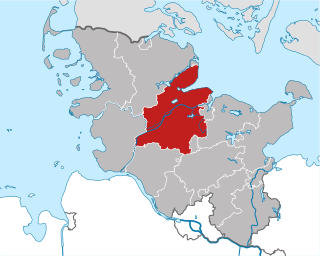
Rendsburg-Eckernförde is a district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is bounded by the city of Kiel, the district of Plön, the city of Neumünster, the districts of Segeberg, Steinburg, Dithmarschen and Schleswig-Flensburg, and the Baltic Sea.

The Berlin tramway is the main tram system in Berlin, Germany. It is one of the oldest tram networks in the world having its origins in 1865 and is operated by Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe (BVG), which was founded in 1929. It is notable for being the third-largest tram system in the world, after Melbourne and St. Petersburg. Berlin's streetcar system is made up of 22 lines that operate across a standard gauge network, with almost 800 stops and measuring almost 190 kilometres (120 mi) in route length and 430 kilometres (270 mi) in line length. Nine of the lines, called Metrotram, operate 24 hours a day and are identified with the letter "M" before their number; the other thirteen lines are regular city tram lines and are identified by just a line number.

Holstein Switzerland is a hilly area with a patchwork of lakes and forest in Schleswig Holstein, Germany, reminiscent of Swiss landscape. Its highest point is the Bungsberg. It is a designated nature park as well as an important tourist destination in Northern Germany situated between the cities of Kiel and Lübeck.

The Basel tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Basel, Switzerland, and the Swiss part of its agglomeration. It consists of 13 lines. Due to its longevity, it is part of Basel's heritage and, alongside the Basel Minster, is one of the symbols of the city.

The Aachen tramway network was the backbone of public transport in Aachen, now in the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, and the surrounding areas from 1880 to 1974. The track gauge was 1,000 mm, see Nordrhein-Westfalen.

Trams in Vienna are a vital part of the public transport system in Vienna, capital city of Austria. In operation since 1865, the network reached its greatest extent during the interwar period (1918–1939). Today, it is the fifth largest tram network in the world, at about 176.9 kilometres (109.9 mi) in total length and 1,071 stations.

The Mainz tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Mainz, the capital city of the federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

The Ulm tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Ulm, a city in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany.

The Düsseldorf tramway network is a network of tramways serving Düsseldorf, the capital city of the federal state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. In combination with the Düsseldorf Stadtbahn and Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn, it forms the backbone of the public transport system in Düsseldorf.

The Gotha tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Gotha, a city in the federal state of Thuringia, Germany.

The Würzburg tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Würzburg, a city in the federal state of Bavaria, Germany.

The Nuremberg tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Nuremberg, a city in the federal state of Bavaria, Germany.

The Rostock tramway network is a network of tramways forming the centrepiece of the public transport system in Rostock, the largest city in the federal state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany.

The Augsburg tramway network is a network of tramways forming the backbone of the public transport system in Augsburg, a city in the federal state of Bavaria, Germany.

The Brandenburg an der Havel tramway network is a network of tramways forming the centrepiece of the public transport system in Brandenburg an der Havel, a city in the federal state of Brandenburg, Germany.

The Braunschweig tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Braunschweig, a city in the federal state of Lower Saxony, Germany.

The Plauen tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Plauen, a city in the federal state of Saxony, Germany.

The Halberstadt tramway network is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Halberstadt, a city in the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany.

The Naumburg (Saale) tramway is a tramline forming part of the public transport system in Naumburg (Saale), a city in the federal state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. At only 2.5 km (1.6 mi) long, it is the smallest urban tramway in Germany, and one of the smallest in Europe.

![Public transport shared transport[ation] service that is available for use by the general public; usually of passengers but sometimes of goods](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/0b/R160A_E_Train_entering_World_Trade_Center.jpg/320px-R160A_E_Train_entering_World_Trade_Center.jpg)