
Are is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae erected by Francis Walker in 1855. The type species is Are druryi, which is found on Jamaica. This species was described by Dru Drury in 1773 under the name Phalaena marginata, but this name is preoccupied by Phalaena marginataLinnaeus, 1758 and a new specific epithet, honouring Drury, was assigned in 1986.

Dactyloceras lucina is a species of very large moth of the family Brahmaeidae. It is found in central and west Africa, where it has been recorded from Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Sierra Leone, Uganda and Zambia. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1782.

Ceretes thais is a moth in the Castniidae family. It is found in Brazil. Superficially it looks very like a butterfly, and was originally placed by Dru Drury in the "Papilio " group which mostly corresponds with modern Nymphalidae.

Antanartia delius, the forest admiral or orange admiral, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Senegal, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Nigeria, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, the Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania. The habitat consists of lowland forests.

Trichura coarctata is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1773. It is found in Brazil.

Strigocossus crassa is a moth in the family Cossidae. It is found in Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana, Wyoming, Nigeria, Sierra Leone and South Africa.

Yramea cytheris is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from the Falkland Islands. In some systems it is included in genus Issoria.

Greta diaphanus, the Antillean clearwing, is a species of clearwing (ithomiine) butterflies, named by Dru Drury in 1773.

Antheua servula is a species of moth of the family Notodontidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Madras. It is also found in other parts of India, Sri Lanka and on Sumatra.

Imbrasia epimethea is a species of moth belonging to the family Saturniidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from the Calabar coast.

Crameria is a monotypic moth genus in the family Noctuidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819. Its only species, Crameria amabilis, was first described by Dru Drury in 1773.

Lucinia cadma is a species of brush-footed butterfly. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica. Distinct subspecies are found on other Caribbean islands.
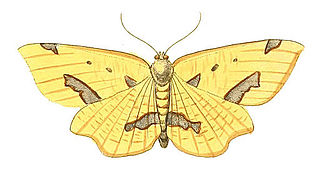
Xanthotype sospeta, the crocus geometer, is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica. It is also found in North America, where it has been recorded from Nova Scotia to southern British Columbia, south to Colorado and Georgia. The habitat consists of deciduous and mixedwood forests.

Letis hercyna is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1773 from Jamaica.

Otroeda cafra is a species of moth in the tussock-moth subfamily Lymantriinae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1782 from Sierra Leone, and is also found in Cameroon, DR Congo, Malawi, and Nigeria.

Pseudobunaea alinda is a species of very large moths in the family Saturniidae. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1782, and is found in Angola, Cameroon, Congo, DR Congo, Gabon, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Sierra Leone, and Tanzania.

Lobobunaea phaedusa is a species of very large moths in the family Saturniidae. It is found in much of sub-saharan Africa, where its host plants include African custard-apple, crown-berry, and Aframomum spp.

Attatha ino is a species of moth of the family Noctuidae. It was described by Dru Drury in 1782 from "Madras".

Pierella nereis is a butterfly species from the subfamily Satyrinae in the family Nymphalidae. It was first described by Dru Drury in 1782 from Brazil.

Lyssa patroclus is a species of moth in the family Uraniidae. The species was described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae from the Moluccas.






















