
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. Active hostilities began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council Resolution 598 by both sides. Iraq's primary rationale for the attack against Iran cited the need to prevent Ruhollah Khomeini—who had spearheaded the Iranian Revolution in 1979—from exporting the new Iranian ideology to Iraq. There were also fears among the Iraqi leadership of Saddam Hussein that Iran, a theocratic state with a population predominantly composed of Shia Muslims, would exploit sectarian tensions in Iraq by rallying Iraq's Shia majority against the Baʽathist government, which was officially secular and dominated by Sunni Muslims. Iraq also wished to replace Iran as the power player in the Persian Gulf, which was not seen as an achievable objective prior to the Islamic Revolution because of Pahlavi Iran's economic and military superiority as well as its close relationships with the United States and Israel.

Iraq actively researched and later employed weapons of mass destruction (WMD) from 1962 to 1991, when it destroyed its chemical weapons stockpile and halted its biological and nuclear weapon programs as required by the United Nations Security Council. The fifth president of Iraq, Saddam Hussein, was internationally condemned for his use of chemical weapons against Iranian and Kurdish civilians during the Iran–Iraq War in the 1980s. Saddam pursued an extensive biological weapons program and a nuclear weapons program, though no nuclear bomb was built. After the Gulf War, the United Nations located and destroyed large quantities of Iraqi chemical weapons and related equipment and materials; Iraq ceased its chemical, biological and nuclear programs.
The Halabja massacre, also known as the Halabja chemical attack, was a massacre of Kurdish people that took place on 16 March 1988, during the Iraqi–Kurdish conflict in the closing days of the Iran–Iraq War in Halabja, Kurdistan, Iraq. The attack was part of the Al-Anfal Campaign in Kurdistan, as well as part of the Iraqi Army's attempt to repel the Iranian Operation Zafar 7. It took place 48 hours after the capture of the town by the Iranian Army. A United Nations (UN) medical investigation concluded that mustard gas was used in the attack, along with unidentified nerve agents.

William Scott Ritter Jr. is an American author, former United States Marine Corps intelligence officer, former United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM) weapons inspector, and a convicted sex offender.
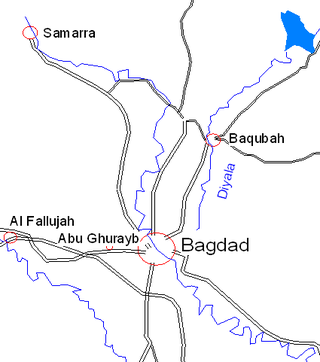
Abu Ghraib is a city in the Baghdad Governorate of Iraq, located just west of Baghdad's city center, or northwest of Baghdad International Airport. It has a population of 189,000 (2003). The old road to Jordan passes through Abu Ghraib. The government of Iraq created the city and Abu Ghraib District in 1944.
Operation Opera, also known as Operation Babylon, was a surprise airstrike conducted by the Israeli Air Force on 7 June 1981, which destroyed an unfinished Iraqi nuclear reactor located 17 kilometres southeast of Baghdad, Iraq. The Israeli operation came a year after the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force had caused minor damage to the same nuclear facility in Operation Scorch Sword, with the damage having been subsequently repaired by French technicians. Operation Opera, and related Israeli government statements following it, established the Begin Doctrine, which explicitly stated the strike was not an anomaly, but instead "a precedent for every future government in Israel". Israel's counter-proliferation preventive strike added another dimension to its existing policy of deliberate ambiguity, as it related to the nuclear weapons capability of other states in the region.

The Iraqi Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of Iraq. They consist of the Iraqi Army, the Iraqi Air Force, and the Iraqi Navy. Along with these three primary service branches, there exists the Iraqi Counter Terrorism Service and the Popular Mobilization Forces. The President of Iraq acts as the supreme commander as outlined by the constitution.
American support for Ba'athist Iraq during the Iran–Iraq War, in which it fought against post-revolutionary Iran, included several billion dollars' worth of economic aid, the sale of dual-use technology, military intelligence, and special operations training. The U.S. refused to sell arms to Iraq directly due to Iraq's ties to terrorist groups, but several sales of "dual-use" technology have been documented; notably, Iraq purchased 45 Bell helicopters for $200 million in 1985. Of particular interest for contemporary Iran–United States relations are accusations that the U.S. government actively encouraged Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein to invade Iran, supported by a considerable amount of circumstantial evidence and generally regarded as the conventional wisdom in the Arab world, but several scholars and former U.S. government officials deny that any such collusion occurred, and no direct documentary proof of it has been found.

In violation of the Geneva Protocol of 1925, the Iraqi Army initiated two failed and one successful (1978–1991) offensive chemical weapons (CW) programs. President Saddam Hussein (1937–2006) pursued the most extensive chemical program during the Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988), when he waged chemical warfare against his foe. He also used chemicals in 1988 in the Al-Anfal Campaign against his civilian Kurdish population and during a popular uprising in the south in 1991.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1747 was a United Nations Security Council resolution, written with reference to some IAEA reports, that tightened the sanctions imposed on Iran in connection with the Iranian nuclear program. It was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on 24 March 2007.
Al Hakum, also romanized Al Hakam, was at one time Iraq's most sophisticated and largest biological weapons (BW) production factory. The facility was part of a large military complex at Jurf Al Sakhar, about 60-70 kilometers southwest of Baghdad, near al-Musayyib. It produced large quantities of botulinum toxin and anthrax from 1989 to 1996. The name derives from the common Arabic name or title Al Hakam, one of the Names of God in the Qur'an.

