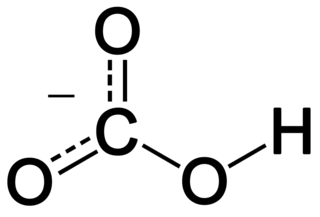
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula HCO−
3.

Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as halides of carbon without carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon bonds, and certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

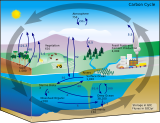
The carbon cycle is that part of the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of Earth. Other major biogeochemical cycles include the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many rocks such as limestone. The carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration (storage) to and release from carbon sinks.

The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments. In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump).
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds—that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as inorganic chemistry.

In oceanic biogeochemistry, the solubility pump is a physico-chemical process that transports carbon as dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) from the ocean's surface to its interior.
A chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic (chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which use photons. Chemotrophs can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Chemotrophs can be found in areas where electron donors are present in high concentration, for instance around hydrothermal vents.

Dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) is the sum of the aqueous species of inorganic carbon in a solution. Carbon compounds can be distinguished as either organic or inorganic, and as dissolved or particulate, depending on their composition. Organic carbon forms the backbone of key component of organic compounds such as – proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.

Total organic carbon (TOC) is an analytical parameter representing the concentration of organic carbon in a sample. TOC determinations are made in a variety of application areas. For example, TOC may be used as a non-specific indicator of water quality, or TOC of source rock may be used as one factor in evaluating a petroleum play. For marine surface sediments average TOC content is 0.5% in the deep ocean, and 2% along the eastern margins.
In analytical chemistry, ashing or ash content determination is the process of mineralization by complete combustion for preconcentration of trace substances prior to a chemical analysis, such as chromatography, or optical analysis, such as spectroscopy.

Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometers. The fraction remaining on the filter is called particulate organic carbon (POC).
Rhenium trioxide or rhenium(VI) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ReO3. It is a red solid with a metallic lustre that resembles copper in appearance. It is the only stable trioxide of the Group 7 elements (Mn, Tc, Re).
pCO2, pCO2, or is the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (CO2), often used in reference to blood but also used in meteorology, climate science, oceanography, and limnology to describe the fractional pressure of CO2 as a function of its concentration in gas or dissolved phases. The units of pCO2 are mmHg, atm, torr, Pa, or any other standard unit of atmospheric pressure. The pCO2 of Earth's atmosphere has risen from approximately 280 ppm (parts-per-million) to a mean 2019 value of 409.8 ppm as a result of anthropogenic release of carbon dioxide from fossil fuel burning. This is the highest atmospheric concentration to have existed on Earth for at least the last 800,000 years.

Dystrophic lakes, also known as humic lakes, are lakes that contain high amounts of humic substances and organic acids. The presence of these substances causes the water to be brown in colour and have a generally low pH of around 4.0-6.0. Due to these acidic conditions, there is little biodiversity able to survive, consisting mostly of algae, phytoplankton, picoplankton, and bacteria. Ample research has been performed on the many dystrophic lakes located in Eastern Poland, but dystrophic lakes can be found in many areas of the world.

In geochemistry, paleoclimatology, and paleoceanography δ13C is an isotopic signature, a measure of the ratio of the two stable isotopes of carbon—13C and 12C—reported in parts per thousand. The measure is also widely used in archaeology for the reconstruction of past diets, particularly to see if marine foods or certain types of plants were consumed.
Ultrapure water (UPW), high-purity water or highly purified water (HPW) is water that has been purified to uncommonly stringent specifications. Ultrapure water is a term commonly used in manufacturing to emphasize the fact that the water is treated to the highest levels of purity for all contaminant types, including: organic and inorganic compounds; dissolved and particulate matter; volatile and non-volatile; reactive, and inert; hydrophilic and hydrophobic; and dissolved gases.

The oceanic carbon cycle is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere, Earth interior, and the seafloor. The carbon cycle is a result of many interacting forces across multiple time and space scales that circulates carbon around the planet, ensuring that carbon is available globally. The Oceanic carbon cycle is a central process to the global carbon cycle and contains both inorganic carbon and organic carbon. Part of the marine carbon cycle transforms carbon between non-living and living matter.

Total inorganic carbon is the sum of the inorganic carbon species.
CO2SYS is a family of software programs that calculate chemical equilibria for aquatic inorganic carbon species and parameters. Their core function is to use any two of the four central inorganic carbon system parameters to calculate various chemical properties of the system. These programs are widely used by oceanographers and limnologists to understand and predict chemical equilibria in natural waters.