| Thermocyclops | |
|---|---|
 | |
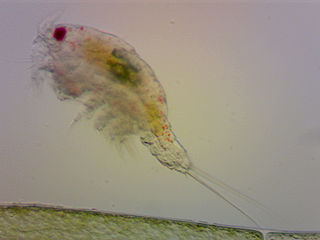
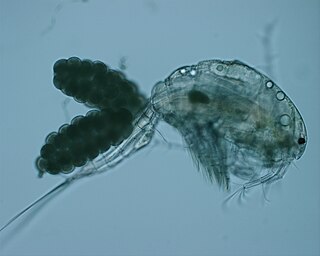
| Thermocyclops inversus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Subclass: | Copepoda |
| Order: | Cyclopoida |
| Family: | Cyclopidae |
| Genus: | Thermocyclops Kiefer, 1927 |
Thermocyclops is a genus of crustacean in family Cyclopidae. It was first described and later extensively researched by Friedrich Kiefer, who discovered some 20 species. [1] The species and subspecies of the genus inhabit fresh and brackish waters alike (rarely ground waters) all around the world, although most are from tropical areas. [1]
The genus contains the following species: [2]
- Thermocyclops africae Baribwegure, Thirion & Dumont, 2001
- Thermocyclops analogus Kiefer, 1936
- Thermocyclops asiaticus (Kiefer, 1932)
- Thermocyclops brehmi (Kiefer, 1927)
- Thermocyclops brevifurcatus (Harada, 1931)
- Thermocyclops byzantinus Kiefer, 1952
- Thermocyclops consimilis Kiefer, 1934
- Thermocyclops conspicuus Lindberg, 1950
- Thermocyclops crassus (Fischer, 1853)
- Thermocyclops crenulatus Brehm, 1949
- Thermocyclops crucis Holynska, 2006
- Thermocyclops dalmaticus Petkovski, 1956
- Thermocyclops decipiens (Kiefer, 1929)
- Thermocyclops decoratus Dussart, 1978
- Thermocyclops dumonti Baribwegure & Mirabdullayev, 2003
- Thermocyclops dybowskii (Landé, 1890)
- Thermocyclops emini (Mrázek, 1898)
- Thermocyclops ethiopiensis Defaye, 1988
- Thermocyclops hastatus (Kiefer, 1952)
- Thermocyclops hooki Löffler, 1968
- Thermocyclops hyalinus (Rehberg, 1880)
- Thermocyclops ianthinus Harada, 1931
- Thermocyclops iguapensis W. M. Silva & Matsumura-Tundisi, 2005
- Thermocyclops incisus (Kiefer, 1932)
- Thermocyclops infrequens (Kiefer, 1929)
- Thermocyclops inopinus (Kiefer, 1926)
- Thermocyclops inversus (Kiefer, 1936)
- Thermocyclops iwoyiensis Onabamiro, 1952
- Thermocyclops kawamurai K. Kikuchi, 1940
- Thermocyclops kivuensis Kiefer, 1952
- Thermocyclops macracanthus (Kiefer, 1929)
- Thermocyclops macrolasius Kiefer, 1952
- Thermocyclops maheensis Lindberg, 1941
- Thermocyclops microspinulosus Lindberg, 1942
- Thermocyclops minutus (Lowndes, 1934)
- Thermocyclops mongolicus Kiefer, 1937
- Thermocyclops ndalaganus Kiefer, 1952
- Thermocyclops neglectus (G. O. Sars, 1909)
- Thermocyclops nigerianus Kiefer, 1932
- Thermocyclops oblongatus (G. O. Sars, 1927)
- Thermocyclops oithonoides (G. O. Sars, 1863)
- Thermocyclops operculifer Kiefer, 1930
- Thermocyclops orghidani (Plesa, 1981)
- Thermocyclops orientalis Dussart & Fernando, 1985
- Thermocyclops ouadanei van de Velde, 1978
- Thermocyclops pachysetosus Lindberg, 1951
- Thermocyclops parvus Reid, 1989
- Thermocyclops philippinensis (Marsh, 1932)
- Thermocyclops pseudoperculifer Holynska, 2006
- Thermocyclops retroversus (Kiefer, 1929)
- Thermocyclops rylovi (Smirnov, 1928)
- Thermocyclops schmeili (Poppe & Mrázek, 1895)
- Thermocyclops schuurmanae (Kiefer, 1928)
- Thermocyclops stephanidesi Kiefer, 1938
- Thermocyclops taihokuensis Harada, 1931
- Thermocyclops tchadensis Dussart & Gras, 1966
- Thermocyclops tenuis (Marsh, 1910)
- Thermocyclops thermocyclopoides (Harada, 1931)
- Thermocyclops tinctus Lindberg, 1936
- Thermocyclops trichophorus Kiefer, 1930
- Thermocyclops uenoi ItoTak, 1952
- Thermocyclops vermifer Lindberg, 1935
- Thermocyclops vizarae (Fryer, 1957)
- Thermocyclops wolterecki Kiefer, 1938