| Basel tramway network | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 A BLT tram in Basel | |||
 | |||
| Operation | |||
| Locale | Basel, Switzerland | ||
| Open | 6 May 1895 | ||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Lines | 12 | ||
| Operators |
| ||
| Infrastructure | |||
| Track gauge | 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) metre gauge | ||
| Electrification | 650 V DC [1] | ||
| Statistics | |||
| Route length | 128.5 km (79.8 mi) | ||
| |||
| Website | http://www.bvb.ch Basler Verkehrs-Betriebe (in German) | ||
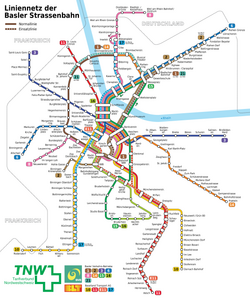
The Basel tramway network (German : Basler Strassenbahn-Netz) is a network of tramways forming part of the public transport system in Basel, Switzerland, and its agglomeration - it also reaches into adjacent suburbs in Germany and France. The only two other tramway networks to cross an international border are Geneva's and Strasbourg's tramways. The Basel tram system consists of 12 lines. Due to its longevity (the network is now more than a century old), it is part of Basel's heritage and, alongside the Basel Minster, is one of the symbols of the city.
Contents
The trams on the network are operated by two transport providers: Basler Verkehrs-Betriebe (Basel Transport Service) (BVB) and Baselland Transport (BLT). Both operators are part of the integrated fare network Tarifverbund Nordwestschweiz (TNW), which in itself is part of the three countries-integrated fare network triregio. [2] [3] [4]
BVB is owned by the Canton of Basel-Stadt. Its green trams operate mostly in the city, although termini of its lines 3, 6, 8 and 14 are across the cantonal or country border.
BLT is owned by the Canton of Basel-Land and has yellow and red livery. It owns the tram infrastructure in Basel-Land and runs the lines 10, 11 and 17 who are passing through Basel on BVB-tracks. At the same time, BVB line 14 runs partially on BLT-tracks. BLT line 10 at one point passes through the territory of France. [5]