
Myrtaceae, the myrtle family, is a family of dicotyledonous plants placed within the order Myrtales. Myrtle, pōhutukawa, bay rum tree, clove, guava, acca (feijoa), allspice, and eucalyptus are some notable members of this group. All species are woody, contain essential oils, and have flower parts in multiples of four or five. The leaves are evergreen, alternate to mostly opposite, simple, and usually entire. The flowers have a base number of five petals, though in several genera, the petals are minute or absent. The stamens are usually very conspicuous, brightly coloured, and numerous.

Putranjivaceae is a rosid family that is composed of 218 species in 2 genera of evergreen tropical trees that are found mainly in the Old World tropics, but with a few species in tropical America.
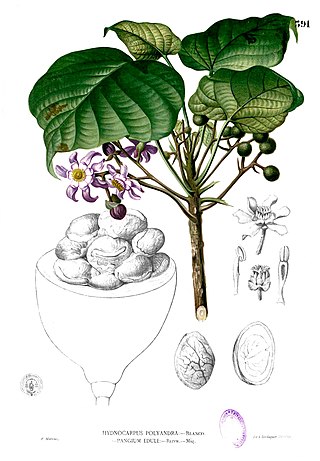
Achariaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of 31 genera and about 155 species of tropical herbs, shrubs, and trees. The APG IV system has greatly expanded the scope of the family by including many genera previously classified in Flacourtiaceae. Molecular data strongly support the inclusion of this family in the order Malpighiales.

Patersonia, is a genus of plants whose species are commonly known as native iris or native flag and are native to areas from Malesia to Australia.

Escalloniaceae is a family of flowering plants consisting of about 130 species in eight genera. In the APG II system it is one of eight families in the euasterids II clade (campanulids) that are unplaced as to order. More recent research has provided evidence that two of those families, Eremosynaceae and Tribelaceae, arose from within Escalloniaceae; the Angiosperm Phylogeny Website therefore merges these two families into Escalloniaceae, and also places the family alone in order Escalloniales.
Perebea is a genus of flowering plants in mulberry family, Moraceae. It includes ten species native to the tropical Americas, ranging from Nicaragua to Bolivia and central Brazil.
Pseudolmedia is a flowering plant genus in the mulberry family (Moraceae). Species are found in southern Mexico, the Caribbean, and Meso- and South America. They are known in Latin America as lechechiva and used for timber, construction wood, and sometimes in folk medicine.

Streblus is a genus of flowering plants in the mulberry family, Moraceae. It includes five species native to the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, southern China, and Malesia.

Aphanopetalum is a genus of twining shrubs or vines in the family Aphanopetalaceae which are endemic to Australia.
Latrobea is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes eight species of shrubs endemic to Southwest Australia. Typical habitats include forest, woodland, and heathland on sandy soils and swampy areas in higher-rainfall areas of the far southwest. The genus belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. The plant is named after Charles Joseph La Trobe.
Elythranthera, commonly known as enamel orchids, is a genus of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two species and a named hybrid, all endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. The genus was first formally described in 1963 by the Australian botanist Alex George who published his description in Western Australian Naturalist.

Anthoxanthum brunonis is a species of grass, native to the South Island of New Zealand and to the Auckland and Campbell Islands.

Fockea is a genus of succulent scrubs native to Africa south of the equator. They are members of the Asclepiadoideae (milkweeds), a subfamily of the dogbane family Apocynaceae. Of the six recognized species, only the two most widely distributed extend north of southern Africa, with F. multiflora reaching as far north as Tanzania and F. angustifolia reaching to southern Kenya. Fockea are known as water roots, a reference to the bulbous caudex characteristic of most species, which is also edible in at least some species.

Maxillaria parviflora, the purple tiger orchid, is a species of epiphytic orchid native to Florida, the West Indies and through Latin America from Mexico to Bolivia.

Kelleria is a genus of miniature shrubs in the family Thymelaeaceae, found in Australia, New Zealand and Papua New Guinea. The centre of species biodiversity is the Lammermoor Range in Central Otago, NZ.

Xanthorrhoea brunonis is a species of grasstree of the genus Xanthorrhoea native to Western Australia.

Ochetophila is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rhamnaceae, native to Chile and Argentina. The species in this genus are actinorhizal plants.
Tordyliopsis is a monotypic genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae. Its only species is Tordyliopsis brunonis. Its native range is Himalaya to Tibet.
Centropappus is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Asteraceae. It contains a single species, Centropappus brunonis.

Scybalium is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Balanophoraceae.














