Related Research Articles

Thiocyanates are salts containing the thiocyanate anion [SCN]−. [SCN]− is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common salts include the colourless salts potassium thiocyanate and sodium thiocyanate. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrotechnics.

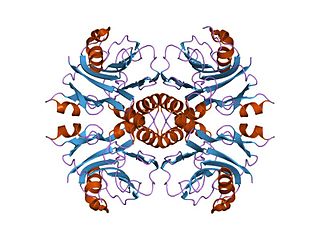
Rhodanese is a mitochondrial enzyme that detoxifies cyanide (CN−) by converting it to thiocyanate. In enzymatology, the common name is listed as thiosulfate sulfurtransferase. The diagram on the right shows the crystallographically-determined structure of rhodanese.

Myrosinase is a family of enzymes involved in plant defense against herbivores, specifically the mustard oil bomb. The three-dimensional structure has been elucidated and is available in the PDB.

Phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32; systematic name: phosphatidylcholine 1-acylhydrolase) encoded by the PLA1A gene is a phospholipase enzyme which removes the 1-acyl group:

In enzymology, a bilirubin oxidase, BOD or BOx, (EC 1.3.3.5) is an enzyme encoded by a gene in various organisms that catalyzes the chemical reaction
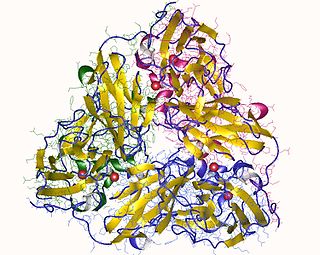
In enzymology, a nitrite reductase (NO-forming) (EC 1.7.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
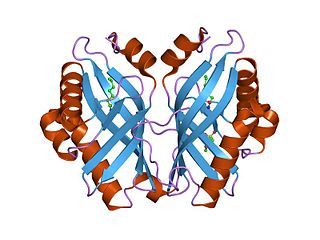
In enzymology, a limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase (EC 3.3.2.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphonoacetaldehyde hydrolase (EC 3.11.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trithionate hydrolase (EC 3.12.1.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme arylesterase (EC 3.1.1.2) catalyzes the reaction
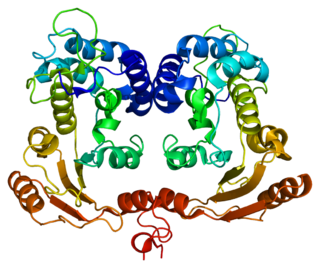
In enzymology, a NAD+ glycohydrolase (EC 3.2.2.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
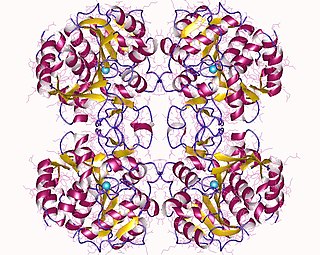
In enzymology, a purine nucleosidase (EC 3.2.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an IMP cyclohydrolase (EC 3.5.4.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-isopropylammelide isopropylaminohydrolase (EC 3.5.99.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-succinylarginine dihydrolase (EC 3.5.3.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a succinylglutamate desuccinylase (EC 3.5.1.96) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Hypothiocyanite is the anion [OSCN]− and the conjugate base of hypothiocyanous acid (HOSCN). It is an organic compound part of the thiocyanates as it contains the functional group SCN. It is formed when an oxygen is singly bonded to the thiocyanate group. Hypothiocyanous acid is a fairly weak acid; its acid dissociation constant (pKa) is 5.3.
PETases are an esterase class of enzymes that catalyze the breakdown (via hydrolysis) of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic to monomeric mono-2-hydroxyethyl terephthalate (MHET). The idealized chemical reaction is:
Carbonyl sulfide hydrolase (EC 3.13.1.7; abbreviated as COSase) is an enzyme that degrades carbonyl sulfide (COS) to hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Isolated from Thiobacillus thioparus bacterium, the potential of COSase would reduce the high global warming effect of COS and change the ozone chemistry, because COS is the source of sulfur in the troposphere.
Transition metal complexes of thiocyanate describes coordination complexes containing one or more thiocyanate (SCN-) ligands. The topic also includes transition metal complexes of isothiocyanate. These complexes have few applications but played significant role in the development of coordination chemistry.
References
- ↑ Tikhonova, Tamara V.; Sorokin, Dimitry Y.; Hagen, Wilfred R.; Khrenova, Maria G.; Muyzer, Gerard; Rakitina, Tatiana V.; Shabalin, Ivan G.; Trofimov, Anton A.; Tsallagov, Stanislav I.; Popov, Vladimir O. (2020). "Trinuclear Copper Biocatalytic Center Forms an Active Site of Thiocyanate Dehydrogenase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (10): 5280–5290. Bibcode:2020PNAS..117.5280T. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922133117 . PMC 7071890 . PMID 32094184.
- Katayama Y, Matsushita Y, Kaneko M, Kondo M, Mizuno T, Nyunoya H (1998). "Cloning of genes coding for the three subunits of thiocyanate hydrolase of Thiobacillus thioparus THI 115 and their evolutionary relationships to nitrile hydratase". J. Bacteriol. 180 (10): 2583–9. doi:10.1128/JB.180.10.2583-2589.1998. PMC 107207 . PMID 9573140.
- Katayama Y, Narahara Y, Inoue Y, Amano F, Kanagawa T, Kuraishi H (1992). "A thiocyanate hydrolase of Thiobacillus thioparus. A novel enzyme catalyzing the formation of carbonyl sulfide from thiocyanate". J. Biol. Chem. 267 (13): 9170–5. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)50404-5 . PMID 1577754.