
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida is a class containing about 162 species of unsegmented marine annelid worms. Sipuncula was once considered a phylum, but was demoted to a class of Annelida, based on recent molecular work.
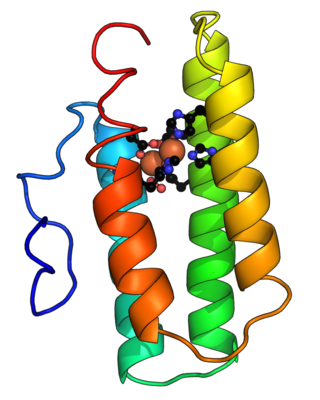
Hemerythrin (also spelled haemerythrin; Ancient Greek: αἷμα, romanized: haîma, lit. 'blood', Ancient Greek: ἐρυθρός, romanized: erythrós, lit. 'red') is an oligomeric protein responsible for oxygen (O2) transport in the marine invertebrate phyla of sipunculids, priapulids, brachiopods, and in a single annelid worm genus, Magelona. Myohemerythrin is a monomeric O2-binding protein found in the muscles of marine invertebrates. Hemerythrin and myohemerythrin are essentially colorless when deoxygenated, but turn a violet-pink in the oxygenated state.

The Aplustridae is a taxonomic family of sea snails or bubble snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Acteonoidea.

The Polyceridae are a taxonomic family of sea slugs, dorid nudibranchs, marine gastropod mollusks within the superfamily Polyceroidea.

Moniliformidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed worms. It is the only family in the Moniliformida order and contains three genera: Australiformis containing a single species, Moniliformis containing eighteen species and Promoniliformis containing a single species. Genetic analysis have determined that the clade is monophyletic despite being distributed globally. These worms primarily parasitize mammals, including humans in the case of Moniliformis moniliformis, and occasionally birds by attaching themselves into the intestinal wall using their hook-covered proboscis. The intermediate hosts are mostly cockroaches. The distinguishing features of this order among archiacanthocephalans is the presence of a cylindrical proboscis with long rows of hooks with posteriorly directed roots and proboscis retractor muscles that pierce both the posterior and ventral end or just posterior end of the receptacle. Infestation with Monoliformida species can cause moniliformiasis, an intestinal condition characterized as causing lesions, intestinal distension, perforated ulcers, enteritis, gastritis, crypt hypertrophy, goblet cell hyperplasia, and blockages.
Diplosentidae is a family of parasitic worms from the order Echinorhynchida.

Chaetopterus or the parchment worm or parchment tube worm is a genus of marine polychaete worm that lives in a tube it constructs in sediments or attaches to a rocky or coral reef substrate. The common name arises from the parchment-like appearance of the tubes that house these worms. Parchment tube worms are filter feeders and spend their adult lives in their tubes, unless the tube is damaged or destroyed. They are planktonic in their juvenile forms, as is typical for polychaete annelids. Species include the recently discovered deep water Chaetopterus pugaporcinus and the well-studied Chaetopterus variopedatus.

Golfingiida, also known as the Golfingiiformes, is an order of peanut worms. The tentacles form a circle around the mouth, while those of the sister taxon, Phascolosomatidea, are only found above the mouth. Most species burrow in the substrate but some live in the empty shells of gastropods. It is an order of the class Sipuncula, and contains the following families:

Marginellinae is a taxonomic subfamily within the larger family of Marginellidae, a group of small sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Volutoidea.

Cirratulidae is a family of marine polychaete worms. Members of the family are found worldwide, mostly living in mud or rock crevices. Most are deposit feeders, but some graze on algae or are suspension feeders. Although subject to multiple revisions over time, cirratulids are among the few polychaete clades with a verified fossil record.

Orbiniidae is a family of polychaete worms. Orbiniids are mostly unselective deposit feeders on marine detritus. They can be found from the neritic zone to abyssal depths.

Teredo is a genus of highly modified saltwater clams which bore in wood and live within the tunnels they create. They are commonly known as "shipworms;" however, they are not worms, but marine bivalve molluscs in the taxonomic family Teredinidae. The type species is Teredo navalis.

Antillesoma is a genus of peanut worms. The genus belongs to the family Phascolosomatidae. Antillesoma was described in 1973 by Stephen and Edmonds.
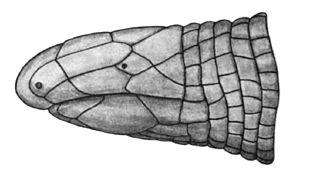
Cadea is a genus of amphisbaenians, commonly known as Cuban keel-headed worm lizards, in the family Cadeidae. Two species are placed in this genus. Both species are endemic to Cuba.

Thylacodes is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Vermetidae, the worm snails or worm shells. The species in this genus were previously placed in the genus Serpulorbis.
Metabonellia is a genus of marine spoon worms in the family Bonelliidae. It is a monotypic genus and Metabonellia haswelli is the only species. It is commonly known as the green spoon worm and is found in shallow waters around Australia.
Themiste cymodoceae is a species of unsegmented benthic marine worm in the phylum Sipuncula, the peanut worms. It is native to shallow waters around Australia and in the South China Sea where it lives in a cavity it creates among seagrass roots and in empty oyster shells.
Themiste hennahi is a species of unsegmented benthic marine worm in the phylum Sipuncula, the peanut worms. It is native to shallow waters on the Pacific coast of North and South America. This worm was first described in 1828 by the British zoologist John Edward Gray as Themiste hennahi, the type specimen having been collected by the Rev. W. Hennah, with the type locality being Peru.

Heterocyathus is a genus of coral of the family Caryophylliidae.

Pararhadinorhynchus is a genus of worms belonging to the family Diplosentidae.
