Tilletia caries is a basidiomycete that causes common bunt of wheat. The common names of this disease are stinking bunt of wheat and stinking smut of wheat. This pathogen infects wheat, rye, and various other grasses. T. caries is economically and agriculturally important because it reduces both the wheat yield and grain quality.

The Iranian Armed Forces, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran Armed Forces, are the combined military forces of Iran, comprising the Islamic Republic of Iran Army (Artesh), the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (Sepah) and the Law Enforcement Force (Faraja).

The AK-63 is a Hungarian variant of the AKM assault rifle manufactured by the Fegyver- és Gépgyár (FÉG) state arms plant in Hungary. It is currently used by the Hungarian Ground Forces as its standard infantry weapon, and by most other branches of the Hungarian Defence Forces.

Saddam Hussein (1937–2006) began an extensive biological weapons (BW) program in Iraq in the early 1980s, despite having signed the Biological Weapons Convention (BWC) of 1972. Details of the BW program and a chemical weapons program surfaced after the Gulf War (1990–91) during the disarmament of Iraq under the United Nations Special Commission (UNSCOM). By the end of the war, program scientists had investigated the BW potential of five bacterial strains, one fungal strain, five types of virus, and four toxins. Of these, three—anthrax, botulinum and aflatoxin—had proceeded to weaponization for deployment. Because of the UN disarmament program that followed the war, more is known today about the once-secret bioweapons program in Iraq than that of any other nation.
Ammochloa is a genus of Mediterranean plants in the grass family, Poaceae.
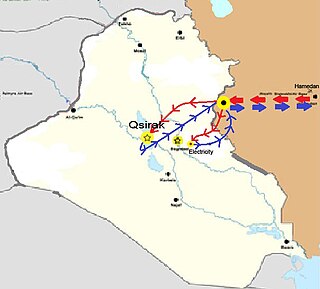
Operation Scorch Sword was a surprise airstrike carried out by the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force on 30 September 1980, that damaged an almost-complete nuclear reactor located 17 kilometres southeast of Baghdad, Iraq. The operation took place eight days into the Iran–Iraq War. At dawn on 30 September 1980, four Iranian McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II jets refuelled mid-air near the Iran–Iraq border. After crossing into Iraq, the fighters climbed to a high altitude in order to stay undetected by Iraqi airspace radar systems. Moments later, two of the F-4s peeled off and dropped to a low altitude again to avoid internal radar detection and proceeded to fly stealthily to the Tuwaitha Nuclear Research Centre just southeast of the capital city of Baghdad, and home to the Osirak nuclear reactor.
Operation Forty Stars, also known as Operation Forty Lights, or Chelcheraq, was a military operation conducted by the People's Mujahedin of Iran (MEK) at the closing stages of the Iran–Iraq War on 18 June 1988. The goal was to occupy the Iranian border city of Mehran to control its oil fields, as well as Kurdish villages in the region.

During the Iran–Iraq War (1980–1988), Iraq engaged in chemical warfare against Iran on multiple occasions, including more than 30 targeted attacks on Iranian civilians. The Iraqi chemical weapons program, which had been active since the 1970s, was aimed at regulated offensive use, as evidenced in the chemical attacks against Iraqi Kurds as part of the Anfal campaign in the late 1980s. The Iraqis had also utilized chemical weapons against Iranian hospitals and medical centres. According to a 2002 article in the American newspaper The Star-Ledger, 20,000 Iranian soldiers and combat medics were killed on the spot by nerve gas. As of 2002, 5,000 of the 80,000 survivors continue to seek regular medical treatment, while 1,000 are hospital inpatients. Though the use of chemical weapons in international armed conflict was banned under the Geneva Protocol, much of the international community remained indifferent to the attacks; Iraq's military campaign in Iran was supported by the United States and the Soviet Union, both of whom had sought to contain Iranian influence after the Islamic Revolution of 1979.

On 28 June 2021, President Biden directed airstrikes against Iran-backed militia groups close to the Syria-Iraq border. F-15E and F-16 aircraft were used to launch the attack in what the U.S. described as a retaliatory attack against U.S. facilities and personnel in Iraq by militia groups. Two operational and weapons storage facilities were targeted in Syria, the U.S. military revealed in a statement. Despite the U.S. not disclosing the information regarding the casualties in the attack, the SOHR stated that at least nine Iran-backed Iraqi militia fighters died, leaving many others injured. Iraqi militia groups aligned with Iran in a statement named four members of the Kataib Sayyed al-Shuhada faction they said were killed in the attack on the Syria-Iraq border.













