
The Atlantic mackerel, also known as Boston mackerel, Norwegian mackerel, Scottish mackerel or just mackerel, is a species of mackerel found in the temperate waters of the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, and the northern Atlantic Ocean, where it is extremely common and occurs in huge shoals in the epipelagic zone down to about 200 m (660 ft). It spends the warmer months close to shore and near the ocean surface, appearing along the coast in spring and departing with the arrival of colder weather in the fall and winter months. During the fall and winter, it migrates out into deeper and more southern water, seeking warmer temperatures.

The Atlantic horse mackerel, also known as the European horse mackerel or common scad, is a species of jack mackerel in the family Carangidae, which includes the jacks, pompanos and trevallies. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean off Europe and Africa and into the south-eastern Indian Ocean. It is an important species in commercial fisheries and is listed as a Vulnerable species on The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

The Atlantic wreckfish, also known as the stone bass or bass groper, is a marine, bathydemersal, and oceanodromous ray-finned fish in the family Polyprionidae. It has a worldwide, if disjunct, distribution in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans.

The ribbonfish are any lampriform fishes in the family Trachipteridae. These pelagic fish are named for their slim, ribbon-like appearance. They are rarely seen alive, as they typically live in deep waters, though are not bottom feeders. The perciform fish known as the red bandfish is sometimes referred to as ribbonfish, but it is unrelated to any ribbonfish in the Trachipteridae.

The European sprat, also known as brisling, brisling sardine, bristling, garvie, garvock, Russian sardine, russlet, skipper or whitebait, is a species of small marine fish in the herring family Clupeidae. Found in European, West Asian and North African waters, it has silver grey scales and white-grey flesh. Specific seas in which the species occurs include the Irish Sea, Black Sea, Baltic Sea and Sea of the Hebrides. The fish is the subject of fisheries, particularly in Scandinavia, and is made into fish meal, as well as being used for human consumption. When used for food it can be canned, salted, breaded, fried, boiled, grilled, baked, deep fried, marinated, broiled, and smoked.
The Atlantic saury is a fish of the family Scomberesocidae found in the North Atlantic Ocean from the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, Canada south to Bermuda and North Carolina in the western Atlantic and from Iceland to Morocco in the eastern Atlantic, it is also found in the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Aegean Sea.
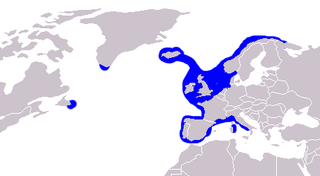
The common ling, also known as the white ling or simply the ling, is a large member of the family Lotidae, a group of cod-like fishes. It resembles the related rocklings, but it is much larger and has a single barbel. This species is unrelated to the pink ling, Genypterus blacodes, from the Southern Hemisphere. The common ling is found in the northern Atlantic, mainly off Europe, and into the Mediterranean Basin. It is an important quarry species for fisheries, especially in the northeastern Atlantic, although some doubts exist as to the sustainability of the fisheries. As an edible species, it is eaten fresh, frozen, or dried, but also preserved in lye, while the roe is a delicacy in Spain.

The blackmouth catshark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, common in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean from Iceland to Senegal, including the Mediterranean Sea. It is typically found over the continental slope at depths of 150–1,400 m (490–4,590 ft), on or near muddy bottoms. The youngest sharks generally inhabit shallower water than the older juveniles and adults. This slim-bodied species is characterized by the black interior of its mouth, a marbled pattern of pale-edged brownish saddles or blotches along its back and tail, and a prominent saw-toothed crest of enlarged dermal denticles along the upper edge of its caudal fin. It reaches lengths of 50–79 cm (20–31 in), with sharks in the Atlantic growing larger than those in the Mediterranean.

The witch, known in English by a variety of other common names including the witch flounder, pole flounder, craig fluke, Torbay sole, and grey sole, is a species of flatfish from the family Pleuronectidae. It occurs on both sides of the North Atlantic Ocean on muddy sea beds in quite deep water. In northern Europe it has some importance in fisheries as a food fish.

The little tunny, also known as the false albacore, little tuna, bonita, or erroneously as the blue bonito, is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It can be found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean and Black seas; in the western Atlantic, it ranges from Brazil to the New England states. The little tunny is a pelagic fish that can be found regularly in both offshore and inshore waters, and it is classified as a highly migratory species. The little tunny is best identified by the "worm-like" markings on its back and the dark spots appearing between its pectoral and ventral fins.

The red porgy, also known as the common seabream or Couch's bream, is a species of marine ray-finned fish in the family Sparidae. It is found in shallow waters on either side of the Atlantic Ocean, being present on the western coast of Europe and the Mediterranean Sea as well as the eastern coasts of North and South America and the Caribbean Sea. It feeds on or near the seabed and most individuals start life as females and later change sex to males.

The greater amberjack, also known as the allied kingfish, great amberfish, greater yellowtail, jenny lind, Sea donkey, purplish amberjack, reef donkey, rock salmon, sailors choice, yellowtail, and yellow trevally, is a species of predatory ray-finned fish in the family Carangidae, the jacks and pompanos. It is found in temperate, subtropical, and tropical seas around the world. It is a popular quarry species for recreational fisheries and is important in commercial fisheries. It is the largest species in the family Carangidae.

The tub gurnard, also known as the sapphirine gurnard, tube-fish, tubfish or yellow gurnard, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. It is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It is exploited by commercial fisheries as a food fish.

Diplodus sargus, the sargo, common white seabream, or white seabream is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Sparidae, which includes the seabreams and porgies. This fish is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean and in the Mediterranean Sea. It is a target species for commercial fisheries and is grown in aquaculture. D. sargussensu lato was formerly thought to be a widespread species in the eastern Atlantic and western Indian Oceans but the taxa outside of D, sargussensu stricto are now recognised as valid species and are part of the D. sargus species complex.

The red gurnard, also known as the East Atlantic red gurnard or soldier, is a benthic species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. This fish is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.

Trachipterus is a genus of ribbonfishes.
The longfin gurnard, the long-finned gurnard or shining gurnard, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. This fish is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea. This species is of commercial importance as a food fish.

The sand steenbras or striped seabream is a species of marine fish in the family Sparidae. It is found in shallow water in the Mediterranean Sea and in the eastern Atlantic Ocean from France to South Africa. It also occurs in the Red Sea and off the coast of Mozambique in the Indian Ocean. The IUCN has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The European flying squid is a species of squid from the continental slope and oceanic waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. It is the type species of the genus Todarodes, the type genus of the subfamily Todarodinae of the pelagic squid family Ommastrephidae. It is a species which is targeted by some fisheries, although it is more often a bycatch.
Zu elongatus, or the taper-tail ribbonfish, is a species of ray-finned fish within the family Trachipteridae. The species distribution is poorly known, and while it likely lives in temperate and tropical waters of all oceans, but has only been encountered in the Atlantic Ocean- off the coasts of Namibia and the western Cape of South Africa- and in the Pacific Ocean off New Zealand. It inhabits mesopelagic waters up to 1200 meters below sea level. Other common names for this species include "scalloped dealfish" and spitsstert-lintvis in Afrikaans.


















