
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
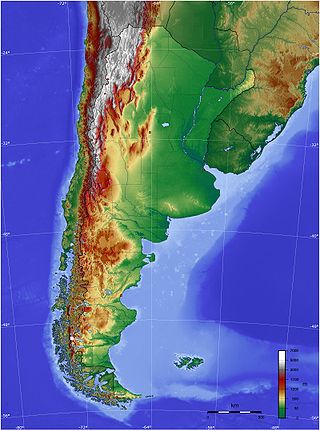
The geography of Argentina describes the geographic features of Argentina, a country located in the Southern Cone of South America. Bordered by the Andes in the west and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, its neighbouring countries are Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, and Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast.

Ushuaia, is the capital of Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur Province, Argentina. With a population of 82,615 and a location below the 54th parallel south latitude, Ushuaia claims the title of world's southernmost city.

Poa flabellata, commonly known as tussac grass or just tussac, is a tussock grass native to southern South America, the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and other islands in the South Atlantic. There are also two isolated records from the herbarium at the French Muséum national d'histoire naturelle for the Île Amsterdam in the Indian Ocean.

Triglochin is a plant genus in the family Juncaginaceae described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. It includes 25 known species. It is very nearly cosmopolitan in distribution, with species on every continent except Antarctica. North America has four accepted species, two of which can also be found in Europe: Triglochin palustris and Triglochin maritima. Australia has many more.

Abrotanella is a genus in the family Asteraceae, of 23 species, native to Australia, New Zealand and southern South America.

Andreaea is a genus of rock mosses described by Johann Hedwig in 1801.

The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom, also the Holantarctic Kingdom, is a floristic kingdom that includes most areas of the world south of 40°S latitude. It was first identified by botanist Ronald Good, and later by Armen Takhtajan. The Antarctic Floristic Kingdom is a classification in phytogeography, different from the Antarctic realm classification in biogeography, and from Antarctic flora genera/species classifications in botany.
The region of the Beagle Channel, explored by Robert FitzRoy in the 1830s, was one of the last to be colonized by Chile and Argentina. The cold weather, the long distances from other inhabited regions, and the shortage of transport and subsistence, kept it far from the governmental task.
Eriachaenium is a genus of South American flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.

Veronica elliptica, synonym Hebe elliptica, is a plant of the family Plantaginaceae. It is native to New Zealand, south Argentina, south Chile and the Falkland Islands. It is an evergreen, bushy shrub of 1 m or more in height, with green, oval leaves, 2–4 cm long. Flowers are white to pale mauve.

The Patagonian blennie, also known as the rock cod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the monotypic family Eleginopidae and monotypic genus Eleginops. It is found in coastal and estuarine habitats around southernmost South America.

Austrolycopodium magellanicum, synonym Lycopodium magellanicum, the Magellanic clubmoss, is a species of vascular plant in the club moss family Lycopodiaceae. The genus Austrolycopodium is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not in other classifications which submerge the genus in Lycopodium.

Gamochaeta is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae. There has not always been agreement among botanists regarding its status as a recognized genus, but it has become more accepted in recent years. It currently includes many plants that previously belonged in genus Gnaphalium. Like many species of Gnaphalium, many Gamochaeta are called cudweeds or everlastings.

Luzuriaga is a genus of flowering plants in the family Alstroemeriaceae. It is native to New Zealand, Chile, Argentina and the Falkland Islands.

Gunnera magellanica is a perennial rhizomatous dioeceous herb native to Chile, Argentina and the Falkland Islands, and Andean areas of Peru, Ecuador. In the southern part of its range it grows in damper parts of the Magellanic subpolar forests and Valdivian temperate forests, and shrub formations on Tierra del Fuego, with an altitudinal range from sea level to 1500m.

Ribes magellanicum is a South American species of shrubs in the currant family, found in Patagonia.
The Botany of Fuegia, the Falklands, Kerguelen's Land, Etc. is a description of the plants discovered in these islands during the Ross expedition written by Joseph Dalton Hooker and published by Reeve Brothers in London between 1845 and 1847. Hooker sailed on HMS Erebus as assistant surgeon. It was the second in a series of four Floras in the Flora Antarctica, the others being the Flora of Lord Auckland and Campbell's Islands (1843-1845), the Flora Novae-Zelandiae (1851–1853), and the Flora Tasmaniae (1853–1859). They were "splendidly" illustrated by Walter Hood Fitch.

The flag of Tierra del Fuego, Antarctica and South Atlantic Islands Province is an Argentinian provincial flag representing Tierra del Fuego Province, Argentina and its constituent parts. The flag was adopted by the provincial government on November 9th, 1999 after it was selected as the winning design in a public contest. It was designed by Teresa Beatríz Martínez.
















