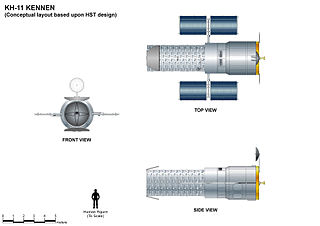
The KH-11 KENNEN is a type of reconnaissance satellite first launched by the American National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) in December 1976. Manufactured by Lockheed in Sunnyvale, California, the KH-11 was the first American spy satellite to use electro-optical digital imaging, and so offer real-time optical observations.

The Satellite Data System (SDS) is a system of United States military communications satellites. At least three generations have been used: SDS-1 from 1976 to 1987; SDS-2 from 1989 to 1996; SDS-3 from 1998 to the present. It is believed that these satellites were known by the code name Quasar. The first generation was named simply 'SDS', the second generation was named 'Quasar' and the third generation each had their own designations.

Delta IV was a group of five expendable launch systems in the Delta rocket family. It flew 45 missions from 2002 to 2024. Originally designed by Boeing's Defense, Space and Security division for the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) program, the Delta IV became a United Launch Alliance (ULA) product in 2006. The Delta IV was primarily a launch vehicle for United States Air Force (USAF) military payloads, but was also used to launch a number of United States government non-military payloads and a single commercial satellite.

United Launch Alliance, LLC (ULA) is an American launch service provider formed in December 2006 as a joint venture between Lockheed Martin Space and Boeing Defense, Space & Security. The company designs, assembles, sells and launches rockets, but the company subcontracts out the production of rocket engines and solid rocket boosters.

Orion, also known as Mentor or Advanced Orion, is a class of United States spy satellites that collect signals intelligence (SIGINT) from space. Operated by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and developed with input from the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), eight have been launched from Cape Canaveral on Titan IV and Delta IV launch vehicles since 1995.

The Delta IV Heavy was an expendable heavy-lift launch vehicle, the largest type of the Delta IV family. It had the highest capacity of any operational launch vehicle in the world after the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011 until the Falcon Heavy debuted in 2018, and it was the world's third highest-capacity launch vehicle in operation at the time of its retirement in 2024. It was manufactured by United Launch Alliance (ULA) and was first launched in 2004. Delta IV Heavy was the last operating member of the Delta IV family, and its final flight was on 9 April 2024. It is succeeded by the Vulcan Centaur rocket.

USA-193, also known as NRO Launch 21, was a United States military reconnaissance satellite launched on 14 December 2006. It was the first launch conducted by the United Launch Alliance (ULA). Owned by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), the craft's precise function and purpose were classified. On 21 February 2008, it was destroyed as a result of Operation Burnt Frost.

USA-200, also known as NRO Launch 28 or NROL-28, is an American signals intelligence satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched in 2008, it has been identified as the second satellite in a series known as Improved Trumpet, Advanced Trumpet, or Trumpet follow-on; a replacement for the earlier Trumpet series of satellites.

USA-212 was the first flight of the Boeing X-37B Orbital Test Vehicle 1, an American robotic vertical-takeoff, horizontal-landing (VTHL) spaceplane. It was launched aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral on 22 April 2010, and operated in low Earth orbit. Its designation is part of the USA series.
USA-223, known before launch as NRO Launch 32, is an American reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2010. It is operated by the United States National Reconnaissance Office. It presently holds the record for being the largest spy satellite ever launched.

USA-224, also known as NROL-49, is an American reconnaissance satellite. Launched in 2011 to replace the decade-old USA-161 satellite, it is the fifteenth KH-11 optical imaging satellite to reach orbit.
Prowler was an American reconnaissance satellite launched aboard Space ShuttleAtlantis in 1990 to study Soviet satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The government of the United States has never acknowledged its existence, however it has been identified by amateur observers and through leaked information.
USA-229, known before launch as NRO Launch 34 (NROL-34), is a pair of American signals intelligence satellites which were launched in 2011. They are operated by the United States National Reconnaissance Office.

USA-215, also known as NRO Launch 41 or NROL-41, is an American reconnaissance satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). Launched in 2010, it has been identified as the first in a new series of imaging radar satellites, developed as part of the Future Imagery Architecture (FIA) programme, to replace the earlier Lacrosse spacecraft.
USA-234, also known as NRO Launch 25 or NROL-25, is an American reconnaissance satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in 2012, it has been identified as the second radar imaging satellite to be launched as part of the Future Imagery Architecture programme.
USA-184, also known as NRO Launch 22 or NROL-22, is an American signals intelligence satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched in 2006, it has been identified as the first in a new series of satellites which are replacing the earlier Trumpet spacecraft.

USA-245 or NRO Launch 65 (NROL-65) is an American reconnaissance satellite which is operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched in August 2013, it is the last Block 4 KH-11 reconnaissance satellite, and the last official spacecraft to be launched in the Keyhole program.

USA-247, also known as NRO Launch 39 or NROL-39, is an American reconnaissance satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office and launched in December 2013. The USA-247 launch received a relatively high level of press coverage due to the mission's choice of logo, which depicts an octopus sitting astride the globe with the motto "Nothing Is Beyond Our Reach". The logo was extensively criticized in light of the surveillance disclosures in July 2013.











