
Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh. Its members are formally referred to as carnivorans, though some species are omnivorous, such as raccoons and bears, and very few species such as pandas are specialized herbivores. The word carnivore is derived from Latin carō 'flesh' and vorāre 'to devour', and refers to any meat-eating organism. The order Carnivora is the fifth largest order of mammals and one of the more successful members of the group, as it comprises at least 279 species.

Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the Trichinella type. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Minor infection may be without symptoms. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs.

Trichinella spiralis is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encountered in undercooked pork products. It should not be confused with the distantly related pork tapeworm.

Trichinella is the genus of parasitic roundworms of the phylum Nematoda that cause trichinosis. Members of this genus are often called trichinella or trichina worms. A characteristic of Nematoda is the one-way digestive tract, with a pseudocoelom.

Altyaghach National Park — is a national park of Azerbaijan. It was established on an area of 11,035 hectares (110.35 km2) in the Khizi Rayon and Siazan Rayon administrative districts on August 31, 2004. It is about 120 km away from the capital Baku.
Capillaria plica is a parasitic nematode which is most often found in the urinary bladder, and occasionally in the kidneys, of dogs and foxes. It has also been found in the domestic cat, and various wild mammals. Its presence usually produces no clinical symptoms, but in some cases, it leads to hematuria, cystitis, or difficulty in urination.

Capillaria aerophila is a nematode parasite found in the respiratory tract of foxes, dogs, and various other carnivorous mammals. A few cases of human infestation have also been reported. Though it is sometimes called a "lungworm", this term usually refers to other species of nematodes. Infestation by C. aerophila is referred to as "pulmonary capillariasis", "bronchial capillariasis," or (rarely) "thominxosis." This parasite has a direct life cycle, meaning that the life cycle can be completed in a single host. C. aerophila usually causes only minor clinical symptoms, such as irritation of the respiratory tract and coughing. However, secondary bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, including pneumonia, may develop in heavy infestations. Treatment with anthelmintics, such as levamisole or fenbendazole, is usually sufficient to cure C. aerophila infestations.

Thelaziasis is the term for infestation with parasitic nematodes of the genus Thelazia. The adults of all Thelazia species discovered so far inhabit the eyes and associated tissues of various mammal and bird hosts, including humans. Thelazia nematodes are often referred to as "eyeworms".

The red fox is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus parts of North Africa. It is listed as least concern by the IUCN. Its range has increased alongside human expansion, having been introduced to Australia, where it is considered harmful to native mammals and bird populations. Due to its presence in Australia, it is included on the list of the "world's 100 worst invasive species".
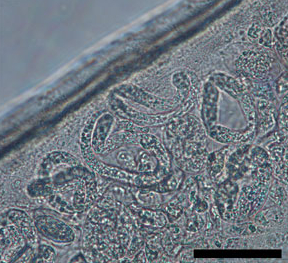
Dirofilaria repens is a filarial nematode that affects dogs and other carnivores such as cats, wolves, coyotes, foxes, and sea lions, as well as muskrats. It is transmitted by mosquitoes. Although humans may become infected as aberrant hosts, the worms fail to reach adulthood while infecting a human body.

Angiostrongylus vasorum, also known as French heartworm, is a species of parasitic nematode in the family Metastrongylidae. It causes the disease canine angiostrongylosis in dogs. It is not zoonotic, that is, it cannot be transmitted to humans.

Trichinella britovi is a nematode parasite responsible for a zoonotic disease called trichinellosis. Currently, eight species of Trichinella are known, only three of which cause trichinellosis, and Trichinella britovi is one of them. Numerous mammal species, as well as birds and crocodiles, can harbor the parasite worldwide, but the sylvatic cycle is mainly maintained by wild carnivores.
Kitee Zoo, located in Kitee, Finland is the fourth biggest zoo in the country. It was opened in 1996 and has over 50 animal species. There are Finnish animals, such as bears and lynxes, as well as more exotic animals. It has the only yaks in Finland. Some of the animals at the zoo include adder, Arctic fox, badger, bear, black grouse, chickens, chinchillas, chipmunks, common quail, eagle owl, emu, fox, geese, gerbils, goats, grey partridge, guinea pigs, hamsters, lynx, mallard, mink, mute swan, northern goshawk, Norway lemming, ostrich, peafowl, pigs, polecat, pony, rabbits, raccoon dog, reindeer, sheep, slow worm, turkeys, white-tailed deer, wild boar, wolverine, and wood grouse.

Naurzum State Nature Reserve is a nature reserve in Kazakhstan. It is part of the UNESCO heritage site Saryarka — Steppe and Lakes of Northern Kazakhstan. It protects about 3,081 square kilometres (1,190 sq mi) of steppes, semi desert and forests.

The Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests ecoregion is located in the mountains of eastern Turkey. It is a Palearctic ecoregion in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome.










