
The Boletaceae are a family of mushroom-forming fungi, primarily characterised by small pores on the spore-bearing hymenial surface, instead of gills as are found in most agarics. Nearly as widely distributed as the agarics, the family is renowned for hosting some prime edible species highly sought after by mushroom hunters worldwide, such as the cep or king bolete . A number of rare or threatened species are also present in the family, that have become the focus of increasing conservation concerns. As a whole, the typical members of the family are commonly known as boletes.

Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 (SARS-CoV-1), previously known as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), is a strain of coronavirus that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the respiratory illness responsible for the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. It is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus that infects the epithelial cells within the lungs. The virus enters the host cell by binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. It infects humans, bats, and palm civets. The SARS-CoV-1 outbreak was largely brought under control by simple public health measures. Testing people with symptoms, isolating and quarantining suspected cases, and restricting travel all had an effect. SARS-CoV-1 was most transmissible when patients were sick, so its spread could be effectively suppressed by isolating patients with symptoms.

Triplophysa is a genus of fish in the family Nemacheilidae found mainly in and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China, as well as inland waters of the larger part of central Asia. Currently, the genus is a mixed assemblage of species. Some lineages have been identified and treated as subgenera, but as Wikipedia follows Fishbase for fish species all but Hedinichthys have been treated as subgenera in Wikipedia, although Kottelat in his revision of the loaches did recognise them as valid. FishBase, however, includes these in Triplophysa without specifying subgenera and treats the names given by Kottelat as synonyms.

Trogia is a genus of fungi in the family Marasmiaceae. It is named after a Swiss mycologist Jacob Gabriel Trog. The genus contains about 20 species that are widely distributed in tropical areas.

The Water Margin is a 1998 Chinese television series adapted from Shi Nai'an's classical 14th-century novel of the same title. It was produced by CCTV with Zhang Jizhong as producer. It was first broadcast in China in January 1998. The series also featured action choreography by Yuen Woo-ping.

The Taiping Heavenly Kingdom is a Chinese television series based on the events of the Taiping Rebellion and the rise and fall of the Taiping Heavenly Kingdom in the late Qing dynasty. The 48-episode series was first broadcast on CCTV in China in 2000. The series was also broadcast on STAR Chinese Channel in Taiwan and on ATV in Hong Kong.

Amanita exitialis, also known as the Guangzhou destroying angel, is a mushroom of the large genus Amanita. It is distributed in eastern Asia, and probably also in India where it has been misidentified as A. verna. Deadly poisonous, it is a member of section Phalloideae and related to the death cap A. phalloides. The fruit bodies (mushrooms) are white, small to medium-sized with caps up to 7 cm (2.8 in) in diameter, a somewhat friable ring and a firm volva. Unlike most agaric mushrooms which typically have four-spored basidia, the basidia of A. exitialis are almost entirely two-spored. Eight people were fatally poisoned in China after consuming the mushroom in 2000, and another 20 have been fatally poisoned since that incident. Molecular analysis shows that the species has a close phylogenetic relationship with three other toxic white Amanitas: A. subjunquillea var. alba, A. virosa and A. bisporigera.
Yunnan sudden death syndrome is a sudden unexplained death from cardiac arrest, which afflicted significant numbers of rural villagers in Yunnan province in southwest China. Cases almost always occurred during the midsummer rainy season, at an altitude of 1,800–2,400 m (5,900–7,900 ft). An estimated 400 deaths occurred over three decades.
Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1, also sometimes called SARS-like coronavirus WIV1, is a strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV) isolated from Chinese rufous horseshoe bats in 2013. Like all coronaviruses, virions consist of single-stranded positive-sense RNA enclosed within an envelope.
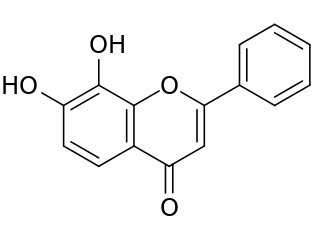
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Penicillium decumbens is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs widespread in nature, mainly in subtropical and tropical soil but it also occur in food. Analysis have shown that Penicillium decumbens has antibiotic activity Penicillium decumbens produces the cyclopentenone cyclopenicillone

Li Jiayang is a Chinese agronomist and geneticist. He is Vice Minister of Agriculture in China and President of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS). He is also Professor and Principal investigator at the Institute of Genetics and Development at the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).

Myelin transcription factor 1 like is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYT1L gene.
SHC014-CoV is a SARS-like coronavirus (SL-COV) which infects horseshoe bats. It was discovered in Kunming in Yunnan Province, China. It was discovered along with SL-CoV Rs3367, which was the first bat SARS-like coronavirus shown to directly infect a human cell line. The line of Rs3367 that infected human cells was named Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1.
Civet SARS-CoV is a coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), which infected humans and caused SARS events from 2002 to 2003. It infected the masked palm civet. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is highly similar, with a genome sequence similarity of about 99.8%. Because several patients infected at the early stage of the epidemic had contact with fruit-eating Japanese raccoon dog in the market, tanuki may be a direct source of human SARS coronavirus. At the end of 2003, four more people in Guangzhou, China, were infected with the disease. Sequence analysis found that the similarity with the tanuki virus reached 99.9%, and the SARS coronavirus was also caused by cases of tanuki transmission.
16BO133 is a SARS-like coronavirus (SL-COV) which was found in the greater horseshoe bat in South Korea. It was published in 2019 and its genome was completely sequenced. The sequenced Korean SARSr-CoV strain belongs to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1, and its genome sequence similarity is 82.8%.
LYRa11 is a SARS-like coronavirus (SL-COV) which was identified in 2011 in samples of intermediate horseshoe bats in Baoshan, Yunnan, China. The genome of this virus strain is 29805nt long, and the similarity to the whole genome sequence of SARS-CoV that caused the SARS outbreak is 91%. It was published in 2014. Like SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, LYRa11 virus uses ACE2 as a receptor for infecting cells.

Cordyceps gunni is a species of fungus in the family Cordycipitaceae, and is of the genus Cordyceps. It was originally found and recorded by Gunn in Tasmania and named as Sphaeria gunnii and later moved into the Cordyceps genus and renamed Cordyceps gunnii. This fungus and its sisters in the genus Cordyceps are known for growing out of insect bodies. C. gunnii can be found at ground level poking out of caterpillar burrows, attached to a caterpillar's head.

Isaria cicadae is an ascomycete fungus that parasitizes cicada larvae. It forms white and yellow asexual fruiting structures resembling synnema. While mostly being found throughout Asia in warm, humid regions, it has been found on various other continents. It is known in Traditional Chinese Medicine as Chan Hua and commonly called “cicada flower.” Its medicinal uses date back to the fifth century AD in China. It can also be used in various foods and tonics.











