
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

The flathead catfish, also called by several common names including mudcat or shovelhead cat, is a large species of North American freshwater catfish in the family Ictaluridae. It is the only species of the genus Pylodictis. Ranging from the lower Great Lakes region to northern Mexico, it has been widely introduced and is an invasive species in some areas. The closest living relative of the flathead catfish is the much smaller widemouth blindcat, Satan eurystomus.

The widemouth blindcat is a species of North American freshwater catfish endemic to Texas in the United States. It is the only species in the genus Satan.

Airbreathing catfish comprise the family Clariidae of the order Siluriformes. Sixteen genera and about 116 species of clariid fishes are described; all are freshwater species. Other groups of catfish also breathe air, such as the Callichthyidae and Loricariidae.

The Ictaluridae, sometimes called ictalurids, are a family of catfish native to North America, where they are an important food source and sometimes fished for sport. The family includes about 51 species, some commonly known as bullheads, madtoms, channel catfish, and blue catfish.

The Loricariidae is the largest family of catfish, with 92 genera and just over 680 species. Loricariids originate from freshwater habitats of Costa Rica, Panama, and tropical and subtropical South America. These fish are noted for the bony plates covering their bodies and their suckermouths. Several genera are sold as "plecos", notably the suckermouth catfish, Hypostomus plecostomus, and are popular as aquarium fish.

The Pimelodidae, commonly known as the long-whiskered catfishes, are a family of catfishes.

The Cetopsidae are a small family of catfishes, commonly called the whale catfishes.

Horabagrus brachysoma or the sun catfish is a species of catfish endemic to rivers in the Western Ghats of India. It is known as Günther's catfish or yellow catfish. It is also known as Manjakoori in its native range. It is also known by a host of other names, such as bullseye catfish, golden red tail catfish and solar catfish.
The Sarcoglanidinae are a subfamily of catfishes of the family Trichomycteridae. It includes six genera: Ammoglanis, Malacoglanis, Microcambeva, Sarcoglanis, Stauroglanis, and Stenolicmus.
Prietella is a small genus of North American freshwater catfishes found in Mexico and Texas, and restricted to underground waters.
The Mexican blindcat, in Spanish bagre de muzquiz, is a species of North American freshwater catfish. Until recently, it was believed to be endemic to Coahuila in the Rio Bravo drainage in northern Mexico; however, in 2016 the species was reported from the Amistad National Recreation Area, Texas, following earlier, unconfirmed sightings of blind, white catfish in the area. The captured specimens were brought to the San Antonio Zoo and Aquarium.
Micromyzon akamai is a species of catfish in the family Aspredinidae.

Cavefish or cave fish is a generic term for fresh and brackish water fish adapted to life in caves and other underground habitats. Related terms are subterranean fish, troglomorphic fish, troglobitic fish, stygobitic fish, phreatic fish and hypogean fish.

The brownsnout spookfish or brown-snout spookfish is a species of barreleye in the family Opisthoproctidae. It and the glasshead barreleye fish are the only vertebrates known to employ a mirror, in addition to a lens, to focus an image in its eyes. This species probably has a worldwide tropical and temperate distribution; in the Atlantic Ocean it is known from Bermuda, the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the Gulf of Mexico, and in the Pacific Ocean it is known from the California Current region and the South China Sea. It is found in the mesopelagic and bathypelagic zones at a depth of 500–2,400 meters (1,600–7,900 ft), but usually occurs below 1,000 meters. In the Gulf of Mexico it is found shallower, at 310–460 meters (1,020–1,510 ft).
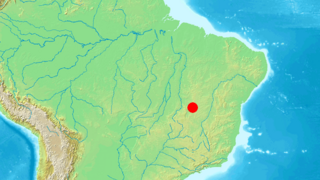
Eigenmannia vicentespelaea is a species of weakly electric knifefish in the family Sternopygidae. Native to the São Domingos karst area in central Brazil, it is the only known knifefish to exclusively inhabit caves. Measuring up to 12 cm (4.7 in) long, E. vicentespelaea can be distinguished from its relatives by its translucent body and reduced or absent eyes. As some individuals retain well-developed eyes, this fish may have colonized caves only recently in evolutionary time.
Microsynodontis vigilis is a species of upside-down catfish endemic to Gabon where it occurs in the Ogowe River. It was first described in 2004 by Ng Heok Hee.
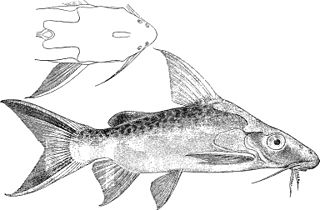
Synodontis pleurops, known as the Congo squeaker, the bigeye squeaker, or the bug eyed synodontis, is a species of upside-down catfish native to the upper Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered at the Boyoma Falls, in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Noturus hildebrandi, also known as the least madtom, is a species of catfish. Its native range stretches from the Obion River in Kentucky to the Homochitto River in Mississippi.
Schilbe intermedius or the silver butter catfish is a widespread species of African catfish. It seems closely related to Schilbe uranoscopus and these two species are sympatric over part of their ranges.














