aquatic plant in the genus Potamogeton. It is found in shallow peaty calcareous lakes, ponds and ditches, commonly associated with lowland fens.

Potamogeton lucens, or shining pondweed, is an aquatic perennial plant native to Eurasia and North Africa. It grows in relatively deep, still or slow-flowing, calcareous freshwater habitats.

Potamogeton alpinus is a species of perennial aquatic plant known by the common names alpine pondweed and red pondweed. It is widespread in the northern hemisphere in both rivers and lakes with good water quality.

Potamogeton epihydrus is a perennial aquatic plant known by the common names ribbonleaf pondweed and Nuttall's pondweed, and American pondweed in the United Kingdom. It is native to much of North America, where it grows in water bodies such as ponds, lakes, ditches, and slow-moving streams.

Potamogeton pusillus is a species of aquatic plant known by the common names small pondweed, lesser pondweed or least pondweed. It occurs in standing and slow-flowing freshwater habitats throughout the Northern Hemisphere.
Ellobiopsis is a genus of unicellular, ectoparasitic eukaryotes causing disease in crustaceans. This genus is widespread and has been found infecting copepods from both marine and freshwater ecosystems. parasitism has been seen to interfere with fertility in both sexes of copepods.
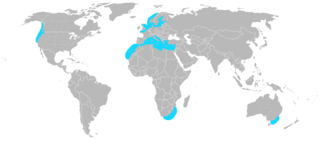
Plasmodiophora bicaudata is a marine pathogen, an obligate parasite of seagrass of the genus Zostera and the causal agent of wasting disease in the genus. These marine plants grow in fine sediment in shallow seas and the pathogen seems to have a worldwide distribution.

Ruppia polycarpa is a submerged aquatic herb species in the genus Ruppia found in shallow brackish waters. It is a common submerged herb on Australasian coasts, including Australia and New Zealand.

Maullinia is a genus of intracellular, phytomyxid parasites found across the Southern Hemisphere though primarily in Chile, The Prince Edward Islands, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. These parasites infiltrate the cells of their brown algal hosts via cytoplasmic extensions called plasmodia that divide synchronously, becoming increasingly multi-nucleate and engulfing the host cell organelles as they grow. Eventually, as the plasmodia fill the entire cell volume, the host cells become hypertrophied and grow to 3- 4x their original size, showing up as swollen appendages or galls on the host tissue at a macroscopic level. These swollen regions will burst alongside the mature Maullinia plasmodia, releasing biflagellated zoospores to the inter- and extracellular space to disperse the infection further. Zoospores can come from sporangial plasmodia, as in M. ectocarpii, or from resting spores, as in M. braseltonii.

The plasmodiophores are a group of obligate endoparasitic protists belonging to the subphylum Endomyxa in Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they are united under a single family Plasmodiophoridae, order Plasmodiophorida, sister to the phagomyxids.
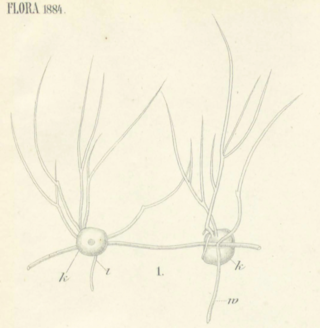
Tetramyxa is a cercozoan protist, member of the plasmodiophores, parasite of several flowering plants. It was first described by Karl von Goebel in 1884, in his work Flora. The genus is characterized by the appearance of resting spores in groups of four.


















