Fracastorius is a genus of Asian seed bugs in the tribe Homoeocerini, erected by William Lucas Distant in 1901. It contains the single species Fracastorius cornutus which was originally recorded from Myanmar.

The Fauna of British India with long titles including The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma, and The Fauna of British India Including the Remainder of the Oriental Region is a series of scientific books that was published by the British government in India and printed by Taylor and Francis of London. The series was started sometime in 1881 after a letter had been sent to the Secretary of State for India signed by Charles Darwin, Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker and other "eminent men of science" forwarded by P.L.Sclater to R.H. Hobart. W. T. Blanford was appointed editor and began work on the volume on mammals.
Wolfius is a monotypic genus of bugs in the tribe Colpurini, erected by William Lucas Distant in 1902. It contains the single species Wolfius exemplificatus, recorded from Thailand and Burma.

Saiva is a genus of Asian planthoppers, family Fulgoridae. They are colourful insects, marked boldly in red, blue, white and black, with a prominent slender stalk like structure arising on the head that points upwards or forward. The known distribution is from India, China and Indochina.

The prehistory of Southeast Europe, defined roughly as the territory of the wider Southeast Europe covers the period from the Upper Paleolithic, beginning with the presence of Homo sapiens in the area some 44,000 years ago, until the appearance of the first written records in Classical Antiquity, in Greece. First Greek language is Linear A and follows Linear B, which is a syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from the older Linear A, an undeciphered earlier script used for writing the Minoan language, as is the later Cypriot syllabary, which also recorded Greek. Linear B, found mainly in the palace archives at Knossos, Kydonia, Pylos, Thebes and Mycenae, but disappeared with the fall of the Mycenean civilisation during the Late Bronze Age collapse.

Acanalonia is a genus of planthopper and contains the majority of the species within the family Acanaloniidae. Species have been recorded from southern Europe and the Americas.

Rhasis is a genus of true bugs in the tribe Mirini.

Pyrops clavatus is a species of true bug in the family Fulgoridae, in the genus Pyrops which are sometimes called "lanternflies". This species is found in parts of northern and northeastern India, Myanmar, northern Thailand, southern China and northern Vietnam. The tip of the elongated head capsule is spheroidal, shiny and chestnut in colour while the remainder of the process is black with fine white spotting. The forewing has a variable patterning of black, grey and white. The hindwing is purplish white with the apical half black. Specimens have been obtained along the Himalayas west to Mussoorie but more often in Assam, Sikkim, Shillong and the Khasi Hills.

Pyrops delessertii is a species of true bug in the family Fulgoridae, in the genus Pyrops which are sometimes called "lanternflies". This species is endemic to peninsular India, mainly in the Western Ghats.
Akam is one of two genres of Classical Tamil poetry that concerns with the subject of love, the other (puṟam) concerns the subject of war. It can also be translated as love and heroism. It is further subdivided into the five thinai. The type of love was divided into seven ranging from unrequited love to mismatched love.

Macrocheraia is a genus of bugs in the family Largidae with a single species, Macrocheraia grandis found mainly in Southeast Asia but extending into parts of South Asia. This was referred to in some older literature under the genus Lohita, a name derived from the Sanskrit word for red.

Kalidasa is a genus of planthoppers in the tribe Aphaenini of the family Fulgoridae. There are five species in the genus, which are found in different parts of tropical Asia.

Dichoptera is a genus of planthoppers found in tropical Asia. They were formerly placed in the family Dictyopharidae but are now considered members of the family Fulgoridae.

Kosovo is characterised by a diverse biodiversity and an abundance of different ecosystems and habitats determined by the climate along with the geology and hydrology. Predominantly mountainous, it is located at the center of the Balkan Peninsula bounded by Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the north and east, North Macedonia to the southeast, and Albania to the southwest.

Montenegro is the smallest Balkan nation in population and second smallest in land mass. The land mass is 13,812 square kilometres with 360 square kilometres of water. Montenegro's geography ranges from mountainous forested regions in the north where larger mammals are most common. Mediterranean coastline makes up the south end of the country, forested area makes up 40.4% of the nation's landmass. The most densely populated area of the country is the south coast and the most sparsely populated is the north east section of the country. The fauna of Montenegro is predominantly shared with surrounding Balkan nations.

Adelidoria glauca is an insect species from Sri Lanka that was first described by William Forsell Kirby in 1891. It is the only species of the genus Adelidoria, which is related to the genus Cerynia, but differs in the neuration, etc.
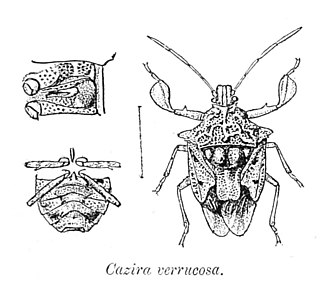
Cazira is a genus of shield bugs found in the Indo-Malayan region.
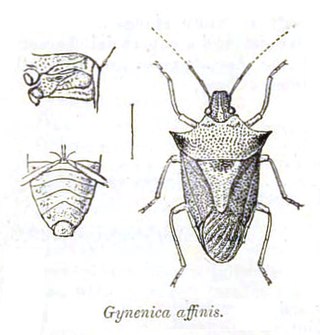
Gynenica is a genus of stink bug with about fourteen species in the Afrotropical and Oriental regions. It is one of four genera placed in the tribe Lestonocorini along with Lestonocoris, Neogynenica, and Umgababa that occur in Africa and India and feed on plants in the family Acanthaceae. Bugs in the genus have the pronotum tips extended into forward and upward curving spines. The scutellum is longer than broad, the apex with a rounded point and not reaching beyond the middle of the abdomen.

Asiarcha is a genus of bugs in the family Tessaratomidae. Species are known from South and Southeast Asia.
















