
Manatees are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee, the West Indian manatee, and the West African manatee. They measure up to 4.0 metres long, weigh as much as 590 kilograms (1,300 lb), and have paddle-like tails.

The Sirenia, commonly referred to as sea cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The extant Sirenia comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae and Trichechidae with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae and Prorastomidae families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene.

Trichechidae is a family of sirenians that includes all living manatees and several extinct genera.

Meganthropus is an extinct genus of non-hominin hominid ape, known from the Pleistocene of Indonesia. It is known from a series of large jaw and skull fragments found at the Sangiran site near Surakarta in Central Java, Indonesia, alongside several isolated teeth. The genus has a long and convoluted taxonomic history. The original fossils were ascribed to a new species, Meganthropus palaeojavanicus, and for a long time was considered invalid, with the genus name being used as an informal name for the fossils.

The Amazonian manatee is a species of manatee that lives in the Amazon Basin in Brazil, Peru, Colombia and Ecuador. It has thin, wrinkled brownish or gray colored skin, with fine hairs scattered over its body and a white chest patch. It is the smallest of the three extant species of manatee.

The West Indian manatee, also known as the North American manatee, is a large, aquatic mammal native to warm coastal areas of the Caribbean, from the eastern US to northern Brazil. Living alone or in herds, it feeds on underwater plants and uses its whiskers to navigate. It is divided into two endangered subspecies, the Florida manatee in the US and the Antillean manatee in the Caribbean, both of which face pressure from habitat loss, pollution, and other human activity. The West Indian manatee is the largest living member of the sirenians, a group of large aquatic mammals that includes the dugong, other manatees, and the extinct Steller's sea cow.

Mammalodontidae is a family of extinct whales known from the Oligocene of Australia and New Zealand.

Iberosuchus is a genus of extinct sebecosuchian mesoeucrocodylian found in Western Europe from the Eocene. Remains from Portugal was described in 1975 by Antunes as a sebecosuchian crocodilian. This genus has one species: I. macrodon. Iberosuchus was a carnivore, unlike the crocodilians today, they are not aquatic and are instead terrestrial.

Pachycostasaurus is an extinct Pliosauroid from the Oxford Clay formation of Peterborough, England.
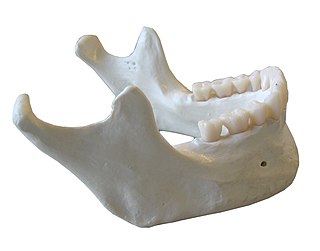
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the bottom skeleton that makes up the lower half of the mouth in jawed vertebrates. In arthropods, the largest pair of appendages of their mouthparts are also named mandibles.

The Caribbean Manatee Conservation Center is a research, education, rescue, and rehabilitation partnership established in 2009 in the Caribbean island of Puerto Rico in order to help endangered manatees survive from extinction.

Astorgosuchus is an extinct monospecific genus of crocodilian, closely related to true crocodiles, that lived in Pakistan during the late Oligocene period. This crocodile may have reached lengths of up to 8 m (26 ft) and is known to have preyed on many of the large mammals found in its environment. Bite marks of a large crocodile have been found on the bones of juvenile Paraceratherium, however if these were left by Astorgosuchus cannot be said with certainty. The genus contains a single species, Astorgosuchus bugtiensis, which was originally named as a species of Crocodylus in 1908 and was moved to its own genus in 2019.
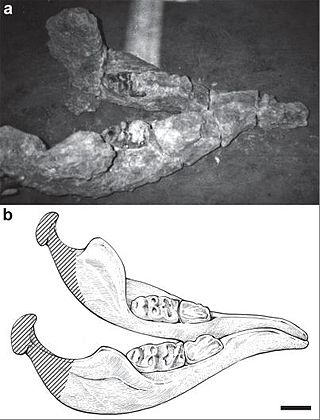
Sinomammut is a mammutid proboscidean from the Miocene of China. Only one species, S. tobieni, is known, named in 2016.
Tapirus rondoniensis is an extinct species of large sized tapir that lived in northwestern parts of Brazil during the Pleistocene. Fossils of the species were found in the Río Madeira Formation of Rondônia, after which the species is named.

The Madeira-Tapajós moist forests (NT0135) is an ecoregion in the Amazon basin. It is part of the Amazon biome. The ecoregion extends southwest from the Amazon River between its large Madeira and Tapajós tributaries, and crosses the border into Bolivia. In the south it transitions into the cerrado biome of Mato Grosso. In the state of Rondônia it contains some of the most degraded land of the Amazon basin.
Caiman brevirostris is an extinct species of caiman that lived during the Late Miocene, around 11.6 million years ago, to the end of the Miocene 5.3 million years ago in Acre and Amazonas, Brazil as well as Urumaco, Venezuela. Several specimens have been referred to the species, but only 3 of them are confidently placed in the species. C. brevirostris was originally named in 1987 on the basis of a single, incomplete rostrum with an associated mandibular ramus that had been found in Acre, Brazil. C. brevirostris is very distinct among Caiman species and caimaninae overall in that it preserves a characteristically short and robust skull that bears blunt posterior teeth that were built to break down harder foods. This was an adaption for durophagy, likely to crush shells of mollusks and clams which were common in the wetlands that C. brevirostris resided in.

Antaeusuchus taouzensis is a species of peirosaurid notosuchian from the Late Cretaceous Kem Kem Group of Morocco. It was described in 2021, and it is the only species in the genus Antaeusuchus. It is the fourth notosuchian described from the region and the second Kem Kem peirosaurid after Hamadasuchus. A 2023 study proposes that Antaeusuchus may not be distinct enough to warrant its own genus and that it instead represents another species of Hamadasuchus.

Kyhytysuka is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurian ichthyosaur from Early Cretaceous Colombia. The animal was previously assigned to the genus Platypterygius, but given its own genus in 2021. Kyhytysuka was a mid-sized ophthalmosaurian with heterodont dentition and several adaptations suggesting that it was a macropredatory vertebrate hunter living in shallow waters. It contains a single species, Kyhytysuka sachicarum.
Baraguatherium is an extinct genus of ground sloths of the family Mylodontidae that lived during the Early Miocene of what is now Venezuela. It dates to the Early Miocene, around 20.44 to 15.97 million years ago and represents the oldest representative of its family in the northern part of South America to date. The structure of the teeth suggests that the genus represents a rather basal form within the Mylodontidae. Unlike other mylodonts, which tended to prefer open grasslands, Baraguatherium lived in a riverine, coastal tropical rainforest.
Vassallia is an extinct genus of cingulate belonging to the family Pampatheriidae. It lived between the Middle Oligocene and the Early Pliocene in what is now South America.
















