
The footballfish form a family, Himantolophidae, of globose, deep-sea anglerfishes found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Ocean. The family contains 23 species, all of which are classified in a single genus, Himantolophus.

Certaiidae, the warty sea devils are a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the suborder Ceratioidei, the deep-sea anglerfishes, in the anglerfish order Lophiiformes. The warty sea devils are sexually dimorphic with the small males being obligate sexual parasites of the much larger females. The fishes in this family are widely distributed from polar to tropical seas around the world.

Fanfins or hairy anglerfish are a family, Caulophrynidae, of marine ray-finned fishes within the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. The fishes in this family are found almost around the world in the deeper, aphotic waters of the oceans.

Double anglers, the family Diceratiidae, is a small and little known family of rarely encountered marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. The two genera and seven species of this family are found in the deeper waters of the tropical and subtropical Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. They are distinguished from other deep sea anglerfishes by the possession of a second bioluminescent cephalic spine. The fishes in this family were known only from metamorphosed females and the males were not described until 1983.

Oneirodidae, the dreamers are a family of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. These fishes are deepwater fishes found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans and it is the most diverse family of fishes in the bathypelagic zone.

The bulbous dreamer, or cosmoplitan dreamer, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep-sea anglerfishes. This fish has a circumglobal distribution in tropical and temperate oceans.

Lasiognathus saccostoma is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Thaumatichthyidae, the wolftrap anglers. This species is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean and tropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean.
Bertella is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. The only species in the genus is Bertella idiomorpha and this can be distinguished from other members of the family by the structure of its hyomandibular bone.

The Wonderfish (Thaumatichthys) is a genus of deep-sea anglerfish in the family Thaumatichthyidae, with three known species. Its scientific name means "wonder-fish" in Greek; oceanographer Anton Bruun described these fishes as "altogether one of the oddest creatures in the teeming variety of the fish world." In contrast to other anglerfishes, the bioluminescent lure of Thaumatichthys is located inside its cavernous mouth. They are worldwide in distribution and are ambush predators living near the ocean floor.

The complete anglerfish (Lasiognathus) is a genus of deep-sea anglerfish in the family Thaumatichthyidae, with six species known from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Its lure apparatus appears to consist of a fishing rod, a fishing line, bait, and hooks. It is also distinctive for an enormous upper jaw with premaxillaries that can be folded down to enclose the much shorter lower jaw.
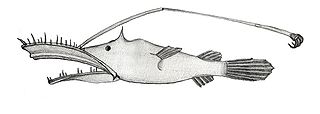
Lasiognathus beebei is a species of marine ray-finned fish belongning to the family Thaumatichthyidae, the wolftrap anglers. This species is known from around the Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean and from around Madeira and Bermuda in the Atlantic.
Lasiognathus intermedius is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Thaumatichthyidae, the wolftrap anglers. This species is known from the deeper waters of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
Lasiognathus waltoni is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Thaumatichthyidae, the wolftrap anglers. This species is known only from the eastern central Pacific Ocean.

Black seadevils are small, deepsea lophiiform fishes of the family Melanocetidae. The five known species are all within the genus Melanocetus. They are found in tropical to temperate waters of the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, with one species known only from the Ross Sea.

Dermatias is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. The only species in the genus is Dermatias platynogaster which is known from 4 metamorphosed female specimens collected from 3 widley sparated localities in the Western Pacific Ocean.

Oneirodes is a genus of is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. These predatory, deep-sea fishes are found around the world. This is the type genus, and the most speciose genus, of the family Oneirodidae. They are sexually dimorphic but, like most taxa within their family, the small males are free living and are not sexual parasites on the larger females. Only the females are used to identify the species in this genus as no species specific charaxcters have been found for males.
Lasiognathus dinema is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Thaumatichthyidae, the wolftrap anglers. This species is known only from the northern Gulf of Mexico.
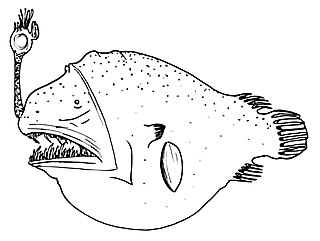
Chaenophryne longiceps, the can-opener smoothdream, longhead dreamer or smooth-head dreamer, is a species marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. This predatory, deep-sea fish is found in the tropical and subtropical oceans around the world. Like other deep-sea anglerfishes it is sexually dimorphic with the matamorphosed females dwarfing the metamorphosed males, the males are not sexual parasites.

Ceratioidei, the deep-sea anglerfishes or pelagic anglerfishes, is a suborder of marine ray-finned fishes, one of four suborders in the order Lophiiformes, the anglerfishes. These fishes are found in tropical and temperate seas throughout the world. One of the better known traits of the deep-sea anglerfishes is their extreme sexual dimorphism where the males are many times smaller than the females, the males seek out females and use their sharp teeth to clamp onto the females where he remains for the rest of his life, in some species he becomes part of the female. This is the only known natural example of a process called parabiosis. Another common trait of deep-sea anglerfishes is that they use bioluminescence on their esca to attract prey in the darkness of the deep oceans they inhabit.
Chaenophryne melanorhabdus is a species marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. This predatory, deep-sea fish is found in the Pacific Ocean. Like other deep-sea anglerfishes dreamers are sexually dimorphic with the matamorphosed females dwarfing the metamorphosed males, the males are not sexual parasites.














