Related Research Articles

A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.
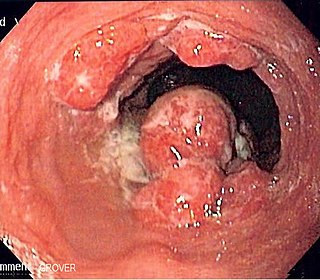
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include difficulty in swallowing and weight loss. Other symptoms may include pain when swallowing, a hoarse voice, enlarged lymph nodes ("glands") around the collarbone, a dry cough, and possibly coughing up or vomiting blood.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.

Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, a lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include spread to the lungs or brain.

Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, especially those under 3 years old.

Head and neck cancer is a general term encompassing multiple cancers that can develop in the head and neck region. These include cancers of the mouth, tongue, gums and lips, voice box (laryngeal), throat, salivary glands, nose and sinuses. Head and neck cancer can present a wide range of symptoms depending on where the cancer developed. These can include an ulcer in the mouth that does not heal, changes in the voice, difficulty swallowing, red or white patches in the mouth, and a neck lump.

Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma that are believed to originate from the oligodendrocytes of the brain or from a glial precursor cell. They occur primarily in adults but are also found in children.

Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is the most aggressive and most common type of cancer that originates in the brain, and has a very poor prognosis for survival. Initial signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality changes, nausea, and symptoms similar to those of a stroke. Symptoms often worsen rapidly and may progress to unconsciousness.

Invasive carcinoma of no special type, invasive breast carcinoma of no special type (IBC-NST), invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), infiltrating ductal carcinoma (IDC) or invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified (NOS) is a disease. For international audiences this article will use "invasive carcinoma NST" because it is the preferred term of the World Health Organization (WHO).

A blastoma is a type of cancer, more common in children, that is caused by malignancies in precursor cells, often called blasts. Examples are nephroblastoma, medulloblastoma, and retinoblastoma. The suffix -blastoma is used to imply a tumor of primitive, incompletely differentiated cells, e.g., chondroblastoma is composed of cells resembling the precursor of chondrocytes.

Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa.

Aggressive fibromatosis or desmoid tumor is a rare condition. Desmoid tumors are a rare type of cancer fibromatosis and related to sarcoma, The tumors arise from cells called fibroblasts, which are found throughout the body and provide structural support, protection to the vital organs, and play a critical role in wound healing. These tumors tend to occur in women in their thirties, but can occur in anyone at any age. They can be either relatively slow-growing or malignant. However, aggressive fibromatosis is locally aggressive and invasive, with spindle-like growths. The tumors can lead to pain, life-threatening problems, or, rarely, death when they invade other soft tissue or compress vital organs such as intestines, kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, or nerves. Most cases are sporadic, but some are associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Approximately 10% of individuals with Gardner's syndrome, a type of FAP with extracolonic features, have desmoid tumors.

Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), also termed primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system (DLBCL-CNS), is a primary intracranial tumor appearing mostly in patients with severe immunodeficiency. It is a subtype and one of the most aggressive of the diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.

A germinoma is a type of germ-cell tumor, which is not differentiated upon examination. It may be benign or malignant.

An atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor (AT/RT) is a rare tumor usually diagnosed in childhood. Although usually a brain tumor, AT/RT can occur anywhere in the central nervous system (CNS), including the spinal cord. About 60% will be in the posterior cranial fossa. One review estimated 52% in the posterior fossa, 39% are supratentorial primitive neuroectodermal tumors (sPNET), 5% are in the pineal, 2% are spinal, and 2% are multifocal.

Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all primary CNS neoplasms.

A brain metastasis is a cancer that has metastasized (spread) to the brain from another location in the body and is therefore considered a secondary brain tumor. The metastasis typically shares a cancer cell type with the original site of the cancer. Metastasis is the most common cause of brain cancer, as primary tumors that originate in the brain are less common. The most common sites of primary cancer which metastasize to the brain are lung, breast, colon, kidney, and skin cancer. Brain metastases can occur months or even years after the original or primary cancer is treated. Brain metastases have a poor prognosis for cure, but modern treatments allow patients to live months and sometimes years after the diagnosis.
Neuro-oncology is the study of brain and spinal cord neoplasms, many of which are very dangerous and life-threatening. Among the malignant brain cancers, gliomas of the brainstem and pons, glioblastoma multiforme, and high-grade astrocytoma/oligodendroglioma are among the worst. In these cases, untreated survival usually amounts to only a few months, and survival with current radiation and chemotherapy treatments may extend that time from around a year to a year and a half, possibly two or more, depending on the patient's condition, immune function, treatments used, and the specific type of malignant brain neoplasm. Surgery may in some cases be curative, but, as a general rule, malignant brain cancers tend to regenerate and emerge from remission easily, especially highly malignant cases. In such cases, the goal is to excise as much of the mass and as much of the tumor margin as possible without endangering vital functions or other important cognitive abilities. The Journal of Neuro-Oncology is the longest continuously published journal in the field and serves as a leading reference to those practicing in the area of neuro-oncology.
Pediatric ependymomas are similar in nature to the adult form of ependymoma in that they are thought to arise from radial glial cells lining the ventricular system. However, they differ from adult ependymomas in which genes and chromosomes are most often affected, the region of the brain they are most frequently found in, and the prognosis of the patients. Children with certain hereditary diseases, such as neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), have been found to be more frequently afflicted with this class of tumors, but a firm genetic link remains to be established. Symptoms associated with the development of pediatric ependymomas are varied, much like symptoms for a number of other pediatric brain tumors including vomiting, headache, irritability, lethargy, and changes in gait. Although younger children and children with invasive tumor types generally experience less favorable outcomes, total removal of the tumors is the most conspicuous prognostic factor for both survival and relapse.

Childhood cancer is cancer in a child. About 80% of childhood cancer cases in high-income countries can be successfully treated via modern medical treatments and optimal patient care. However, only about 10% of children diagnosed with cancer reside in high-income countries where the necessary treatments and care is available. Childhood cancer represents only about 1% of all types of cancers diagnosed in children and adults, It is often more complex than adult cancers with unique biological characteristics and research and treatment is yet very challenging and limited. For this reason, childhood cancer is often ignored in control planning, contributing to the burden of missed opportunities for its diagnoses and management in countries that are low- and mid-income.
References
- ↑ Kivelä T (June 1999). "Trilateral retinoblastoma: a meta-analysis of hereditary retinoblastoma associated with primary ectopic intracranial retinoblastoma". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 17 (6): 1829–37. doi:10.1200/JCO.1999.17.6.1829. PMID 10561222.
- ↑ De Jong MC, Kors WA, De Graaf P, Castelijns JA, Kivelä T, Moll AC (September 2014). "Trilateral retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis". The Lancet Oncology. 15 (10): 1157–67. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(14)70336-5. PMID 25126964.