
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of 1,435 mm. The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge, international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with about 55% of the lines in the world using it.

The Mass Transit Railway (MTR) is a major public transport network serving Hong Kong. Operated by the MTR Corporation (MTRCL), it consists of heavy rail, light rail, and feeder bus service centred on a 10-line rapid transit network serving the urbanised areas of Hong Kong Island, Kowloon, and the New Territories. The system included 245.3 km (152.4 mi) of rail as of December 2022 with 179 stations, including 99 heavy rail stations, 68 light rail stops and 1 high-speed rail terminus.

The Kowloon–Canton Railway was a railway network in Hong Kong. It was owned and operated by the Kowloon–Canton Railway Corporation (KCRC) until 2007. Rapid transit services, a light rail system, feeder bus routes within Hong Kong, and intercity passenger and freight train services to China on the KCR network, have been operated by the MTR Corporation since 2007.

The Tsuen Wan line is one of the ten lines of the metro network in Hong Kong's MTR. It is indicated in red on the MTR map.

The Kwun Tong line is a rapid transit line of the MTR network in Hong Kong, coloured green on the MTR map. Starting at Whampoa in Hung Hom and ending at Tiu Keng Leng in Tseung Kwan O, Sai Kung, the route has 17 stations and takes 35 minutes to complete. The Kwun Tong line is one of the busiest railway lines on the network connecting the central and the eastern portions of Kowloon via Wong Tai Sin. The line is mostly underground, but includes a lengthy elevated section, and runs generally in an east-west direction. During the morning rush hour, the Kwun Tong line utilises 33 trains running at 29tph to achieve a route capacity of 85,000 pphpd.

The East Rail line is one of the ten lines that form MTR, the mass transit system in Hong Kong. The railway line starts at Lo Wu or Lok Ma Chau, both of which are boundary crossing points into Shenzhen and joins in the north at Sheung Shui and ends at Admiralty station on Hong Kong Island. At approximately 46 km (29 mi), the line is the second longest line within the network, behind the Tuen Ma line. The line's colour is light blue.

Kowloon Tong is a station on MTR's Kwun Tong line and East Rail line in New Kowloon, Hong Kong. The station serves Kowloon Tong and its vicinity, including Yau Yat Tsuen, the Festival Walk shopping centre, City University of Hong Kong and Hong Kong Baptist University.

Whampoa is the western terminus of the Kwun Tong line of the MTR in Hong Kong. It is located in Hung Hom, Kowloon City District within the developed area of Whampoa Garden immediately adjacent to the stern of The Whampoa, a symbol of identity for the area and its history.

Ho Man Tin is an underground MTR rapid transit station on the Kwun Tong line and the Tuen Ma line, located beneath Valley Road in Lo Lung Hang, as part of the Sha Tin to Central Link project. The station's lower platforms opened on 23 October 2016 along with Whampoa station as part of the Kwun Tong line extension, while the upper platforms of the Tuen Ma line opened on 27 June 2021.

Mong Kok East station – formerly Mong Kok railway station and Yaumati railway station – is a station on Hong Kong's East Rail line. Only out-of-system interchange is available with Kwun Tong line and Tsuen Wan line at Mong Kok station via a footbridge. The station is connected to Grand Century Place, a large shopping mall.

With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally cannot run through without some form of conversion between gauges, leading to passengers having to change trains and freight requiring transloading or transshipping; this can add delays, costs, and inconvenience to travel on such a route.

The Disneyland Resort line is a commuter rail line connecting Sunny Bay to the Hong Kong Disneyland Resort, coloured pink on the network diagram. It is the seventh line of the former MTR network before the merger of MTR and KCR, and the world's first metro line designed to service a Disney theme park. There are only two stations on this line, Sunny Bay and Disneyland Resort, and the line operates as a shuttle service between these two stations. Sunny Bay station is an interchange station with the Tung Chung line between Tsing Yi and Tung Chung stations. Administratively, the entire line is in Tsuen Wan District, despite being situated on Lantau Island, and is the only MTR line in Hong Kong to run within a single district.
East Kowloon line was one of the original five MTR lines proposed in the late 1970s in Hong Kong, which would have connected Sheung Wan with East Kowloon.
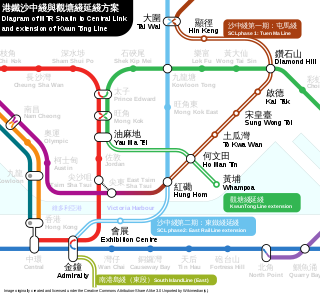
The Sha Tin to Central Link was an expansion project of the MTR public transport network in Hong Kong. It was divided into two sections and expanded the network’s heavy rail lines.

Beacon Hill Tunnel is a railway tunnel in Hong Kong on the original Kowloon–Canton Railway, linking Kowloon Tong to its immediate south and Sha Tin to its north. The nearest stations to the south and north of the tunnel are Kowloon Tong and Tai Wai respectively. Today, the tunnel carries the MTR East Rail line metro service and through trains to mainland China.
Kowloon is an urban area that is part of Hong Kong.

The Tuen Ma lineis a rapid transit line that forms part of the Mass Transit Railway (MTR) system in Hong Kong. Coloured brown on the map, the Tuen Ma line is 56.2 kilometres (34.9 mi) in length, making it the longest line of the MTR network. It has a total of 27 stations, more than any other in the MTR system.

Hong Kong's rail network mainly comprises public transport trains operated by the MTR Corporation Limited (MTRC). The MTRC operates the metro network of the territory, the commuter rail network connecting the northeastern, northwestern and southwestern New Territories to the urban areas, and a light rail network in northwestern New Territories. The operations of the territory's two leading railway companies, MTRC and the Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation (KCRC), were merged in 2007 on grounds of economies of scale and cost effectiveness. The Hong Kong Government has an explicit stated transport policy of using railways as its transport backbone.
Asia has many narrow-gauge railways. The railways of Japan, Indonesia and the Philippines are predominantly 1,067 mm narrow gauge. Those in mainland Southeast Asia, which includes Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar and Malaysia, are predominantly metre gauge. The proposed ASEAN Railway would be standard or dual gauge, using metre- and standard-gauge regional railway networks and linking Singapore through Malaysia, Thailand, Laos and Vietnam to China's standard-gauge rail network. In Western Asia, Jordan uses 1,050 mm narrow gauge.

The Kwun Tong line extension is an extension of the MTR rapid transit network in Hong Kong. It extends the existing train service of Kwun Tong line to Ho Man Tin station and Whampoa station. Construction started on 25 July 2011 and opened for service on 23 October 2016.













