Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia, or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as Aysheaia and Hallucigenia.

Marrella is an extinct genus of marrellomorph arthropod known from the Middle Cambrian of North America and Asia. It is the most common animal represented in the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada, with tens of thousands of specimens collected. Much rarer remains are also known from deposits in China.

Wiwaxia is a genus of soft-bodied animals that were covered in carbonaceous scales and spines that protected it from predators. Wiwaxia fossils—mainly isolated scales, but sometimes complete, articulated fossils—are known from early Cambrian and middle Cambrian fossil deposits across the globe. The living animal would have measured up to 5 centimetres (2 in) when fully grown, although a range of juvenile specimens are known, the smallest being 2 millimetres (0.08 in) long.

Sidneyia is an extinct arthropod known from fossils found from the Early to the Mid Cambrian of China and the Mid Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada.

Anomalocaris is an extinct genus of radiodont, an order of early-diverging stem-group arthropods.

Waptia is an extinct genus of arthropod from the Middle Cambrian of North America. It grew to a length of 6.65 cm (3 in), and had a large bivalved carapace and a segmented body terminating into a pair of tail flaps. It was an active swimmer and likely a predator of soft-bodied prey. It is also one of the oldest animals with direct evidence of brood care. Waptia fieldensis is the only species classified under the genus Waptia, and is known from the Burgess Shale Lagerstätte of British Columbia, Canada. Specimens of Waptia are also known from the Spence Shale of Utah, United States.

Choia is a genus of extinct demosponge ranging from the Cambrian until the Lower Ordovician periods. Fossils of Choia have been found in the Burgess Shale in British Columbia; the Maotianshan shales of China; the Wheeler Shale in Utah; and the Lower Ordovician Fezouata formation. It was first described in 1920 by Charles Doolittle Walcott.

Urokodia aequalis is an extinct genus of arthropod from the early Cambrian. The taxon is only known from the Maotianshan Shales of China based on some 15 specimens. Its segmentation resembles that of a millipede and it possessed head and tail shields with thorny spikes. It has some similarities to the arthropod Mollisonia that is known from both the Burgess Shale of Canada and the Kaili biota of China. Recently, the taxon has been considered a member of the order Mollisoniida, alongside Mollisonia, Thelxiope, and Corcorania, the group are suggested to be stem-chelicerates.
The Burgess Shale of British Columbia is famous for its exceptional preservation of mid-Cambrian organisms. Around 69 other sites have been discovered of a similar age, with soft tissues preserved in a similar, though not identical, fashion. Additional sites with a similar form of preservation are known from the Ediacaran and Ordovician periods.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.

The Wheeler Shale is a Cambrian (c. 507 Ma) fossil locality world-famous for prolific agnostid and Elrathia kingii trilobite remains and represents a Konzentrat-Lagerstätte. Varied soft bodied organisms are locally preserved, a fauna and preservation style normally associated with the more famous Burgess Shale. As such, the Wheeler Shale also represents a Konservat-Lagerstätten.

Tuzoia is an extinct genus of large bivalved arthropod known from Early to Middle Cambrian marine environments from what is now North America, Australia, China, Europe and Siberia. The large, domed carapace reached lengths of 180 millimetres (7.1 in), making them amongst the largest known Cambrian arthropods.
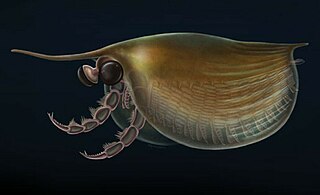
Isoxys is a genus of extinct bivalved Cambrian arthropod; the various species of which are thought to have been freely swimming predators. It had a pair of large spherical eyes, and two large frontal appendages used to grasp prey.

Radiodonta is an extinct order of stem-group arthropods that was successful worldwide during the Cambrian period. They may be referred to as radiodonts, radiodontans, radiodontids, anomalocarids, or anomalocaridids, although the last two originally refer to the family Anomalocarididae, which previously included all species of this order but is now restricted to only a few species. Radiodonts are distinguished by their distinctive frontal appendages, which are morphologically diverse and used for a variety of functions. Radiodonts included the earliest large predators known, but they also included sediment sifters and filter feeders. Some of the most famous species of radiodonts are the Cambrian taxa Anomalocaris canadensis, Hurdia victoria, Peytoia nathorsti, Titanokorys gainessii, Cambroraster falcatus and Amplectobelua symbrachiata, the Ordovician Aegirocassis benmoulai and the Devonian Schinderhannes bartelsi.

Eldonia is an extinct soft-bodied cambroernid animal of unknown affinity, best known from the Fossil Ridge outcrops of the Burgess Shale, particularly in the 'Great Eldonia layer' in the Walcott Quarry. In addition to the 550 collected by Walcott, 224 specimens of Eldonia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.43% of the community. Species also occur in the Chengjiang biota, Siberia, and in Upper Ordovician strata of Morocco.

Mollisonia is an extinct genus of Cambrian arthropod. Species are known from the Burgess Shale, Langston Formation, and Wheeler Shale of North America, as well as the Chengjiang Biota of China. Twenty-one specimens of Mollisonia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise less than 0.1% of the community. Remains possibly attributable to the genus are also known from the Ordovician Fezouata Formation of Morocco and Bøggild Fjord Formation Greenland. An observation published in 2019 suggests this genus is a basal chelicerate, closer to crown group Chelicerata than members of Habeliida. It is suggested to be closely related to Corcorania, Urokodia, and Thelxiope, which together form the clade Mollisoniida, which are thought to be closely related to Chelicerata.

The Fezouata Formation or Fezouata Shale is a geological formation in Morocco which dates to the Early Ordovician. It was deposited in a marine environment, and is known for its exceptionally preserved fossils, filling an important preservational window beyond the earlier and more common Cambrian Burgess shale-type deposits. The fauna of this geological unit is often described as the Fezouata biota, and the particular strata within the formation which exhibit exceptional preservation are generally termed the Fezouata Lagerstätte.
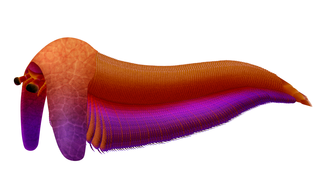
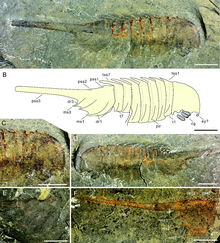
Balhuticaris is a genus of extinct bivalved hymenocarine arthropod that lived in the Cambrian aged Burgess Shale in what is now British Columbia around 506 million years ago. This extremely multisegmented arthropod is the largest member of the group, and it was even one of the largest animals of the Cambrian, with individuals reaching lengths of 245 mm (9 in). Fossils of this animal suggests that gigantism occurred in more groups of Arthropoda than had been previously thought. It also presents the possibility that bivalved arthropods were very diverse, and filled in a lot of ecological niches.

This is a list of the biota of the Burgess Shale, a Cambrian lagerstätte located in Yoho National Park in Canada.

Cordaticaris is a genus of extinct hurdiid radiodont that lived in what is now northern China during the middle Cambrian period. This animal was described in 2020 based off remains found in the Zhangxia Formation, located in the Shandong Province. It is differentiated from other members of its family by its unique heart-shaped frontal sclerite, and its frontal appendages bearing nine endites and seven more elongated subequal endites. This animal was important as it was the first Miaolingian aged hurdiid known from rock layers outside of laurentia, allowing paleontologists to get a better grasp of this families geographic range in life.